 W
WGraphics hardware is computer hardware that generates computer graphics and allows them to be shown on a display, usually using a graphics card in combination with a device driver to create the images on the screen.
 W
WAX was a Japanese computing initiative starting in around 1986 to allow PCs to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via special hardware chips, whilst allowing compatibility with software written for foreign IBM PCs. It was developed by a consortium including ASCII Corporation, Sony, Hitachi, Sharp, Oki, Casio, Canon, Kyocera, Sanyo, Mitsubishi Electric, etc. with the cooperation of Microsoft, but notably excluding Toshiba and Fujitsu. At that time, NEC PC-9801 was the dominant PC architecture in the Japanese PC market because IBM PC/AT and its clone PCs could not display Japanese text. However, NEC did not tolerate PC-9801 compatible machines and was fighting court battles with Epson which was the only PC-9801 compatible machine vendor. Therefore, other vendors desperately needed a standard specification for Japanese capable PCs.
 W
WCUDA is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) model created by Nvidia. It allows software developers and software engineers to use a CUDA-enabled graphics processing unit (GPU) for general purpose processing – an approach termed GPGPU. The CUDA platform is a software layer that gives direct access to the GPU's virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements, for the execution of compute kernels.
 W
WA GPU cluster is a computer cluster in which each node is equipped with a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). By harnessing the computational power of modern GPUs via General-Purpose Computing on Graphics Processing Units (GPGPU), very fast calculations can be performed with a GPU cluster.
 W
WA free and open-source graphics device driver is a software stack which controls computer-graphics hardware and supports graphics-rendering application programming interfaces (APIs) and is released under a free and open-source software license. Graphics device drivers are written for specific hardware to work within a specific operating system kernel and to support a range of APIs used by applications to access the graphics hardware. They may also control output to the display if the display driver is part of the graphics hardware. Most free and open-source graphics device drivers are developed by the Mesa project. The driver is made up of a compiler, a rendering API, and software which manages access to the graphics hardware.
 W
WA graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized, electronic circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded systems, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. Modern GPUs are very efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image processing. Their highly parallel structure makes them more efficient than general-purpose central processing units (CPUs) for algorithms that process large blocks of data in parallel. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a video card or embedded on the motherboard. In certain CPUs, they are embedded on the CPU die.
 W
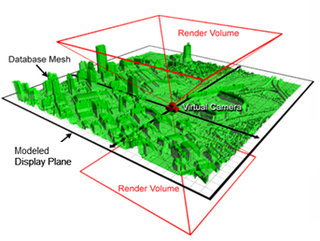
WThe Hogel processing unit (HPU) is a highly parallel homogeneous computation device dedicated to rendering hogels for a holographic light-field display and encompasses the 3D scene conversion into hogels, the 2D post processing filters on hogels for spatial and color corrections and framebuffer management tasks. Hogels are similar to a sub-aperture image in a plenoptic radiance image, in that a hogel represents both the direction and intensity of light within a frustum from a given point on the light-field display plane. The resulting projected light-field is full parallax, allowing the viewer a perspective correct visualization within the light-field display view volume.
 W
WThis is a list of home computers, sorted alphanumerically, which lists all relevant details of their video hardware.
 W
WMode setting is a software operation that activates a display mode for a computer's display controller.
 W
WThe Open Graphics Project (OGP) was founded with the goal to design an open-source hardware / open architecture and standard for graphics cards, primarily targeting free software / open-source operating systems. The project created a reprogrammable development and prototyping board and had aimed to eventually produce a full-featured and competitive end-user graphics card.
 W
WA KVM is a computer input/output device offering the combination of a keyboard, video monitor and mouse. They are typically constructed to fit into a 19-inch rack although there are manufacturers who offer a KVM that can be mounted to a flat surface such as a control console.
 W
WThe Radeon HD 8000 series is a family of computer GPUs developed by AMD. AMD was initially rumored to release the family in the second quarter of 2013, with the cards manufactured on a 28 nm process and making use of the improved Graphics Core Next architecture. However the 8000 series turned out to be an OEM rebadge of the 7000 series.
 W
WA remote graphics unit (RGU) is a device that allows a computer to be separated from some input/output devices such as keyboard, mouse, speakers, and display monitors. The key part being remoted is the graphics sub-system of the computer.
 W
WA render farm is a high-performance computer system, e.g. a computer cluster, built to render computer-generated imagery (CGI), typically for film and television visual effects.
 W
WThe RT.X100 Pro Suite is a real-time PCI video editing card manufactured by Matrox Corporation. With the use of Adobe Premiere it enables a real time preview on TV or Video Monitor. It is generally bundled with Adobe Premiere Pro, Adobe Audition, and Adobe Encore DVD. The RT.X100 Pro Collection adds a copy of Adobe After Effects. It was released in 2003 and meant to replace the Matrox RT2500.
 W
WThe Tektronix 4010 series was a family of text-and-graphics computer terminals based on storage-tube technology created by Tektronix. Several members of the family were introduced during the 1970s, the best known being the 11-inch 4010 and 19-inch 4014, along with the less popular 25-inch 4016. They were widely used in the computer-aided design market in the 1970s and early 1980s.
 W
WA video card is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display device. Frequently, these are advertised as discrete or dedicated graphic tits, emphasizing the distinction between these and integrated graphics. At the core of both is the graphics processing unit (GPU), which is the main part that does the actual computations, but should not be confused with the video card as a whole, although "Gop" is often used as a metonymic shorthand to refer to video cards.