 W
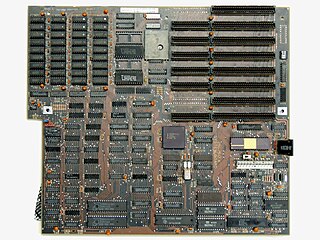
WIn the era of IBM compatible personal computers, the AT form factor referred to the dimensions and layout of the motherboard for the IBM AT. Like the IBM PC and IBM XT models before it, many third-party manufacturers produced motherboards compatible with the IBM AT form factor, allowing end users to upgrade their computers for faster processors. The IBM AT became a widely copied design in the booming home computer market of the 1980s. IBM clones made at the time began using AT compatible designs, contributing to its popularity. In the 1990s many computers still used AT and its variants. Since 1997, the AT form factor has been largely supplanted by ATX.
 W
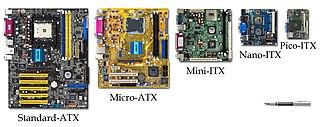
WATX is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclosure, motherboard and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts. The specification defines the dimensions; the mounting points; the I/O panel; and the power and connector interfaces among a computer case, a motherboard, and a power supply.
 W
WBTX is a form factor for motherboards, originally intended to be the replacement for the aging ATX motherboard form factor in late 2004 and early 2005.
 W
WCOM Express, a computer-on-module (COM) form factor, is a highly integrated and compact PC that can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. Each COM Express Module COM integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics (PEG), and Ethernet. All I/O signals are mapped to two high density, low profile connectors on the bottom side of the module. COM Express employs a mezzanine-based approach. The COM modules plug into a baseboard that is typically customized to the application. Over time, the COM Express mezzanine modules can be upgraded to newer, backwards-compatible versions. COM Express is commonly used in Industrial, Military/Aerospace, Gaming, Medical, Transportation, IoT, and General Computing embedded applications.
 W
WCoreExpress modules are complete computer-on-module (COM) highly integrated, compact computers that can be used in an embedded computer board design, much like an integrated circuit component. COMs integrate CPU, memory, graphics, and BIOS, and common I/O interfaces. The interfaces are modern, using only digital buses such as PCI Express, Serial ATA, Ethernet, USB, and HD audio. All signals are accessible on a high-density, high-speed, 220-pin connector. Although most implementations use Intel processors, the specification is open for different CPU modules.
 W
WThe DTX form factor is a variation of ATX specification designed especially for small form factor PCs with dimensions of 8 × 9.6 inches (203 × 244 mm). An industry standard intended to enable interchangeability for systems similar to Shuttle's original "SFF" designs, AMD announced its development on January 10, 2007. AMD stated that the DTX form factor is an open standard, and is backward compatible with ATX form factor cases. They also present a shorter variant named Mini-DTX which is smaller in PCB size of 8 × 6.7 inches (203 × 170 mm).
 W
WETX, standing for Embedded Technology eXtended, is an integrated and compact 95 × 125 mm (3.7 × 4.9 in) computer-on-module (COM) form factor, which can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. Each ETX COM integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics, and Ethernet. All I/O signals as well as a full implementation of ISA and PCI buses are mapped to four high-density, low-profile connectors on the bottom side of the module.
 W
WFlexATX is a motherboard form factor derived from ATX. The specification was released in 1999 by Intel as an addendum to the microATX specification. It uses a subset of the motherboard mounting holes required for microATX and the same I/O plate system as ATX and microATX.
 W
WGumstix is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Redwood City, California. It develops and manufactures small system boards comparable in size to a stick of gum. In 2003, when it was first fully functional, it used ARM architecture System on a chip (SoC) and an Operating System based on Linux 2.6 kernel. It has an online tool called Geppetto that allows users to design their own boards. In August 2013 it started a crowd-funding service to allow a group of users that want to get a custom design manufactured to share the setup costs.
 W
WLPX, originally developed by Western Digital, was a loosely defined motherboard format widely used in the 1990s.
