 W
WThe Joint Polarization Experiment (JPOLE) was a test for evaluating the performance of the WSR-88D in order to modify it to include dual polarization. This program was a joint project of the National Weather Service (NWS), the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and the US Air Force Meteorological Agency (AFWA), which took place from 2000-2004. It has resulted in the upgrading of the entire meteorological radar network in the United States by adding dual polarization to better determine the type of hydrometeor, and quantities that have fallen.
 W
WThe Langley Hill Doppler radar (KLGX) is a National Weather Service NEXRAD Doppler weather radar station on the Pacific coast of Washington State, in the United States. Prior to its construction, Washington's Olympic Peninsula coast was the only portion of the U.S. coastline without weather radar coverage, and "virtually no radar coverage [is] available over the ocean, where the majority of western Washington's weather originates" according to a Weather Service report to the United States Congress. Its location was announced in early 2011, construction started in March, and the unit was commissioned in September, 2011. A major motivation for the station was early detection of Pacific Northwest windstorms; a proponent, Professor Cliff Mass of the University of Washington, said it would provide an additional 6 to 12 hour storm warning to residents of the Pacific Northwest.
 W
WMultifunction Phased Array Radar (MPAR) was an experimental Doppler radar system that utilized phased array technology. MPAR could scan at angles as high as 60 degrees in elevation, and simultaneously track meteorological phenomena, biological flyers, non-cooperative aircraft, and air traffic. From 2003 through 2016, there was one operational MPAR within the mainland United States—a repurposed AN/SPY-1A radar set loaned to NOAA by the U.S. Navy. The MPAR was decommissioned and removed in 2016.
 W
WNEXRAD or Nexrad is a network of 159 high-resolution S-band Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service (NWS), an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) within the United States Department of Commerce, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) within the Department of Transportation, and the U.S. Air Force within the Department of Defense. Its technical name is WSR-88D.
 W
WNOAA's 10 cm Doppler Weather Radar was a 10 cm wavelength S-band Doppler Weather Radar, commonly referred to as "NSSL Doppler" and was used to track severe weather and related meteorological phenomena. The radar became operational soon after its donation, collecting its first data in May 1971. Data was collected on magnetic tapes and processed on a NASA computer post event due to the lack of real-time capability at the time.
 W
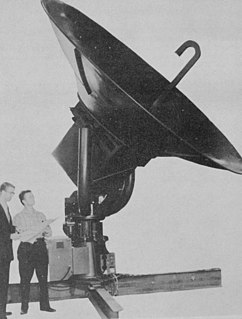
WThe WSR-1 or Weather Surveillance Radar-1 was one of the first weather radars and the first used by a civilian organization in the US. The WSR-1 series was a modified version of the AN/APS-2F radar, which the Weather Bureau acquired from the Navy. The WSR-1A, WSR-3, and WSR-4 were also variants of this radar. The first WSR-1 in the USA was at Washington National Airport in Washington, D.C. in 1947, and the last WSR-3 was retired by 1978.
 W
WThe WSR-1 or Weather Surveillance Radar-1 was one of the first weather radars and the first used by a civilian organization in the US. The WSR-1 series was a modified version of the AN/APS-2F radar, which the Weather Bureau acquired from the Navy. The WSR-1A, WSR-3, and WSR-4 were also variants of this radar. The first WSR-1 in the USA was at Washington National Airport in Washington, D.C. in 1947, and the last WSR-3 was retired by 1978.
 W
WThe WSR-1 or Weather Surveillance Radar-1 was one of the first weather radars and the first used by a civilian organization in the US. The WSR-1 series was a modified version of the AN/APS-2F radar, which the Weather Bureau acquired from the Navy. The WSR-1A, WSR-3, and WSR-4 were also variants of this radar. The first WSR-1 in the USA was at Washington National Airport in Washington, D.C. in 1947, and the last WSR-3 was retired by 1978.
 W
WWSR-57 radars were the USA's main weather surveillance radar for over 35 years. The National Weather Service operated a network of this model radar across the country, watching for severe weather.
 W
WWSR-74 radars were Weather Surveillance Radars designed in 1974 for the National Weather Service. They were added to the existing network of the WSR-57 model to improve forecasts and severe weather warnings. Some have been sold to other countries like Australia, Greece, and Pakistan.
 W
WNEXRAD or Nexrad is a network of 159 high-resolution S-band Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service (NWS), an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) within the United States Department of Commerce, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) within the Department of Transportation, and the U.S. Air Force within the Department of Defense. Its technical name is WSR-88D.