 W
WApple TV is a digital media player and microconsole developed and sold by Apple Inc. It is a small network appliance and entertainment device that can receive digital data for visual and audio content such as music, video, video games, or the screen display of certain other devices, and play it on a connected television set or other video display.
 W
WThe Enthusiast System Architecture (ESA) specification is a royalty-free protocol for two-way communication of PC components. Announced in 2007, ESA is used for monitoring temperature of computer hardware components such as the computer case and power supply unit. The first and last official release of the ESA specification is version 1.0, released in 2007. The ESA USB specification was created by a joint venture between Microsoft, Nvidia, Logitech and several other companies. The protocol remains open and royalty-free; but, no manufacturers are currently utilizing its specification at this time. The last known devices to utilize the ESA specifications were the Dell XPS 730x and Alienware Area-51 ALX computer systems that utilized the ESA specification to control its fans, LEDs, and motorized doors as well as the monitoring of available Water cooling systems such as the Dell XPS 730x's Dell H2Ceramic Cooling System.
 W
WGmail is a free email service developed by Google. Users can access Gmail on the web and using third-party programs that synchronize email content through POP or IMAP protocols. Gmail started as a limited beta release on April 1, 2004 and ended its testing phase on July 7, 2009. By October 2019, Gmail had 1.5 billion active users worldwide.
 W
WGoogle Street View is a technology featured in Google Maps and Google Earth that provides interactive panoramas from positions along many streets in the world. It was launched in 2007 in several cities in the United States, and has since expanded to include cities and rural areas worldwide. Streets with Street View imagery available are shown as blue lines on Google Maps.
 W
WGoogle Sync was a file synchronization service from Google that provided over-the-air synchronization of Gmail, Google Contacts, and Google Calendar with PC and mobile device Mail, Calendar and Address Book applications. It used Microsoft® Exchange ActiveSync® to let service users synchronize their Google Apps mail, contacts, and calendars to their mobile devices, wherein the users can also set up or customize the alerts for incoming messages and upcoming meetings. Google Sync worked with PC, Mac, Linux, Android, BlackBerry, Symbian S60, iPhone, iPad, Windows Mobile, and other devices. Google Sync was announced in February 2009 and discontinued for non-business users in December 2012.
 W
WThe iPhone is a line of touchscreen-based smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. that use Apple's iOS mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by Apple co-founder Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007. Since then Apple has annually released new iPhone models and iOS updates. As of November 1, 2018, more than 2.2 billion iPhones had been sold.
 W
WThe iPhone is the first smartphone designed and marketed by Apple Inc. After years of rumors and speculation, it was officially announced in January 2007, and was released in the United States in June.
 W
WThe iPod Touch is a line of iOS-based mobile devices designed and marketed by Apple Inc. with a touchscreen-controlled user interface. As with other iPod models, it can be used as a music player and a handheld gaming device, but it can also be used as a digital camera, a web browser and for messaging. It is similar in design to the iPhone, and it connects to the Internet only through Wi-Fi and does not use cellular network data, thus it is not a smartphone. As of May 2013, 100 million iPod Touch units had been sold since 2007.
 W
WIn computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database.
 W
WMac OS X Leopard is the sixth major release of Mac OS X, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on October 26, 2007 as the successor of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger, and is available in two editions: a desktop version suitable for personal computers, and a server version, Mac OS X Server. It retailed for $129 for the desktop version and $499 for Server. Leopard was superseded by Snow Leopard. Leopard is the final version of macOS to support the PowerPC architecture as Snow Leopard functions solely on Intel based Macs.
 W
WMicrosoft PixelSense is an interactive surface computing platform that allows one or more people to use and touch real-world objects, and share digital content at the same time. The PixelSense platform consists of software and hardware products that combine vision based multitouch PC hardware, 360-degree multiuser application design, and Windows software to create a natural user interface (NUI).
