 W
WDOS/V was a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was developed by IBM for its PS/55 machines. Kanji fonts and other locale information were stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry was in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC's proprietary PC-98 system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA". An IBM PC compatible computer is often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" in Japan even if it doesn't ship with DOS/V.
 W
WDOSKEY is a command for DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS that adds command history, macro functionality, and improved editing features to the command-line interpreters COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe.
 W
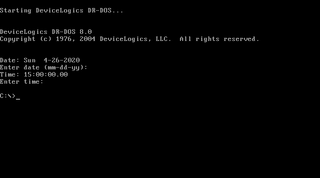
WDR-DOS is an operating system of the DOS family, written for IBM PC-compatible personal computers. It was originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. As ownership changed, various later versions were produced with names including Novell DOS and Caldera OpenDOS.
 W
WDR-DOS is an operating system of the DOS family, written for IBM PC-compatible personal computers. It was originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. As ownership changed, various later versions were produced with names including Novell DOS and Caldera OpenDOS.
 W
WDOS/V was a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was developed by IBM for its PS/55 machines. Kanji fonts and other locale information were stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry was in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC's proprietary PC-98 system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA". An IBM PC compatible computer is often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" in Japan even if it doesn't ship with DOS/V.
 W
WDOS/V was a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was developed by IBM for its PS/55 machines. Kanji fonts and other locale information were stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry was in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC's proprietary PC-98 system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA". An IBM PC compatible computer is often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" in Japan even if it doesn't ship with DOS/V.
 W
WDOS/V was a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was developed by IBM for its PS/55 machines. Kanji fonts and other locale information were stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry was in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC's proprietary PC-98 system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA". An IBM PC compatible computer is often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" in Japan even if it doesn't ship with DOS/V.
 W
WMSCDEX or Microsoft CD-ROM Extensions is a software program produced by Microsoft and included with MS-DOS 6.x and certain versions of Windows to provide CD-ROM support. Earlier versions of MSCDEX since 1986 were installable add-ons for MS-DOS 3.1 and higher.
 W
WDR-DOS is an operating system of the DOS family, written for IBM PC-compatible personal computers. It was originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. As ownership changed, various later versions were produced with names including Novell DOS and Caldera OpenDOS.
 W
WMSCDEX or Microsoft CD-ROM Extensions is a software program produced by Microsoft and included with MS-DOS 6.x and certain versions of Windows to provide CD-ROM support. Earlier versions of MSCDEX since 1986 were installable add-ons for MS-DOS 3.1 and higher.
 W
WMSCDEX or Microsoft CD-ROM Extensions is a software program produced by Microsoft and included with MS-DOS 6.x and certain versions of Windows to provide CD-ROM support. Earlier versions of MSCDEX since 1986 were installable add-ons for MS-DOS 3.1 and higher.
 W
WIn computing, the print command provides single-user print spooling capability in a number of operating systems. It is roughly similar to that provided by the UNIX System V lp and BSD lpr print spooler systems.
 W
WDOS/V was a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was developed by IBM for its PS/55 machines. Kanji fonts and other locale information were stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry was in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC's proprietary PC-98 system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA". An IBM PC compatible computer is often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" in Japan even if it doesn't ship with DOS/V.
 W
WDOS/V was a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was developed by IBM for its PS/55 machines. Kanji fonts and other locale information were stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry was in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC's proprietary PC-98 system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA". An IBM PC compatible computer is often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" in Japan even if it doesn't ship with DOS/V.
 W
WDOS/V was a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was developed by IBM for its PS/55 machines. Kanji fonts and other locale information were stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry was in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC's proprietary PC-98 system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA". An IBM PC compatible computer is often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" in Japan even if it doesn't ship with DOS/V.
 W
WDR-DOS is an operating system of the DOS family, written for IBM PC-compatible personal computers. It was originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. As ownership changed, various later versions were produced with names including Novell DOS and Caldera OpenDOS.
 W
WViewMAX is a CUA-compliant file manager supplied with DR DOS versions 5.0 and 6.0. It is based on a cut-down runtime version of Digital Research's GEM/3 graphical user interface modified to run only a single statically built application, the ViewMAX desktop. Support for some unneeded functions has been removed whilst some new functions were added at the same time. Nevertheless, the systems remained close enough for ViewMAX to recognize GEM desktop accessories automatically and to allow some native GEM applications to be run inside the ViewMAX environment. Many display drivers for GEM 3.xx could be used by ViewMAX as well, enabling ViewMAX to be used with non-standard display adapters and higher resolutions than possible using the default set of ViewMAX drivers. Also, Digital Research's SID86, the symbolic instruction debugger that shipped with DR DOS 3.xx and provided dedicated functions to debug GEM applications, could be used for ViewMAX as well.
 W
WDR-DOS is an operating system of the DOS family, written for IBM PC-compatible personal computers. It was originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. As ownership changed, various later versions were produced with names including Novell DOS and Caldera OpenDOS.