 W
W78xx is a family of self-contained fixed linear voltage regulator integrated circuits. The 78xx family is commonly used in electronic circuits requiring a regulated power supply due to their ease-of-use and low cost.
 W
WThe 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. Derivatives provide two (556) or four (558) timing circuits in one package. It was commercialized in 1972 by Signetics and it was reported to still be in wide use as of 2013. Numerous companies have made the original bipolar timers and similar low-power CMOS timers too. In 2017, it was said over a billion 555 timers are produced annually by some estimates, and "probably the most popular integrated circuit ever made."
 W
WCX is a noise reduction system for recorded analog audio. It was developed by CBS Laboratories in the late 1970s as a competitor to other noise reduction (NR) systems such as Dolby and dbx, and was officially introduced in 1981. The name CX was derived from "Compatible eXpansion", a feature of the technique. The CX integrated circuit U2141B was developed by AEG-Telefunken, Germany, in 1982, by Ernst F. Schröder, Dietrich Höppner and Kurt Hintzmann, the same team who also designed the High Com noise reduction system, a broadband compander with up to 20 dB of noise reduction. Hitachi also offered dedicated CX chips named HA12043 and HA12044 in 1983. Telefunken also used, in their RS 120 CX a dual trans-conductance amplifier 13700D made by JRC, coupled with a pair of quad J-FET OpAmp chips TL084.
 W
WCX is a noise reduction system for recorded analog audio. It was developed by CBS Laboratories in the late 1970s as a competitor to other noise reduction (NR) systems such as Dolby and dbx, and was officially introduced in 1981. The name CX was derived from "Compatible eXpansion", a feature of the technique. The CX integrated circuit U2141B was developed by AEG-Telefunken, Germany, in 1982, by Ernst F. Schröder, Dietrich Höppner and Kurt Hintzmann, the same team who also designed the High Com noise reduction system, a broadband compander with up to 20 dB of noise reduction. Hitachi also offered dedicated CX chips named HA12043 and HA12044 in 1983. Telefunken also used, in their RS 120 CX a dual trans-conductance amplifier 13700D made by JRC, coupled with a pair of quad J-FET OpAmp chips TL084.
 W
WThe ICL8038 waveform generator was an Integrated circuit by Intersil designed to generate sine, square and triangular waveforms, based on bipolar monolithic technology involving Schottky barrier diodes. ICL8038 was a voltage-controlled oscillator capable of producing frequencies between a millihertz and 100kHz., some specimens capable of reaching 300kHz. The device has been discontinued by Intersil in 2002.
 W
WThe following is a list of linear integrated circuits. Many were among the first analog integrated circuits commercially produced; some were groundbreaking innovations, and many are still being used.
 W
WThe following is a list of LM-series integrated circuits. Many were among the first analog integrated circuits commercially produced; some were groundbreaking innovations, and many are still being used. The LM series originated with integrated circuits made by National Semiconductor. The prefix LM stands for linear monolithic, referring to the analog components integrated onto a single piece of silicon. Because of the popularity of these parts, many of them were second-sourced by other manufacturers who kept the sequence number as an aid to identification of compatible parts. Several generations of pin-compatible descendants of the original parts have since become de facto standard electronic components.
 W
WThe LM317 is a popular adjustable positive linear voltage regulator. It was designed by Bob Dobkin in 1976 while he worked at National Semiconductor.
 W
WThe LM358 is a low power dual operational amplifier integrated circuit originally introduced by National Semiconductor.
 W
WThe LM386 is an integrated circuit containing a low-voltage audio power amplifier. It is suitable for battery-powered devices such as radios, guitar amplifiers, and hobby electronics projects. The IC consists of an 8-pin dual in-line package (DIP-8) and can output 0.25 to 1 watts of power, depending on the model, using a 9-volt power supply.
 W
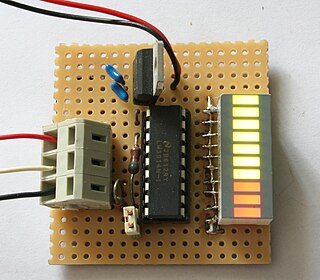
WThe LM3914 is an integrated circuit (IC), designed by National Semiconductor in 1980, used to operate displays that visually show the magnitude of an analog signal. It can drive up to 10 LEDs, LCDs, or vacuum fluorescent displays on its outputs. The linear scaling of the output thresholds makes the device usable, for example, as a voltmeter. In the basic configuration it provides a ten step scale which is expandable to over 100 segments with other LM3914 ICs in series.
