 W
WThe Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System located at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, US, consists of astronomical cameras, telescopes and a computing facility that is surveying the sky for moving or variable objects on a continual basis, and also producing accurate astrometry and photometry of already-detected objects. In January 2019 the second Pan-STARRS data release was announced. At 1.6 petabytes, it is the largest volume of astronomical data ever released.
 W
W2012 TC4 is a tumbling micro-asteroid classified as a bright near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 10 meters (30 feet) in diameter. It was first observed by Pan-STARRS at Haleakala Observatory on the Hawaiian island of Maui, in the United States. As of 1 October 2017, it had a small Earth minimum orbital intersection distance of 0.000149 AU (22,300 km). On 12 October 2017, it passed Earth at 0.00033524 AU (50,151 km).
 W
W2017 VR12 is a sub-kilometer asteroid with a somewhat elongated and angular shape, approximately 160 meters (500 feet) in diameter. It is classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo or Amor group. The V-type asteroid has a rotation period of approximately 1.5 hours. It was first observed on 10 November 2017 by the 60-inch Pan-STARRS 1 telescope at Haleakala Observatory in Hawaii.
 W
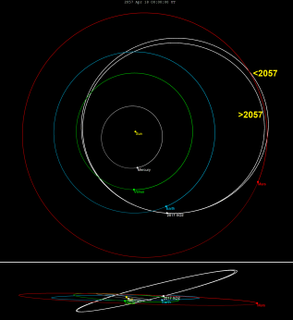
W2017 XO2, also written 2017 XO2, is a sub-kilometer asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group approximately 110 meters (360 feet) in diameter. The asteroid was discovered by Pan-STARRS in December 2017, after it already had approached Earth at 0.051 AU (7,600,000 km) or 20 lunar distances (LD) on 6 November 2017. On 26 April 2057, it will pass Earth at a similar distance of 21 LD again.
 W
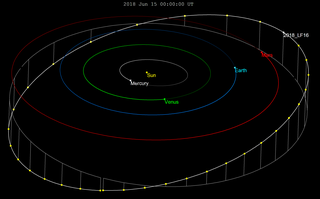
W2018 LF16 is a small near-Earth asteroid of the Amor group, first observed by astronomers with the Pan-STARRS survey at Haleakala Observatory on 14 June 2018. Based on limited observations, early estimates of its size of 213 m (699 ft) would make it extremely destructive if it collided with Earth, but predicted orbits make a collision unlikely.
 W
W2018 XB4 (also written 2018 XB4) is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid roughly 53 meters (170 feet) in diameter. It was discovered on 13 December 2018 when the asteroid was about 0.125 AU (18,700,000 km; 11,600,000 mi) from Earth and had a solar elongation of 146°. It passed closest approach to Earth on 1 January 2019. Of the asteroids discovered in 2018, it had the highest Palermo scale rating at –3.6. In mid-2019 it was recovered which extended the observation arc to 177 days and was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 12 June 2019. It is now known that on 22 June 2092 the asteroid will pass about 0.033±0.015 AU from Earth.
 W
WʻOumuamua is the first known interstellar object detected passing through the Solar System. Formally designated 1I/2017 U1, it was discovered by Robert Weryk using the Pan-STARRS telescope at Haleakalā Observatory, Hawaii, on 19 October 2017, 40 days after it passed its closest point to the Sun on 9 September. When it was first observed, it was about 33 million km from Earth, and already heading away from the Sun.
 W
W2019 PG1 is a potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo class, discovered by Pan-STARRS on 8 August 2019. It has an average estimated diameter of 325 meters according to NASA's Center for Near-Earth Object Studies. The next minimum possible close-approach distance of 2019 PG1 will happen the 9 July 2111, at a nominal distance of 1.22×10−6 AU, or 182 kilometers from the Earth.
 W
W2020 SO is a near-Earth object identified to be the Surveyor 2 Centaur rocket booster launched on 20 September 1966. The object was discovered by the Pan-STARRS1 survey at the Haleakala Observatory on 17 September 2020. The object was initially suspected to be an artificial object due to its low velocity relative to Earth and later on the noticeable effects of solar radiation pressure on its orbit. Spectroscopic observations by NASA's Infrared Telescope Facility in December 2020 found that the object's spectrum is similar to that of stainless steel, confirming the object's artificial nature.
 W
W(436724) 2011 UW158, provisionally known as 2011 UW158, is a stony, walnut-shaped asteroid and fast rotator, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 300 meters in diameter. It was discovered on 25 October 2011, by Pan-STARRS at Haleakala Observatory on the island of Maui, Hawaii, in the United States.
 W
W469219 Kamoʻoalewa, provisional designation 2016 HO3, is a very small asteroid, fast rotator and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 41 meters (135 feet) in diameter. It is currently the smallest, closest, and most stable (known) quasi-satellite of Earth. The asteroid was discovered by Pan-STARRS at Haleakala Observatory on 27 April 2016. It was named Kamoʻoalewa, a Hawaiian word that refers to an oscillating celestial object.
 W
W(511002) 2013 MZ5 , provisional designation 2013 MZ5, is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Amor group, estimated to measure approximately 300 meters (1,000 feet) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 June 2013, by astronomers with the Pan-STARRS survey at Haleakala Observatory on the island of Maui, Hawaii, in the United States. It was the 10,000th near-Earth object ever discovered.
 W
W514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, provisional designation 2015 BZ509 and nicknamed Bee-Zed, is a small asteroid, approximately 3 kilometers (2 miles) in diameter, in a resonant, co-orbital motion with Jupiter. Its orbit is retrograde, which is opposite to the direction of most other bodies in the Solar System. It was discovered on 26 November 2014, by astronomers of the Pan-STARRS survey at Haleakala Observatory on the island of Maui, United States. The unusual object is the first example of an asteroid in a 1:–1 resonance with any of the planets. A study has suggested it may be an interstellar asteroid captured 4.5 billion years ago into an orbit around the Sun.