 W
WMicrosoft RoundTable was a videoconferencing device with a 360-degree camera that was designed to work with Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 or Microsoft Office Live Meeting. RoundTable provided remote meeting participants with panoramic video of everyone sitting around the conference table. In addition, RoundTable contained active speaker detection technology that provides high-resolution video of the active speaker in a meeting, and tracked the flow of conversation in real time, switching between different meeting participants as they speak.
 W
WThe Nokia N800 Internet tablet is a wireless Internet appliance from Nokia, originally announced at the Las Vegas CES 2007 Summit in January 2007. N800 allows the user to browse the Internet and communicate using Wi-Fi networks or with mobile phone via Bluetooth. The N800 was developed as the successor to the Nokia 770. It includes FM and Internet radio, an RSS news reader, image viewer and a media player for audio and video files.
 W
WOAuth is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for Internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords. This mechanism is used by companies such as Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft and Twitter to permit the users to share information about their accounts with third party applications or websites.
 W
WOpencard was a municipal smart card system in Prague, Czech Republic. Introduced in 2008, the card served as an alternative electronic ticket for all services of the Prague Integrated Transport system and as a payment card for parking fees at most city paid parking zones. It was also replacement of a library card for the Municipal Library and the National Library of Technology and had benefits from various discounts.
 W
WThe Palm Foleo was a planned subnotebook computer that was announced by mobile device manufacturer Palm Inc. on May 30, 2007, and canceled three months later. It intended to serve as a companion for smartphones including Palm's own Treo line. The device ran on the Linux operating system and featured 256 MB of flash memory and an immediate boot-up feature.
 W
WThe POWER6 is a microprocessor developed by IBM that implemented the Power ISA v.2.03. When it became available in systems in 2007, it succeeded the POWER5+ as IBM's flagship Power microprocessor. It is claimed to be part of the eCLipz project, said to have a goal of converging IBM's server hardware where practical.
 W
WSafari is a graphical web browser developed by Apple, based on the WebKit engine. First released on desktop in 2003 with Mac OS X Panther, a mobile version has been bundled with iOS devices since the iPhone's introduction in 2007. Safari is the default browser on Apple devices. A Windows version was available from 2007 to 2012.
 W
WLiveXLive is a music streaming platform, combining audio and video, available in the US and Canada. Users can access the service on the web, through mobile apps on smartphones and on OTT devices. It allows users to create and share customized music stations. LiveXLive allows users to customize one of their programmed stations or start with music similar to an artist or song, and then customize that. Currently, LiveXLive powered by Slacker has 420 expert-curated music stations.
 W
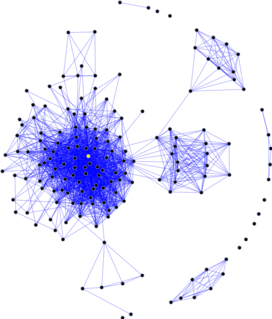
WThe social graph is a graph that represents social relations between entities. In short, it is a model or representation of a social network, where the word graph has been taken from graph theory. The social graph has been referred to as "the global mapping of everybody and how they're related".
 W
WTILE64 is a multicore processor manufactured by Tilera. It consists of a mesh network of 64 "tiles", where each tile houses a general purpose processor, cache, and a non-blocking router, which the tile uses to communicate with the other tiles on the processor.
 W
WWikiScanner was a publicly searchable database operating between 2002 and 2007 that linked millions of anonymous edits on Wikipedia to the organizations where those edits apparently originated, by cross-referencing the edits with data on the owners of the associated block of IP addresses though it did not investigate edits made under a username. It was created by Virgil Griffith and released on August 14, 2007.
 W
WYahoo! Pipes was a web application from Yahoo! that provided a graphical user interface for building data mashups that aggregate web feeds, web pages, and other services; creating Web-based apps from various sources; and publishing those apps. The application worked by enabling users to "pipe" information from different sources and then set up rules for how that content should be modified. Other than the pipe editing page, the website had a documentation page and a discussion page. The documentation page contained information about pipes including guides for the pipe editor and troubleshooting. The discussion page enabled users to discuss the pipes with other users.