 W
WA multi-agent system is a computerized system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents. Multi-agent systems can solve problems that are difficult or impossible for an individual agent or a monolithic system to solve. Intelligence may include methodic, functional, procedural approaches, algorithmic search or reinforcement learning.
 W
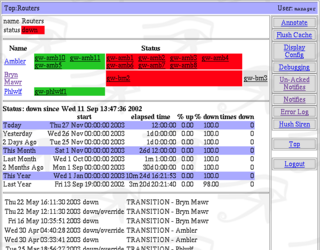
WAdmon is a Zabbix-based open-source computer system and network monitoring application software. It watches hosts and services specified by users, alerting them via e-mail or short-message service when issues arise.
 W
WArgus is a systems and network monitoring application. It is designed to monitor the status of network services, servers, and other network hardware. It will send alerts when it detects problems.
 W
WA botnet is a number of Internet-connected devices, each of which is running one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, steal data, send spam, and allow the attacker to access the device and its connection. The owner can control the botnet using command and control (C&C) software. The word "botnet" is a portmanteau of the words "robot" and "network". The term is usually used with a negative or malicious connotation.
 W
WNaemon is an open-source computer system monitoring, network monitoring and infrastructure monitoring software application. Naemon offers monitoring and alerting services for servers, switches, applications, and services. It alerts the users when things go wrong and alerts them a second time when the problem has been resolved. Naemon was created in 2014 as a fork of Nagios.
 W
WNetXMS is an open-source network management system. It can be used for monitoring entire IT infrastructures, starting with SNMP-capable hardware and ending with applications on servers.
 W
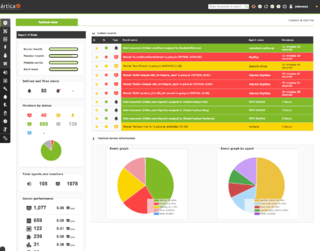
WPandora FMS is software for monitoring computer networks. Pandora FMS allows the visual monitoring of the status and performance of several parameters from different operating systems, servers, applications and hardware systems such as firewalls, proxies, databases, web servers or routers.
 W
WJuan Pavón is a Spanish computer scientist, full professor of the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM). He is a pioneer researcher in the field of Software Agents, co-creator of the FIPA MESSAGE and INGENIAS methodologies, and founder and director of the research group GRASIA: GRoup of Agent-based, Social and Interdisciplinary Applications at UCM. He is known for his work in the field of Artificial Intelligence, specifically in agent-oriented software engineering.
 W
WShinken is an open source computer system and network monitoring software application compatible with Nagios. It watches hosts and services, gathers performance data and alerts users when error conditions occur and again when the conditions clear.
 W
WThe spiral optimization (SPO) algorithm is an uncomplicated search concept inspired by spiral phenomena in nature. The first SPO algorithm was proposed for two-dimensional unconstrained optimization based on two-dimensional spiral models. This was extended to n-dimensional problems by generalizing the two-dimensional spiral model to an n-dimensional spiral model. There are effective settings for the SPO algorithm: the periodic descent direction setting and the convergence setting.
 W
WThe Storm botnet or Storm worm botnet is a remotely controlled network of "zombie" computers that have been linked by the Storm Worm, a Trojan horse spread through e-mail spam. At its height in September 2007, the Storm botnet was running on anywhere from 1 million to 50 million computer systems, and accounted for 8% of all malware on Microsoft Windows computers. It was first identified around January 2007, having been distributed by email with subjects such as "230 dead as storm batters Europe," giving it its well-known name. The botnet began to decline in late 2007, and by mid-2008 had been reduced to infecting about 85,000 computers, far less than it had infected a year earlier.
 W
WXymon, a network monitoring application using free software, operates under the GNU General Public License; its central server runs on Unix and Linux hosts.
 W
WZabbix is an open-source monitoring software tool for diverse IT components, including networks, servers, virtual machines (VMs) and cloud services. Zabbix provides monitoring metrics, among others network utilization, CPU load and disk space consumption. Zabbix monitoring configuration can be done using XML based templates which contain elements to monitor. The software monitors operations on Linux, Hewlett Packard Unix (HP-UX), Mac OS X, Solaris and other operating systems (OSes); however, Windows monitoring is only possible through agents. Zabbix can use MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle or IBM DB2 to store data. Its backend is written in C and the web frontend is written in PHP. Zabbix offers several monitoring options:Simple checks can verify the availability and responsiveness of standard services such as SMTP or HTTP without installing any software on the monitored host. A Zabbix agent can also be installed on UNIX and Windows hosts to monitor statistics such as CPU load, network utilization, disk space, etc. As an alternative to installing an agent on hosts, Zabbix includes support for monitoring via SNMP, TCP and ICMP checks, as well as over IPMI, JMX, SSH, Telnet and using custom parameters. Zabbix supports a variety of near-real-time notification mechanisms, including XMPP.