 W
WFlortaucipir (18F), sold under the brand name Tauvid, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging to image the brain.
 W
WFluciclovine (18F), also known as anti-1-amino-3-18F-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (FACBC), or as Axumin, and colloquially as anti-3[18F] FACBC or F18, is a diagnostic agent "indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels."
 W
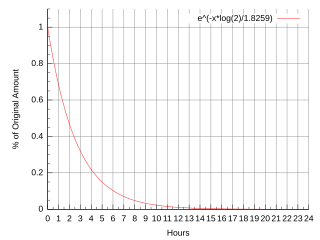
WFluorine-18 (18F) is a fluorine radioisotope which is an important source of positrons. It has a mass of 18.0009380(6) u and its half-life is 109.771(20) minutes. It decays by positron emission 97% of the time and electron capture 3% of the time. Both modes of decay yield stable oxygen-18.
 W
WFluorodeoxyglucose (18F) (INN), or fluorodeoxyglucose F 18, also commonly called fluorodeoxyglucose and abbreviated [18F]FDG, 18F-FDG or FDG, is a radiopharmaceutical used in the medical imaging modality positron emission tomography (PET). Chemically, it is 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose, a glucose analog, with the positron-emitting radionuclide fluorine-18 substituted for the normal hydroxyl group at the C-2 position in the glucose molecule.
 W
WFluoroestradiol F-18, also known as [18F]16α-fluoroestradiol and sold under the brand name Cerianna, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. It is an analog of estrogen and is used to detect estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer lesions.
 W
WGeorge Charles de Hevesy was a Hungarian radiochemist and Nobel Prize in Chemistry laureate, recognized in 1943 for his key role in the development of radioactive tracers to study chemical processes such as in the metabolism of animals. He also co-discovered the element hafnium.
 W
WPET radiotracer is a type of radioligand that is used for the diagnostic purposes via positron emission tomography imaging technique.
 W
WPositron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, NaF-F18 is widely used for detecting bone formation, and oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow.
 W
WRadiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents.
 W
WRadiopharmacology is radiochemistry applied to medicine and thus the pharmacology of radiopharmaceuticals. Radiopharmaceuticals are used in the field of nuclear medicine as radioactive tracers in medical imaging and in therapy for many diseases. Many radiopharmaceuticals use technetium-99m (Tc-99m) which has many useful properties as a gamma-emitting tracer nuclide. In the book Technetium a total of 31 different radiopharmaceuticals based on Tc-99m are listed for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood and tumors.
 W
WTechnetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99, symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope in the world.