 W
WA light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device.
 W
WAn LED lamp or LED light bulb is an electric light for use in light fixtures that produces light using one or more light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps have a lifespan many times longer than equivalent incandescent lamps, and are significantly more efficient than most fluorescent lamps, with some manufacturers claiming LED chips with a luminous efficacy of up to 303 lumens per watt. However, LED lamps require an electronic LED driver circuit when operated from mains power lines, and losses from this circuit means that the efficiency of the lamp is lower than the efficiency of the LED chips it uses. The most efficient commercially available LED lamps have efficiencies of 200 lumens per watt (Lm/W). The LED lamp market is projected to grow by more than twelve-fold over the next decade, from $2 billion in the beginning of 2014 to $25 billion in 2023, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25%. As of 2016, many LEDs use only about 10% of the energy an incandescent lamp requires.
 W
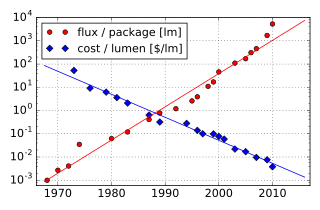
WHaitz's law is an observation and forecast about the steady improvement, over many years, of light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
 W
WHigh-CRI LED lighting is a light-emitting diode (LED) lighting source that offers a high color rendering index (CRI).
 W
WLED art is a form of light art constructed from light-emitting diodes. LEDs are very inexpensive to purchase and have become a new way to make street art. Many artists who use LEDs are guerrilla artists, incorporating LEDs to produce temporary pieces in public places. LEDs may be used in installation art, sculptural pieces and interactive artworks.
 W
WA backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). As LCDs do not produce light by themselves—unlike, for example, cathode ray tube (CRT) displays—they need illumination to produce a visible image. Backlights illuminate the LCD from the side or back of the display panel, unlike frontlights, which are placed in front of the LCD. Backlights are used in small displays to increase readability in low light conditions such as in wristwatches, and are used in smart phones, computer displays and LCD televisions to produce light in a manner similar to a CRT display. A review of some early backlighting schemes for LCDs is given in a report Engineering and Technology History by Peter J. Wild.
 W
WIn electronics, an LED circuit or LED driver is an electrical circuit used to power a light-emitting diode (LED). The circuit must provide sufficient current to light the LED at the required brightness, but must limit the current to prevent damaging the LED. The voltage drop across an LED is approximately constant over a wide range of operating current; therefore, a small increase in applied voltage greatly increases the current. Very simple circuits are used for low-power indicator LEDs. More complex, current source circuits are required when driving high-power LEDs for illumination to achieve correct current regulation.
 W
WA LED display is a flat panel display that uses an array of light-emitting diodes as pixels for a video display. Their brightness allows them to be used outdoors where they are visible in the sun for store signs and billboards. In recent years, they have also become commonly used in destination signs on public transport vehicles, as well as variable-message signs on highways. LED displays are capable of providing general illumination in addition to visual display, as when used for stage lighting or other decorative purposes. LED displays can offer higher contrast ratios than a projector and are thus an alternative to traditional projection screens, and they can be used for large, uninterrupted video walls. microLED displays are LED displays with smaller LEDs, which poses significant development challenges.
 W
WIn electronics, an LED circuit or LED driver is an electrical circuit used to power a light-emitting diode (LED). The circuit must provide sufficient current to light the LED at the required brightness, but must limit the current to prevent damaging the LED. The voltage drop across an LED is approximately constant over a wide range of operating current; therefore, a small increase in applied voltage greatly increases the current. Very simple circuits are used for low-power indicator LEDs. More complex, current source circuits are required when driving high-power LEDs for illumination to achieve correct current regulation.
 W
WAn LED filament light bulb is an LED lamp which is designed to resemble a traditional incandescent light bulb with visible filaments for aesthetic and light distribution purposes, but with the high efficiency of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). It produces its light using LED filaments, which are series-connected strings of diodes that resemble in appearance the filaments of incandescent light bulbs. They are direct replacements for conventional clear incandescent bulbs, as they are made with the same envelope shapes, the same bases that fit the same sockets, and work at the same supply voltage. They may be used for their appearance, similar when lit to a clear incandescent bulb, or for their wide angle of light distribution, typically 300°. They are also more efficient than many other LED lamps.
 W
WAn LED street light or road light is an integrated light-emitting diode (LED) light fixture that is used for street lighting.
