 W
WThe classic Mac OS is the series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Inc. from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept. It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era in which it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems.
 W
WColossal Typewriter by John McCarthy and Roland Silver was one of the earliest computer text editors. The program ran on the PDP-1 at Bolt, Beranek and Newman (BBN) by December 1960.
 W
WDale Heatherington helped Dennis C. Hayes in the development of Hayes Microcomputer Products, the company that pioneered the Hayes modem and the Hayes command set.
 W
WExpensive Desk Calculator by Robert A. Wagner is thought to be computing's first interactive calculation program.
 W
WDelphi is a software product that uses the Object Pascal programming language and provides an integrated development environment (IDE) for rapid application development of desktop, mobile, web, and console software, currently developed and maintained by Embarcadero Technologies. Delphi evolved from Borland's "Turbo Pascal for Windows", itself an evolution with Windows support from Borland's Turbo Pascal and Borland Pascal with Objects, very fast 16-bit native-code MS-DOS compilers with their own sophisticated integrated development environment (IDE) and textual user interface toolkit for DOS. Early Turbo Pascal was written in a dialect of the Pascal programming language; in later versions support for objects was added, and it was named Object Pascal.
 W
WThe LEO I was the first computer used for commercial business applications.
 W
WThe family of Macintosh operating systems developed by Apple Inc. includes the graphical user interface-based operating systems it has designed for use with its Macintosh series of personal computers since 1984, as well as the related system software it once created for compatible third-party systems.
 W
WThe Michigan Terminal System (MTS) is one of the first time-sharing computer operating systems. Developed in 1967 at the University of Michigan for use on IBM S/360-67, S/370 and compatible mainframe computers, it was developed and used by a consortium of eight universities in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom over a period of 33 years.
 W
WThis article presents a timeline of events in the history of Microsoft Windows operating systems from 1985.
 W
WThe first version of Microsoft Word was developed by Charles Simonyi and Richard Brodie, former Xerox programmers hired by Bill Gates and Paul Allen in 1981. Both programmers worked on Xerox Bravo, the first WYSIWYG word processor. The first Word version, Word 1.0, was released in October 1983 for Xenix and MS-DOS; it was followed by four very similar versions that were not very successful. The first Windows version was released in 1989, with a slightly improved interface. When Windows 3.0 was released in 1990, Word became a huge commercial success. Word for Windows 1.0 was followed by Word 2.0 in 1991 and Word 6.0 in 1993. Then it was renamed to Word 95 and Word 97, Word 2000 and Word for Office XP. With the release of Word 2003, the numbering was again year-based. Since then, Windows versions include Word 2007, Word 2010, Word 2013, Word 2016, and most recently, Word for Office 365.
 W
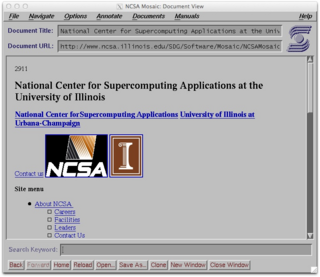
WNCSA Mosaic is one of the first web browsers. It was instrumental in popularizing the World Wide Web and the general Internet by integrating multimedia such as text and graphics. It is a client for earlier internet protocols such as File Transfer Protocol, Network News Transfer Protocol, and Gopher. It was named for its support of multiple Internet protocols. Its intuitive interface, reliability, personal computer support, and simple installation all contributed to its popularity within the web. Mosaic is the first browser to display images inline with text instead of in a separate window. It is often described as the first graphical web browser, though it was preceded by WorldWideWeb, the lesser-known Erwise, and ViolaWWW.
 W
WThe Munching Square is a display hack dating back to the PDP-1, which employs a trivial computation to produce an impressive display of moving and growing squares that devour the screen. The initial value of T is treated as a parameter, which, when well-chosen, can produce amazing effects. Some of these, later (re)discovered on the LISP machine, have been christened munching triangles, munching w's, and munching mazes. More generally, suppose a graphics program produces an impressive and ever-changing display of some basic form, foo, on a display terminal, and does it using a relatively simple program; then the program is likely to be referred to as munching foos.
 W
WThe Nokia Asha platform is a mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for low-end borderline smartphones, based on software from Smarterphone which was acquired by Nokia. The platform inherits UI similarities mostly from MeeGo "Harmattan", and replaces Series 40 on Nokia's low-end devices. The user interface design team was headed by Peter Skillman, who had worked previously on webOS and the design of MeeGo for the Nokia N9.
 W
WFrom the invention of computer programming languages up to the mid-1970s, most computer programmers created, edited and stored their programs line by line on punch cards.
 W
WA punched card is a piece of stiff paper that can be used to contain digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Digital data can be used for data processing applications or used to directly control automated machinery.
 W
WSymbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. Symbian was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for PDAs in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian OS is a descendant of Psion's EPOC, and was released exclusively on ARM processors, although an unreleased x86 port existed. Symbian was used by many major mobile phone brands, like Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, and above all by Nokia. It was also prevalent in Japan by brands including Fujitsu, Sharp and Mitsubishi. As a pioneer that established the smartphone industry, it was the most popular smartphone OS on a worldwide average until the end of 2010—at a time when smartphones were in limited use—when it was overtaken by iOS and Android. It was notably not as popular in North America.
 W
WThe HP LX System Manager is the application manager and GUI for HP LX-series Palmtop computers.
 W
WTJ-2 was published by Peter Samson in May 1963 and is thought to be the first page layout program. Although it lacks page numbering, page headers and footers, TJ-2 is the first word processor to provide a number of essential typographic alignment and automatic typesetting features:Columnation, indentation, margins, justification, and centering Word wrap, page breaks and automatic hyphenation Tab stop simulation
 W
WA type-in program or type-in listing was computer source code printed in a home computer magazine or book. It was meant to be entered via the keyboard by the reader and then saved to cassette tape or floppy disk. The result was a usable game, utility, or application program.
 W
WWindows 2.0 is an obsoleted 16-bit Microsoft Windows GUI-based operating environment that was released on December 9, 1987, and the successor to Windows 1.0.
 W
WWindows 2.1x is a historical version of Windows graphical user interface-based operating systems.
 W
WWindows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, launched in 1990. Like its predecessors, it is not an operating system, but rather a graphical operating environment that runs on top of DOS. It features a new graphical user interface (GUI) where applications are represented as clickable icons, as opposed to the list of file names seen in its predecessors. Later updates would expand the software's capabilities, one of which added multimedia support for sound recording and playback, as well as support for CD-ROMs.
 W
WWindows 3.1 is a series of obsolete 16-bit operating environments produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, released on April 6, 1992. The series began with Windows 3.1, which was first sold during April 1992 as a successor to Windows 3.0. Subsequent versions were released between 1992 and 1993, notably Windows 3.11, until the series was superseded by the Windows 9x series starting in 1995 with Windows 95. During its lifespan, Windows 3.1 introduced several enhancements to the still MS-DOS-based platform, including improved system stability, expanded support for multimedia, TrueType fonts, and workgroup networking.
 W
WXcode is Apple's integrated development environment (IDE) for macOS, used to develop software for macOS, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, and tvOS. It was first released in 2003; the latest stable release is version 12.2, released on November 12, 2020, and is available via the Mac App Store free of charge for macOS Catalina users. Registered developers can download preview releases and prior versions of the suite through the Apple Developer website. Xcode includes Command Line Tools (CLT), which enable UNIX-style development via the Terminal app in macOS. They can also be downloaded and installed without the main IDE.