 W
WThe Acorn Atom is a home computer made by Acorn Computers Ltd from 1980 to 1982, when it was replaced by the BBC Micro. The Micro began life as an upgrade to the Atom, originally known as the Proton.
 W
WThe Acorn Electron is a budget version of the BBC Micro educational/home computer introduced by Acorn Computers Ltd on 25 August 1983. It has 32 kilobytes of RAM, and its ROM includes BBC BASIC v2 along with its operating system.
 W
WThe Acorn Eurocard systems were a series of modular microcomputer systems based on rack-mounted Eurocards developed by Acorn Computers from 1979 to 1982, aimed primarily at industrial and laboratory use, but also home enthusiasts.
 W
WThe Acorn System 1, initially called the Acorn Microcomputer (Micro-Computer), was an early 8-bit microcomputer for hobbyists, based on the MOS 6502 CPU, and produced by British company Acorn Computers from 1979.
 W
WThe Acorn Eurocard systems were a series of modular microcomputer systems based on rack-mounted Eurocards developed by Acorn Computers from 1979 to 1982, aimed primarily at industrial and laboratory use, but also home enthusiasts.
 W
WThe Acorn Eurocard systems were a series of modular microcomputer systems based on rack-mounted Eurocards developed by Acorn Computers from 1979 to 1982, aimed primarily at industrial and laboratory use, but also home enthusiasts.
 W
WThe Acorn Eurocard systems were a series of modular microcomputer systems based on rack-mounted Eurocards developed by Acorn Computers from 1979 to 1982, aimed primarily at industrial and laboratory use, but also home enthusiasts.
 W
WThe Acorn Eurocard systems were a series of modular microcomputer systems based on rack-mounted Eurocards developed by Acorn Computers from 1979 to 1982, aimed primarily at industrial and laboratory use, but also home enthusiasts.
 W
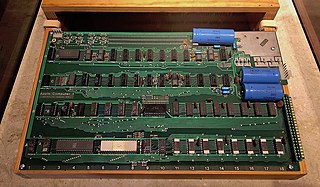
WThe Apple Computer 1, originally released as the Apple Computer and known later as the Apple I, or Apple-1, is a desktop computer released by the Apple Computer Company in 1976. It was designed and hand-built by Steve Wozniak. The idea of selling the computer came from Wozniak's friend Steve Jobs. The Apple I was Apple's first product, and to finance its creation, Jobs sold his only motorized means of transportation, a VW Microbus, for a few hundred dollars, and Wozniak sold his HP-65 calculator for $500. Wozniak demonstrated the first prototype in July 1976 at the Homebrew Computer Club in Palo Alto, California.
 W
WThe Apple II is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Steve Jobs oversaw the development of the Apple II's foam-molded plastic case and Rod Holt developed the switching power supply. It was introduced by Jobs and Wozniak at the 1977 West Coast Computer Faire and marks Apple's first launch of a personal computer aimed at a consumer market—branded toward American households rather than businessmen or computer hobbyists.
 W
WThe Atari 8-bit family is a series of 8-bit home computers introduced by Atari, Inc. in 1979 as the Atari 400 and Atari 800 and manufactured until 1992. All of the machines in the family are technically similar and differ primarily in packaging. They are based on the MOS Technology 6502 CPU running at 1.79 MHz, and were the first home computers designed with custom coprocessor chips. This architecture enabled graphics and sound more advanced than contemporary machines, and gaming was a major draw. First-person space combat simulator Star Raiders is considered the platform's killer app. The systems launched with plug and play peripherals using the Atari SIO serial bus, an early analog of USB.
 W
WThe BBC Master is a home computer released by Acorn Computers in early 1986. It was designed and built for the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) and was the successor to the BBC Micro Model B. The Master 128 remained in production until 1993.
