 W
WA solar observatory is an observatory that specializes in monitoring the Sun. As such, they usually have one or more solar telescopes.
 W
WBig Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO) is a university-based solar observatory in the United States. It is operated by New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT). BBSO has a 1.6 m clear aperture Goode Solar Telescope (GST), which has no obscuration in the optical train. Light corrected by adaptive optics is fed to either the visible (VIS) or near-infrared (NIRIS) spectro-polarimeter. Additionally, uncorrected light can be fed to a cryogenic spectrograph (CYRA) operating out to wavelengths of 5 microns. BBSO also operates full-disk patrol telescopes. The telescopes and instruments at the observatory are designed and employed specifically for studying the activities and phenomena of the Sun.
 W
WBleien Radio Observatory is a radio astronomy observatory located halfway between Zurich and Bern in Switzerland. Its focus is on large bandwidth radio spectroscopy. The observatory is near the village of Bleien, 5 km south of Gränichen in the Canton of Aargau. The place is in a shallow valley that is relatively well protected against terrestrial interference.
 W
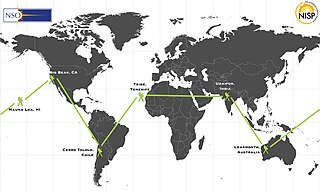
WThe Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) is a worldwide network of six identical telescopes, designed to have 24/7 observations of the Sun. The network serves multiple purposes, including the provision of operation data for use in space weather prediction, and the study of solar internal structure and dynamics using helioseismology.
 W
WThe Haleakalā Observatory, also known as the Haleakalā High Altitude Observatory Site, is Hawaii's first astronomical research observatory. It is located on the island of Maui and is owned by the Institute for Astronomy of the University of Hawai'i, which operates some of the facilities on the site and leases portions to other organizations. Tenants include the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) and the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network (LCOGTN). At over 3,050 meters (10,010 ft) in altitude, the summit of Haleakalā is above one third of the Earths's troposphere and has excellent astronomical seeing conditions.
 W
WThe High Altitude Observatory (HAO) conducts research and provides support and facilities for the solar-terrestrial physics research community in the areas of solar and heliospheric physics, and the effects of solar variability on the Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere, and upper atmosphere.
 W
WMauna Loa Solar Observatory (MLSO) is a solar observatory located on the slopes of Mauna Loa on the island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii. It is operated by the High Altitude Observatory (HAO), a laboratory within the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). The MLSO sits on property managed by the Mauna Loa Observatory (MLO), which is part of the U.S. Department of Commerce National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). MLSO was built in 1965.
 W
WDonald Howard Menzel was one of the first theoretical astronomers and astrophysicists in the United States. He discovered the physical properties of the solar chromosphere, the chemistry of stars, the atmosphere of Mars, and the nature of gaseous nebulae. The minor planet 1967 Menzel was named in his honor, as well as a small lunar crater located in the southeast of Mare Tranquilitatis, the Sea of Tranquility.
 W
WOwens Valley Radio Observatory (OVRO) is a radio astronomy observatory located near Big Pine, California (US) in Owens Valley. It lies east of the Sierra Nevada, approximately 350 kilometers (220 mi) north of Los Angeles and 20 kilometers (12 mi) southeast of Bishop. It was established in 1956, and is owned and operated by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The Owens Valley Solar Array portion of the observatory has been operated by New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) since 1997.
 W
WSOLAR was an ESA science observatory on the Columbus Laboratory, which is part of the International Space Station. SOLAR was launched with Columbus on February 2008 aboard STS-122. It was externally mounted to Columbus with the European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF). SOLAR has three main space science instruments: SOVIM, SOLSPEC and SOL-ACES. Together they provide detailed measurements of the Sun's spectral irradiance. The SOLAR platform and its instruments are controlled from the Belgian User Support and Operations Centre (B.USOC), located at the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy (BISA) in Uccle, Belgium.
 W
WThe Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) was a NASA-sponsored satellite mission that measured incoming X-ray, ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, and total solar radiation. These measurements specifically addressed long-term climate change, natural variability, atmospheric ozone, and UV-B radiation, enhancing climate prediction. These measurements are critical to studies of the Sun, its effect on our Earth system, and its influence on humankind. SORCE was launched on 25 January 2003 on a Pegasus XL launch vehicle to provide NASA's Earth Science Enterprise (ESE) with precise measurements of solar radiation.