 W
WA telephone jack and a telephone plug are electrical connectors for connecting a telephone set or other telecommunications apparatus to the telephone wiring inside a building, establishing a connection to a telephone network. The plug is inserted into its counterpart, the jack, which is commonly affixed to a wall or baseboard. The standards for telephone jacks and plugs vary from country to country, though the RJ11 modular connector has become by far the most common type.
 W
WA 600 series connector is an obsolete three-pin connector with up to six conductors.
 W
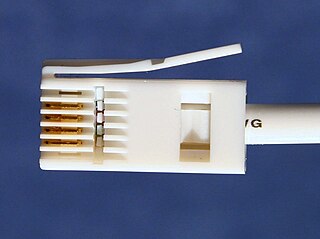
WBritish telephone sockets were introduced in their current plug and socket form on 19 November 1981 by British Telecom to allow subscribers to connect their own telephones. The connectors are specified in British Standard BS 6312. Electrical characteristics of the telephone interface are specified by individual network operators, e.g. in British Telecom's SIN 351. Electrical characteristics required of British telephones used to be specified in BS 6305.
 W
WThe Danish telephone plug is the special flat round telephone plug used in Denmark for POTS (analog) telephone lines and some "raw copper" telephone lines. The plug has 3 flat pins arranged at right angles to each other. This plug is used in few if any other places in the world, and most equipment now made uses the US/International RJ11 socket on the device end and includes either a cable with the Danish Telephone Plug at the wall end, or a standard RJ11 to RJ11 cable with a bundled Telephone Adapter.
 W
WF-010 or T plug or PTT plug is a type of telephone plug and matching socket. The F-010 standard originated in France and is used there and in other countries, including Algeria, Andorra, Bhutan, Burkina Faso, Chad, Comoros, Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Grenadines, Ivory Coast, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Monaco, Morocco, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Somalia, Togo and Tunisia.
 W
WAn insulation-displacement contact (IDC), also known as insulation-piercing contact (IPC), is an electrical connector designed to be connected to the conductor(s) of an insulated cable by a connection process which forces a selectively sharpened blade or blades through the insulation, bypassing the need to strip the conductors of insulation before connecting. When properly made, the connector blade cold-welds to the conductor, making a theoretically reliable gas-tight connection.
 W
WKrone LSA-PLUS is an insulation-displacement connector for telecommunications. It is a proprietary European alternative to 110 block. The Krone LSA-PLUS system is not limited to telecommunications, as it is also popular in broadcast systems, where audio interconnections and their associated control systems often use krone wiring. Multipair audio cables have been specifically designed for the system by organisations such as the BBC.
 W
WA modular connector is a type of electrical connector for cords and cables of electronic devices and appliances, such in computer networking, telecommunication equipment, and audio headsets.
 W
WA phone connector, also known as phone jack, audio jack, headphone jack or jack plug, is a family of electrical connectors typically used for analog audio signals. The standard is that a plug will connect with a jack.
 W
WThe Protea telephone plug, sometimes called simply the South African telephone plug, was widely used in South Africa from the 1970s until the 1990s. As of 2004, telephone installations in South Africa use RJ11 plugs, but Protea plugs are still often encountered in older installations.
 W
WA punch down tool, also called a punchdown tool, IDC tool or a krone tool, a small hand tool used by telecommunication and network technicians. It is used for inserting wire into insulation-displacement connectors on punch down blocks, patch panels, keystone modules, and surface mount boxes.
 W
WA punch-down block is a type of electrical connection often used in telephony. It is named because the solid copper wires are "punched down" into short open-ended slots which are a type of insulation-displacement connector. These slots, usually cut crosswise across an insulating plastic bar, contain two sharp metal blades which cut through the wire's insulation as it is punched down. These blades hold the wire in position and make the electrical contact with the wire as well.
 W
WA registered jack (RJ) is a standardized telecommunication network interface for connecting voice and data equipment to a service provided by a local exchange carrier or long distance carrier. Registration interfaces were first defined in the Universal Service Ordering Code (USOC) system of the Bell System in the United States for complying with the registration program for customer-supplied telephone equipment mandated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the 1970s. They were subsequently codified in title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations Part 68. Registered Jack connections began to see use after their invention in 1973 by Bell Labs. The specification includes physical construction, wiring, and signal semantics. Accordingly, registered jacks are primarily named by the letters RJ, followed by two digits that express the type. Additional letter suffixes indicate minor variations. For example, RJ11, RJ14, and RJ25 are the most commonly used interfaces for telephone connections for one-, two-, and three-line service, respectively. Although these standards are legal definitions in the United States, some interfaces are used worldwide.
 W
WA standard Swedish telephone plug carries one telephone line and has four flat metal pins and one plastic pin. The design is only used in Sweden and older installations in Iceland. Neither plug nor socket is compatible with other plugs and sockets. It is defined in Swedish Standard SS 455 15 50.
 W
WTAE is the German standard for telephone plugs and sockets.
 W
WTDO (Telefonsteckdose) is the telephone plug used by A1 Telekom Austria.
 W
WThe Telebrás plug is the old Brazilian telephone plug and socket system. It uses a large plug with 2 flat metal pins + 2 flat plastic pins. Three of the pins have the same orientation and the fourth pin being rotated 90 degrees to make it impossible to plug in the wrong orientation.
 W
WA standard tetrapolar telephone plug has four round metal pins and one plastic pin. The design is only used in Belgium for telephone wiring. It is similar to the tripolar telephone plug of Italy and also the Swedish telephone plug.
 W
WThe telefonic tripolar plug is the first type of telephone plug used in Italy. It has also been used in Finland, Norway and Turkey in older installations.