 W
WmicroATX is a standard for motherboards that was introduced in December 1997. The maximum size of a microATX motherboard is 9.6 × 9.6 in (244 × 244 mm). The standard ATX size is 25% longer, at 12 × 9.6 in (305 × 244 mm).
 W
WMini ATX or Mini-ATX is a name used for various motherboard form factors, as there is no single widely accepted form factor by this name.
 W
WMini-ITX is a 17 × 17 cm (6.7 × 6.7 in) motherboard form-factor, developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. They are commonly used in small-configured computer systems. Originally, they were a niche product, designed for fan-less cooling with a low power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience. The four mounting holes in a Mini-ITX board line up with four of the holes in ATX-specification motherboards, and the locations of the backplate and expansion slot are the same. Mini-ITX boards can therefore often be used in cases designed for ATX, micro-ATX and other ATX variants if desired.
 W
WMobile-ITX is the smallest x86 compliant motherboard form factor presented by VIA Technologies in December, 2009. The motherboard size is 60 × 60 mm (2.4 × 2.4 in). There are no computer ports on the CPU module and it is necessary to use an I/O carrier board. The design is intended for medical, transportation and military embedded markets.
 W
WNano-ITX is a computer motherboard form factor first proposed by VIA Technologies at CeBIT in March 2003, and implemented in late 2005. Nano-ITX boards measure 12 × 12 cm (4.7 × 4.7 in), and are fully integrated, very low power consumption motherboards with many uses, but targeted at smart digital entertainment devices such as DVRs, set-top boxes, media centers, car PCs, and thin devices.
 W
WPico-ITX is a PC motherboard form factor announced by VIA Technologies in January 2007 and demonstrated later the same year at CeBIT. The formfactor was transferred over to SFF-SIG in 2008. The Pico-ITX form factor specifications call for the board to be 10 × 7.2 cm (3.9 × 2.8 in), which is half the area of Nano-ITX. The processor can be a VIA C7, a VIA Eden V4, a VIA Nano or any other that uses VIA's NanoBGA2 technology for speeds up to 1.5 GHz, with 128KB L1 & L2 caches. It uses DDR2 400/533 SO-DIMM memory, with support for up to 1GB. Video is supplied via AGP by VIA's UniChrome Pro II GPU with built-in MPEG-2, 4, and WMV9 decoding acceleration. The BIOS is a 4 or 8 Mbit Award BIOS.
 W
WPico-ITXe is a PC Pico-ITX motherboard specification created by VIA Technologies and SFF-SIG. It was announced by VIA Technologies on October 29, 2008 and released in December 2008. The Pico-ITXe specifications call for the board to be 10 × 7.2 cm (3.9 × 2.8 in), which is half the area of Nano-ITX, and 12 layers deep. The processor can be a VIA C7 that uses VIA's NanoBGA2 technology. It uses DDR2 667/533 SO-DIMM memory, with support for up to 2GB. Video is supplied by VIA's Chrome9 HC3 GPU with built-in MPEG-2, 4, WMV9, and VC1 decoding acceleration. The BIOS is a 4 or 8 Mbit Award BIOS.
 W
WQseven, a computer-on-module (COM) form factor, is a small, highly integrated computer module that can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. It's smaller than other computer-on-module standards such as COM Express, ETX or XTX and is limited to very low power consuming CPUs. The maximum power consumption should be no more than 12 watt.
 W
WSmall Form Factor is a term used for desktop computers, and their enclosures and motherboards, to indicate that they are designed in accordance with one of several standardized computer form factors intended to minimize the volume and footprint of a desktop computer compared to the standard ATX form factor.
 W
WThe Small Form Factor Special Interest Group or SFF-SIG is an international non-profit standards body focused on modular computer hardware technologies used in embedded and small form factor computers and controllers. Members are mainly computer board and component manufacturers.
 W
WWTX was a motherboard form factor specification introduced by Intel at the IDF in September 1998, for its use at high-end, multiprocessor, multiple-hard-disk servers and workstations. The specification had support from major OEMs and motherboard manufacturers and was updated (1.1) in February 1999. As of 2008, the specification has been discontinued and the URL www.wtx.org no longer hosts a website and has not been owned by Intel since at least 2004.