 W
WAn air core gauge is a specific type of rotary actuator in an analog display gauge that allows an indicator to rotate a full 360 degrees. It is used in gauges and displays, most commonly automotive instrument clusters.
 W
WA ball screw is a mechanical linear actuator that translates rotational motion to linear motion with little friction. A threaded shaft provides a helical raceway for ball bearings which act as a precision screw. As well as being able to apply or withstand high thrust loads, they can do so with minimum internal friction. They are made to close tolerances and are therefore suitable for use in situations in which high precision is necessary. The ball assembly acts as the nut while the threaded shaft is the screw. In contrast to conventional leadscrews, ballscrews tend to be rather bulky, due to the need to have a mechanism to re-circulate the balls.
 W
WA linear actuator is an actuator that creates motion in a straight line, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in valves and dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor.
 W
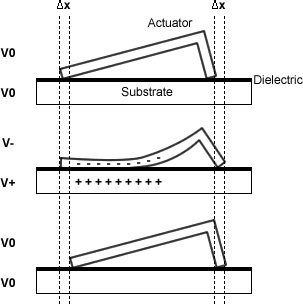
WComb-drives are microelectromechanical actuators, often used as linear actuators, which utilize electrostatic forces that act between two electrically conductive combs. Comb drive actuators typically operate at the micro- or nanometer scale and are generally manufactured by bulk micromachining or surface micromachining a silicon wafer substrate.
 W
WA helical band actuator, generally known by the trademark Spiralift, is a complex and specialized linear actuator used in stage lifts and material handling lifts. The actuator forms a high-capacity telescoping tubular column.
 W
WA hoist is a device used for lifting or lowering a load by means of a drum or lift-wheel around which rope or chain wraps. It may be manually operated, electrically or pneumatically driven and may use chain, fiber or wire rope as its lifting medium. The most familiar form is an elevator, the car of which is raised and lowered by a hoist mechanism. Most hoists couple to their loads using a lifting hook. Today, there are a few governing bodies for the North American overhead hoist industry which include the Hoist Manufactures Institute, ASME, and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. HMI is a product counsel of the Material Handling Industry of America consisting of hoist manufacturers promoting safe use of their products.
 W
WA hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment, manufacturing machinery, and civil engineering.
 W
WA jackscrew, or screw jack, is a type of jack that is operated by turning a leadscrew. It is commonly used to lift moderately heavy weights, such as vehicles; to raise and lower the horizontal stabilizers of aircraft; and as adjustable supports for heavy loads, such as the foundations of houses.
 W
WA linear actuator is an actuator that creates motion in a straight line, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in valves and dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor.
 W
WPlasma actuators are a type of actuator currently being developed for aerodynamic flow control. Plasma actuators impart force in a similar way to ionocraft. Plasma flows control has drawn considerable attention and been used in boundary layer acceleration, airfoil separation control, forebody separation control, turbine blade separation control, axial compressor stability extension, heat transfer and high-speed jet control.
 W
WA rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear engaging a linear gear, which operate to translate rotational motion into linear motion. Driving the pinion into rotation causes the rack to be driven linearly. Driving the rack linearly will cause the pinion to be driven into a rotation. A rack and pinion drive can use both straight and helical gears. Helical gears are preferred due to their quieter operation and higher load bearing capacity. The maximum force that can be transmitted in a rack and pinion mechanism is determined by the tooth pitch and the size of the pinion.
 W
WA rigid belt actuator, also known as a push-pull belt actuator or zipper belt actuator, is a specialized mechanical linear actuator used in push-pull and lift applications. The actuator is a belt and pinion device that forms a telescoping beam or column member to transmit traction and thrust. Rigid belt actuators can move dynamic loads up to approximately 230 pounds over about 3 feet of travel.
 W
WA rigid chain actuator, known variously as a linear chain actuator, push-pull chain actuator, electric chain actuator or column-forming chain actuator, is a specialized mechanical linear actuator used in window operating, push-pull material handling and lift applications. The actuator is a chain and pinion device that forms an articulated telescoping member to transmit traction and thrust. High-capacity rigid chain lifting columns (jacks) can move dynamic loads exceeding 10 tonnes over more than 7 metres of travel.
 W
WA roller screw, also known as a planetary roller screw or satellite roller screw, is a low-friction precision screw-type actuator, a mechanical device for converting rotational motion to linear motion, or vice versa. Planetary roller screws are used as the actuating mechanism in many electro-mechanical linear actuators. Due to its complexity the roller screw is a relatively expensive actuator, but may be suitable for high-precision, high-speed, heavy-load, long-life and heavy-use applications.
 W
WA rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
 W
WA scratch drive actuator (SDA) is a microelectromechanical system device that converts electrical energy into one-dimensional motion.
 W
WThe serpentine plasma actuator represents a broad class of plasma actuator. The actuators vary from the standard type in that their electrode geometry has been modified in to be periodic across its span.
 W
WServos are small, cheap, mass-produced servomotors or other actuators used for radio control and small-scale robotics.
 W
WA servomotor is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration. It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller, often a dedicated module designed specifically for use with servomotors.
 W
WA solenoid is a type of electromagnet, the purpose of which is to generate a controlled magnetic field through a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. The coil can be arranged to produce a uniform magnetic field in a volume of space when an electric current is passed through it. The term solenoid was coined in 1823 by André-Marie Ampère to designate a helical coil.
 W
WA stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can then be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any position sensor for feedback, as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application in respect to torque and speed.
 W
WA valve actuator is the mechanism for opening and closing a valve. Manually operated valves require someone in attendance to adjust them using a direct or geared mechanism attached to the valve stem. Power-operated actuators, using gas pressure, hydraulic pressure or electricity, allow a valve to be adjusted remotely, or allow rapid operation of large valves. Power-operated valve actuators may be the final elements of an automatic control loop which automatically regulates some flow, level or other process. Actuators may be only to open and close the valve, or may allow intermediate positioning; some valve actuators include switches or other ways to remotely indicate the position of the valve.
 W
WThe wig-wag is the common name for the unusual solenoid mechanism used in belt-drive washing machines made by Whirlpool, Kenmore and many others, from approximately 1950 to 1987 in the United States. It was used in belt-drive Brastemp and Consul models built in Brazil from 1959 to 1990.
 W
W