 W
WThe British Broadcasting Corporation Microcomputer System, or BBC Micro, is a series of microcomputers and associated peripherals designed and built by the Acorn Computer company in the 1980s for the BBC Computer Literacy Project, operated by the British Broadcasting Corporation. Designed with an emphasis on education, it was notable for its ruggedness, expandability, and the quality of its operating system. An accompanying 1982 television series, The Computer Programme, featuring Chris Serle learning to use the machine, was broadcast on BBC2.
 W
WThe C-One is a single-board computer (SBC) created in 2002 as an enhanced version of the Commodore 64, a home computer popular in the 1980s. Designed by Jeri Ellsworth, a self-taught designer, and Jens Schönfeld from Individual Computers, who manufactured the boards themselves, the C-One has been re-engineered to allow cloning of other 8-bit computers.
 W
WThe Commodore 64, also known as the C64 or the CBM 64, is an 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International. It has been listed in the Guinness World Records as the highest-selling single computer model of all time, with independent estimates placing the number sold between 12.5 and 17 million units. This claim is in spite of the Commodore 64 having three different Kernal ROM versions, two different SID sound chip versions, a few different motherboard versions and two different cases during its lifetime. Volume production started in early 1982, marketing in August for US$595. Preceded by the Commodore VIC-20 and Commodore PET, the C64 took its name from its 64 kilobytes (65,536 bytes) of RAM. With support for multicolor sprites and a custom chip for waveform generation, the C64 could create superior visuals and audio compared to systems without such custom hardware.
 W
WThe Commodore 128, also known as the C128, C-128, C= 128, is the last 8-bit home computer that was commercially released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM). Introduced in January 1985 at the CES in Las Vegas, it appeared three years after its predecessor, the bestselling Commodore 64.
 W
WThe Commodore MAX Machine, also known as Ultimax in the United States and Canada and VC-10 in Germany, is a home computer designed and sold by Commodore International in Japan, beginning in early 1982, a predecessor to the popular Commodore 64. The Commodore 64 manual mentions the machine by name, suggesting that Commodore intended to sell the machine internationally; however, it is unclear whether the machine was ever actually sold outside Japan. It is considered a rarity.
 W
WThe Commodore PET is a line of home/personal computers produced starting in 1977 by Commodore International. The system combined a MOS 6502 microprocessor, Commodore BASIC in read-only memory (ROM), a keyboard, a computer monitor and a cassette deck for data and program storage in a single all-in-one case.
 W
WThe Commodore VIC-20 is an 8-bit home computer that was sold by Commodore Business Machines. The VIC-20 was announced in 1980, roughly three years after Commodore's first personal computer, the PET. The VIC-20 was the first computer of any description to sell one million units. It was described as "one of the first anti-spectatorial, non-esoteric computers by design...no longer relegated to hobbyist/enthusiasts or those with money, the computer Commodore developed was the computer of the future."
 W
WThe Compukit UK101 microcomputer (1979) is a kit clone of the Ohio Scientific Superboard II single-board computer, with a few enhancements for the UK market - notably replacing the 24×24 screen display with a more useful 48×16 layout working at UK video frequencies. The video output is black and white with 256 characters generated by a two kilobyte ROM. It has no bit-mapped graphics capability. The video is output through a UHF modulator, designed to connect to a TV set.
 W
WThe Laser 128 is an Apple II clone, released by VTech in 1986 and comparable to the Apple IIe and Apple IIc.
 W
WOhio Scientific Inc. was an Ohio-based computer company that built and marketed microcomputers from 1975 to 1981. Their best-known products were the Challenger series of microcomputers and Superboard single-board computer kits.
 W
WOric was the name used by UK-based Tangerine Computer Systems for a series of 6502-based home computers sold in the 1980s, primarily in Europe.
 W
WThe Tangerine Microtan 65 is a 6502 based single board microcomputer, first sold in 1979, which could be expanded into, what was for its day, a comprehensive and powerful system. The design became the basis for what later became the ORIC ATMOS and later computers, which has similar keyboard addressing and tape I/O as in the Microtan 65. The Microtan 65 has a single step function that can be used for debugging at the hardware level. The computer was available as ready-built boards or as kits consisting of board and components requiring soldering together.