 W
W80 Plus is a voluntary certification program intended to promote efficient energy use in computer power supply units (PSUs). Launched in 2004, it certifies products that have more than 80% energy efficiency at 20%, 50% and 100% of rated load, and a power factor of 0.9 or greater at 100% load. Such PSUs waste 20% or less electric energy as heat at the specified load levels, reducing electricity use and bills compared to less efficient PSUs.
 W
WCOM Express, a computer-on-module (COM) form factor, is a highly integrated and compact PC that can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. Each COM Express Module COM integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics (PEG), and Ethernet. All I/O signals are mapped to two high density, low profile connectors on the bottom side of the module. COM Express employs a mezzanine-based approach. The COM modules plug into a baseboard that is typically customized to the application. Over time, the COM Express mezzanine modules can be upgraded to newer, backwards-compatible versions. COM Express is commonly used in Industrial, Military/Aerospace, Gaming, Medical, Transportation, IoT, and General Computing embedded applications.
 W
WCoreExpress modules are complete computer-on-module (COM) highly integrated, compact computers that can be used in an embedded computer board design, much like an integrated circuit component. COMs integrate CPU, memory, graphics, and BIOS, and common I/O interfaces. The interfaces are modern, using only digital buses such as PCI Express, Serial ATA, Ethernet, USB, and HD audio. All signals are accessible on a high-density, high-speed, 220-pin connector. Although most implementations use Intel processors, the specification is open for different CPU modules.
 W
WElectronic voting in the United States involves several types of machines: touch screens for voters to mark choices, scanners to read paper ballots, scanners to verify signatures on envelopes of absentee ballots, and web servers to display tallies to the public. Aside from voting, there are also computer systems to maintain voter registrations and display these electoral rolls to polling place staff.
 W
WETX, standing for Embedded Technology eXtended, is an integrated and compact 95 × 125 mm (3.7 × 4.9 in) computer-on-module (COM) form factor, which can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. Each ETX COM integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics, and Ethernet. All I/O signals as well as a full implementation of ISA and PCI buses are mapped to four high-density, low-profile connectors on the bottom side of the module.
 W
WIndustry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles.
 W
WIntel High Definition Audio (IHDA) is a specification for the audio sub-system of personal computers. It was released by Intel in 2004 as successor to its AC'97 PC audio standard.
 W
WThe Low Pin Count bus, or LPC bus, is a computer bus used on IBM-compatible personal computers to connect low-bandwidth devices to the CPU, such as the boot ROM, "legacy" I/O devices, and Trusted Platform Module (TPM). "Legacy" I/O devices usually include serial and parallel ports, PS/2 keyboard, PS/2 mouse, and floppy disk controller.
 W
WMultichannel Audio Digital Interface (MADI) or AES10 is an Audio Engineering Society (AES) standard that defines the data format and electrical characteristics of an interface that carries multiple channels of digital audio. The AES first documented the MADI standard in AES10-1991, and updated it in AES10-2003 and AES10-2008. The MADI standard includes a bit-level description and has features in common with the two-channel AES3 interface.
 W
WMIDI is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing and recording music. The specification originates in a paper titled Universal Synthesizer Interface, published by Dave Smith and Chet Wood, then of Sequential Circuits, at the October 1981 Audio Engineering Society conference in New York City.
 W
WParallel ATA (PATA), originally AT Attachment, also known as ATA or IDE is standard interface for IBM computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, and optical disc drives in computers.
 W
WQseven, a computer-on-module (COM) form factor, is a small, highly integrated computer module that can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. It's smaller than other computer-on-module standards such as COM Express, ETX or XTX and is limited to very low power consuming CPUs. The maximum power consumption should be no more than 12 watt.
 W
WThe MPU-401, where MPU stands for MIDI Processing Unit, is an important but now obsolete interface for connecting MIDI-equipped electronic music hardware to personal computers. It was designed by Roland Corporation, which also co-authored the MIDI standard.
 W
WThe Small Form Factor Special Interest Group or SFF-SIG is an international non-profit standards body focused on modular computer hardware technologies used in embedded and small form factor computers and controllers. Members are mainly computer board and component manufacturers.
 W
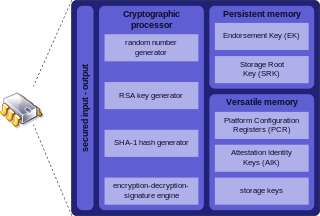
WTrusted Platform Module is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys.