 W
WThe Crookes radiometer consists of an airtight glass bulb containing a partial vacuum, with a set of vanes which are mounted on a spindle inside. The vanes rotate when exposed to light, with faster rotation for more intense light, providing a quantitative measurement of electromagnetic radiation intensity.
 W
WECOSTRESS is an ongoing scientific experiment in which a radiometer mounted on the International Space Station measures the temperature of plants growing in specific locations on Earth over the course of a solar year. These measurements give scientists insight into the effects of events like heat waves and droughts on crops.
 W
WA fluorometer or fluorimeter is a device used to measure parameters of visible spectrum fluorescence: its intensity and wavelength distribution of emission spectrum after excitation by a certain spectrum of light. These parameters are used to identify the presence and the amount of specific molecules in a medium. Modern fluorometers are capable of detecting fluorescent molecule concentrations as low as 1 part per trillion.
 W
WA light meter is a device used to measure the amount of light. In photography, a light meter is used to determine the proper exposure for a photograph. The meter will include either a digital or analog calculator which displays the correct shutter speed and f-number for optimum exposure, given a certain lighting situation and film speed. Similarly, exposure meters are also used in the fields of cinematography and scenic design, in order to determine the optimum light level for a scene.
 W
WA microwave power meter is an instrument which measures the electrical power at microwave frequencies typically in the range 100 MHz to 40 GHz.
 W
WA microwave radiometer (MWR) is a radiometer that measures energy emitted at millimetre-to-centimetre wavelengths known as microwaves. Microwave radiometers are very sensitive receivers designed to measure thermal electromagnetic radiation emitted by atmospheric gases. They are usually equipped with multiple receiving channels in order to derive the characteristic emission spectrum of the atmosphere or extraterrestrial objects. Microwave radiometers are utilized in a variety of environmental and engineering applications, including weather forecasting, climate monitoring, radio astronomy and radio propagation studies.
 W
WA net radiometer is a type of actinometer used to measure net radiation (NR) at the Earth's surface for meteorological applications. The name net radiometer reflects the fact that it measures the difference between downward/incoming and upward/outgoing radiation from Earth. It is most commonly used in the field of ecophysiology.
 W
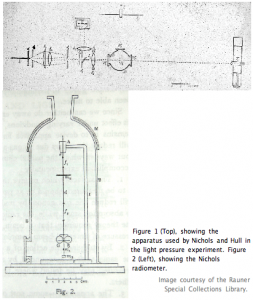
WA Nichols radiometer was the apparatus used by Ernest Fox Nichols and Gordon Ferrie Hull in 1901 for the measurement of radiation pressure. It consisted of a pair of small silvered glass mirrors suspended in the manner of a torsion balance by a fine quartz fibre within an enclosure in which the air pressure could be regulated. The torsion head to which the fiber was attached could be turned from the outside using a magnet. A beam of light was directed first on one mirror and then on the other, and the opposite deflections observed with mirror and scale. By turning the mirror system around to receive the light on the unsilvered side, the influence of the air in the enclosure could be ascertained. This influence was found to be of almost negligible value at an air pressure of about 16 mmHg. The radiant energy of the incident beam was deduced from its heating effect upon a small blackened silver disk, which was found to be more reliable than the bolometer when it was first used. With this apparatus, the experimenters were able to obtain an agreement between observed and computed radiation pressures within about 0.6%. The original apparatus is at the Smithsonian Institution.
 W
WA photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier.
 W
WA pyrgeometer is a device that measures near-surface infra-red radiation spectrum in the wavelength spectrum approximately from 4.5 μm to 100 μm.
 W
WThe Radiation Budget Instrument (RBI) is a scanning radiometer capable of measuring Earth's reflected sunlight and emitted thermal radiation. The project was cancelled on January 26, 2018; NASA cited technical, cost, and schedule issues and the impact of anticipated RBI cost growth on other programs.
 W
WA radiometer or roentgenometer is a device for measuring the radiant flux (power) of electromagnetic radiation. Generally, a radiometer is an infrared radiation detector or an ultraviolet detector. Microwave radiometers operate in the microwave wavelengths.
 W
WA sun photometer is a type of photometer conceived in such a way that it points at the sun. Recent sun photometers are automated instruments incorporating a sun-tracking unit, an appropriate optical system, a spectrally filtering device, a photodetector, and a data acquisition system. The measured quantity is called direct-sun radiance.