 W
WThe LM13700 is an integrated circuit consisting of two current controlled operational transconductance amplifiers (OTA), each having differential inputs and a push-pull output. The LM13700 is like a standard op-amp: each has a pair of differential inputs and a single output, but an OTA is voltage in and current out rather than voltage in and voltage out; and OTAs are programmable via the IABC pin. Linearizing diodes at the input reduce distortion and allow increased input levels. The darlington output buffers provided are specifically designed to complement the wide dynamic range of the OTA. This chip is very useful in audio electronics especially in analog synthesizer circuits like voltage controlled oscillators, voltage controlled filters, and voltage controlled amplifiers. The darlington output buffers on the LM13700 are different from those on the LM13600 in that their bias currents are independent of IABC pin. This usually results in performance superior to that of the LM13600 in audio applications.
 W
WA low-dropout regulator is a DC linear voltage regulator that can regulate the output voltage even when the supply voltage is very close to the output voltage.
 W
WThe MK484 AM radio IC is a fully functional AM radio detector on a chip. It is constructed in a TO-92 case, resembling a small transistor. It replaces the similar ZN414 AM radio IC from the 1970s. The MK484 is favored by many hobbyists. It is advantageous in that it performs well with minimal discrete components, and can run from a single 1.5-volt cell.
 W
WThe NE612 is an integrated circuit for processing of signals, such as in the transmission of radio signals. It comprises an oscillator and a mixer. It can handle signal frequencies up to 500 MHz and local oscillator frequencies up to 200 MHz. The mixer is a “Gilbert cell” multiplier configuration which provides both a gain of 14 dB and a noise figure of 5 dB at 45 MHz. The IC belongs to a family of the following ICs: NE602, SA602, NE612 and SA612. It is widely used in amateur radio applications, e.g. in the commercial Elecraft products, and others.
 W
WAn operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential that is typically 100,000 times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals. Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to perform mathematical operations in linear, non-linear, and frequency-dependent circuits.
 W
WThe operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) is an amplifier whose differential input voltage produces an output current. Thus, it is a voltage controlled current source (VCCS). There is usually an additional input for a current to control the amplifier's transconductance. The OTA is similar to a standard operational amplifier in that it has a high impedance differential input stage and that it may be used with negative feedback.
 W
WThe TL431 is a three-terminal adjustable precision shunt voltage regulator integrated circuit. With the use of an external voltage divider, a TL431 can regulate voltages ranging from 2.5 to 36 V, at currents up 100 mA. The typical initial deviation of reference voltage from the nominal 2.495 V level is measured in millivolts, the maximum worst-case deviation is measured in tens of millivolts. The circuit can control power transistors directly; combinations of the TL431 with power MOS transistors are used in high efficiency, very low dropout linear regulators. The TL431 is the de facto industry standard error amplifier circuit for switched-mode power supplies with optoelectronic coupling of the input and output networks.
 W
WCX is a noise reduction system for recorded analog audio. It was developed by CBS Laboratories in the late 1970s as a competitor to other noise reduction (NR) systems such as Dolby and dbx, and was officially introduced in 1981. The name CX was derived from "Compatible eXpansion", a feature of the technique. The CX integrated circuit U2141B was developed by AEG-Telefunken, Germany, in 1982, by Ernst F. Schröder, Dietrich Höppner and Kurt Hintzmann, the same team who also designed the High Com noise reduction system, a broadband compander with up to 20 dB of noise reduction. Hitachi also offered dedicated CX chips named HA12043 and HA12044 in 1983. Telefunken also used, in their RS 120 CX a dual trans-conductance amplifier 13700D made by JRC, coupled with a pair of quad J-FET OpAmp chips TL084.
 W
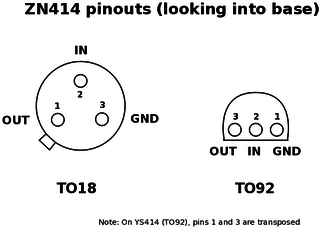
WThe ZN414 is a low cost, single-chip AM radio integrated circuit. Launched in 1972, the part was designed and supplied by Ferranti, but was also available from GEC-Plessey. The ZN414 was popular amongst hobbyists as a fully working AM radio could be made with just a few external components, a crystal earpiece and a 1.5 V cell.