 W
WAn LED strip light is a flexible circuit board populated by surface mounted light-emitting diodes and other components that usually comes with an adhesive backing. Traditionally, strip lights had been used solely in accent lighting, backlighting, task lighting, and decorative lighting applications. Increased luminous efficacy and higher-power SMDs have allowed LED strip lights to be used in applications such as high brightness task lighting, fluorescent and halogen lighting fixture replacements, indirect lighting applications, Ultra Violet inspection during manufacturing processes, set and costume design, and even growing plants.
 W
WLED to LED communication, also known as “Mobile Device Light Communications” are sundry techniques which repurpose mobile computer devices, including mobile telephones, to communicate with other devices, using visual or infrared light.
 W
WLED wallpaper is the integration of light-emitting diodes into flat substrates suitable to be applied to walls for interior decoration purposes.
 W
WA LED-backlit LCD is a liquid-crystal display that uses LED backlighting instead of traditional cold cathode fluorescent (CCFL) backlighting. LED-backlit displays use the same TFT LCD technologies as CCFL-backlit LCDs, but offer a variety of advantages over them.
 W
WThe most common way for LEDs to fail is the gradual lowering of light output and loss of efficiency. Sudden failures, however rare, can occur as well. Early red LEDs were notable for their short lifetime.
 W
WAn organic light-emitting diode, also known as organic electroluminescent diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light in response to an electric current. This organic layer is situated between two electrodes; typically, at least one of these electrodes is transparent. OLEDs are used to create digital displays in devices such as television screens, computer monitors, portable systems such as smartphones, handheld game consoles and PDAs. A major area of research is the development of white OLED devices for use in solid-state lighting applications.
 W
WOPPLE Lighting is a Chinese multinational lighting corporation headquartered in Shanghai, China. Founded in 1996, The firm's sales and service cover over 50 countries with over 30,000 sales outlets.
 W
WKoninklijke Philips N.V. is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is still in Eindhoven. Philips was formerly one of the largest electronics companies in the world, currently focused in the area of health technology, with other divisions being divested.
 W
WPixMob is a wireless lighting company specialized in creating immersive experiences and performances that break the barrier between the crowd and the stage. PixMob's wearable LED devices are controlled with infrared light, generating colorful effects synchronized with sound and visuals. People become a part of the show—each PixMob device turns every person into a pixel, transforming the crowd into a huge canvas.
 W
WA plant LED incubator is a chamber which can automatically control the environment of the plant. It can control the temperature, moisture, and especially light regime of the plant based on light emitting diodes (LEDs). LEDs have efficient electric lighting with desired wavelengths (Red+Blue) which support greenhouse production in a minimum time and with high quality and quantity. As LEDs are cool it helps plants to be placed as close as possible to light sources without overheating or scorching. This saves space for intense cultivation. It could provide the opportunity of greenhouse-produced fruits and vegetable to be available for the market more quickly and less expensively due to the effect of LED lighting on earliness, compactness and quality of products.
 W
WA rope light is primarily used as a decorative lighting fixture, featuring small light bulbs linked together and encased in a PVC jacket to create a string of lights. Rope lights can be used in many applications both indoors and outdoors. Used in place of neon signs, it is sometimes called soft neon.
 W
WA solar lamp also known as solar light or solar lantern, is a lighting system composed of a LED lamp, solar panels, battery, charge controller and there may also be an inverter. The lamp operates on electricity from batteries, charged through the use of solar photovoltaic panel.
 W
WSolid-state lighting (SSL) is a type of lighting that uses semiconductor light-emitting diodes (LEDs), organic light-emitting diodes (OLED), or polymer light-emitting diodes (PLED) as sources of illumination rather than electrical filaments, plasma, or gas.
 W
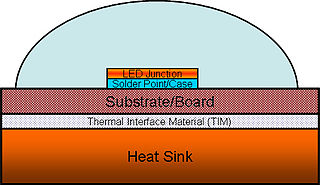
WHigh power light-emitting diodes (LEDs) can use 350 milliwatts or more in a single LED. Most of the electricity in an LED becomes heat rather than light. If this heat is not removed, the LEDs run at high temperatures, which not only lowers their efficiency, but also makes the LED less reliable. Thus, thermal management of high power LEDs is a crucial area of research and development. It is necessary to limit both the junction and the phosphor particles temperatures to a value that will guarantee the desired LED lifetime.