 W
WActive camouflage or adaptive camouflage is camouflage that adapts, often rapidly, to the surroundings of an object such as an animal or military vehicle. In theory, active camouflage could provide perfect concealment from visual detection.
 W
WAn airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system is an airborne radar picket system designed to detect aircraft, ships and vehicles at long ranges and perform command and control of the battlespace in an air engagement by directing fighter and attack aircraft strikes. AEW&C units are also used to carry out surveillance, including over ground targets and frequently perform C2BM functions similar to an Air Traffic Controller given military command over other forces. When used at altitude, the radar on the aircraft allows the operators to detect and track targets and distinguish between friendly and hostile aircraft much farther away than a similar ground-based radar. Like a ground-based radar, it can be detected by opposing forces, but because of its mobility and extended sensor range, it is much less vulnerable to counter-attacks.
 W
WThe Battlefield Airborne Communications Node (BACN) is a United States Air Force (USAF) airborne communications relay and gateway system carried by the unmanned EQ-4B and the manned Bombardier E-11A aircraft. BACN enables real-time information flow across the battlespace between similar and dissimilar tactical data link and voice systems through relay, bridging, and data translation in line-of-sight and beyond-line-of-sight situations. Its ability to translate between dissimilar communications systems allows them to interoperate without modification.
 W
WThe Mini TSFO was the first artillery call-for-fire simulation designed for the personal computer. It was started in 1985 as an outgrowth of a Field Artillery Officer Advanced Course battlefield research project at the U.S. Army Field Artillery School (USAFAS) to develop a concept for incorporating PCs into artillery training, and was completed in 1986. It replaced summer artillery live fire training for cadets at West Point in 1986 and 1987.
 W
WThe Cora was a digital fire-control system designed by Peter Toth and produced by the Swiss company Contraves.
 W
WAn electro-optical targeting system (EOTS), is a system employed to track and locate targets in aerial warfare. It can use charge-coupled device TV cameras, laser rangefinders and laser designators.
 W
WThe EuroFirst Passive Infrared Airborne Track Equipment (PIRATE) is the Forward looking infrared (FLIR) / Infra-red search and track (IRST) for the Eurofighter Typhoon. It is produced by the EuroFIRST consortium consisting of Leonardo S.p.A. of Italy, THALES Land & Joint Systems of the UK, and TECNOBIT of Spain. The system is mounted on the port side of the fuselage, forward of the windscreen and provides passive and thus undetectable and unjammable means of long range surveillance. In addition the system has been shown to locate stealth aircraft at a "significant distance" with further improvements in detection through software updates. PIRATE detects heat caused on an aircraft's skin caused by air friction.
 W
WForward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation.
 W
WA helmet-mounted display (HMD) is a device used in aircraft to project information to the pilot's eyes. Its scope is similar to that of head-up displays (HUD) on an aircrew's visor or reticle. An HMD provides the pilot with situation awareness, an enhanced image of the scene, and in military applications cue weapons systems, to the direction their head is pointing. Applications which allow cuing of weapon systems are referred to as helmet-mounted sight and display (HMSD) or helmet-mounted sights (HMS).
 W
WHyperspectral imaging, like other spectral imaging, collects and processes information from across the electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of hyperspectral imaging is to obtain the spectrum for each pixel in the image of a scene, with the purpose of finding objects, identifying materials, or detecting processes. There are three general branches of spectral imagers. There are push broom scanners and the related whisk broom scanners, which read images over time, band sequential scanners, which acquire images of an area at different wavelengths, and snapshot hyperspectral imaging, which uses a staring array to generate an image in an instant.
 W
WAn infrared search and track (IRST) system is a method for detecting and tracking objects which give off infrared radiation such as jet aircraft and helicopters.
 W
WA magnetic anomaly detector (MAD) is an instrument used to detect minute variations in the Earth's magnetic field. The term refers specifically to magnetometers used by military forces to detect submarines ; military MAD equipment is a descendant of geomagnetic survey or aeromagnetic survey instruments used to search for minerals by detecting their disturbance of the normal earth-field.
 W
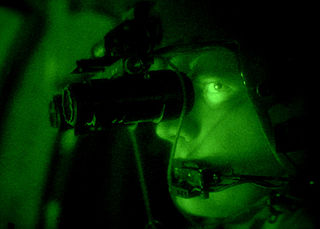
WA night-vision device (NVD), also known as night optical/observation device (NOD) and night-vision goggles (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows images to be produced in levels of light approaching total darkness. The image may be a conversion to visible light of both visible light and near-infrared, while by convention detection of thermal infrared is denoted thermal imaging. The image produced is typically monochrome, e.g. shades of green. NVDs are most often used by the military and law enforcement agencies, but are available to civilian users. The term usually refers to a complete unit, including an image intensifier tube, a protective and generally water-resistant housing, and some type of mounting system. Many NVDs include a protective sacrificial lens, or optical components such as telescopic lenses or mirrors. An NVD may have an IR illuminator, making it an active as opposed to passive night-vision device.
 W
WThe Orkney Wireless Museum in Kirkwall, Orkney, Scotland, houses a collection of domestic and military wireless equipment. It developed from the private collection of the late Jim MacDonald from St Margaret's Hope and marks the importance of wireless communications in Orkney during World War II.
 W
WPeople sniffer was the field name for a series of U.S. Army issued "personnel detectors" used during the Vietnam War. The purpose was to detect enemy soldiers in hidden positions, which were often employed in the jungle combat conditions of Vietnam. The U.S. military used two different versions of the people sniffer, one backpack version and one helicopter-mounted version.