 W
WA bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, use only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between two other terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching.
 W
WThe 2N107 is an early germanium alloy junction PNP transistor developed by General Electric (GE) in 1955, to become GE's entry into the electronic hobbyist market successfully started with the CK722 transistor. Like the CK722, it enjoyed a long-standing popularity. General Electric decided to designate it with a JEDEC 2N- series identification. This is unusual for a hobby device. Soon after, other manufacturers got involved in the hobby business like Sylvania, Tung-Sol and RCA.
 W
WThe 2N2222 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It was originally made in the TO-18 metal can as shown in the picture.
 W
WThe 2N3055 is a silicon NPN power transistor intended for general purpose applications. It was introduced in the early 1960s by RCA using a hometaxial power transistor process, transitioned to an epitaxial base in the mid-1970s. Its numbering follows the JEDEC standard. It is a transistor type of enduring popularity.
 W
WThe 2N3904 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor used for general-purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low current and power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds.
 W
WThe 2N3906 is a commonly used PNP bipolar junction transistor intended for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low electric current and power and medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds.
 W
WThe germanium alloy-junction transistor, or alloy transistor, was an early type of bipolar junction transistor, developed at General Electric and RCA in 1951 as an improvement over the earlier grown-junction transistor.
 W
WThe BC548 is a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor commonly used in European and American electronic equipment. It is notably often the first type of bipolar transistor hobbyists encounter and is often featured in designs in hobby electronics magazines where a general-purpose transistor is required. The BC548 is low in cost and widely available.
 W
WThe CK722 was the first low-cost junction transistor available to the general public. It was a PNP germanium small signal unit. Developed by Norman Krim, it was introduced by Raytheon in early 1953 for $7.60 each; the price was reduced to $3.50 in late 1954 and to $0.99 in 1956. Norm Krim selected Radio Shack to sell the CK721 and CK722 through their catalog. Krim had a long-standing personal and business relationship with Radio Shack. The CK722s were selected "fall out" from the Raytheon's premium-priced CK721. Raytheon actively encouraged hobbyists with design contests and advertisements.
 W
WAn insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily used as an electronic switch which, as it was developed, came to combine high efficiency and fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (P-N-P-N) that are controlled by a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) gate structure without regenerative action. Although the structure of the IGBT is topologically the same as a thyristor with a 'MOS' gate, the thyristor action is completely suppressed and only the transistor action is permitted in the entire device operation range. It is used in switching power supplies in high-power applications: variable-frequency drives (VFDs), electric cars, trains, variable speed refrigerators, lamp ballasts, arc-welding machines, and air conditioners.
 W
WThe 2N3055 is a silicon NPN power transistor intended for general purpose applications. It was introduced in the early 1960s by RCA using a hometaxial power transistor process, transitioned to an epitaxial base in the mid-1970s. Its numbering follows the JEDEC standard. It is a transistor type of enduring popularity.
 W
WThe KT315 is a Soviet silicon NPN bipolar junction transistor used for general-purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications, enclosed in the plastic KT-13 package. It was widely used in Soviet electronic equipment. The KT361 is a complementary (PNP) for the KT315 transistor, so it was often paired with it in push-pull stages.
 W
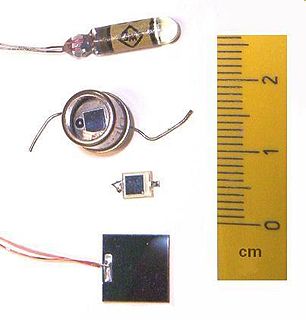
WA photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current. The current is generated when photons are absorbed in the photodiode. Photodiodes may contain optical filters, built-in lenses, and may have large or small surface areas. Photodiodes usually have a slower response time as their surface area increases. The common, traditional solar cell used to generate electric solar power is a large area photodiode.
 W
WThe point-contact transistor was the first type of transistor to be successfully demonstrated. It was developed by research scientists John Bardeen and Walter Brattain at Bell Laboratories in December 1947. They worked in a group led by physicist William Shockley. The group had been working together on experiments and theories of electric field effects in solid state materials, with the aim of replacing vacuum tubes with a smaller device that consumed less power.
 W
WThe surface-barrier transistor is a type of transistor developed by Philco in 1953 as an improvement to the alloy-junction transistor and the earlier point-contact transistor. Like the modern Schottky transistor, it offered much higher speed than earlier transistors and used metal–semiconductor junctions, but unlike the schottky transistor, both junctions were metal–semiconductor junctions.