 W
W3D XPoint is a non-volatile memory (NVM) technology developed jointly by Intel and Micron Technology. It was announced in July 2015 and is available on the open market under the brand name Optane (Intel) since April 2017. Bit storage is based on a change of bulk resistance, in conjunction with a stackable cross-gridded data access array. Initial prices are less than dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) but more than flash memory.
 W
WThe Intel 82497 is a Cache Controller for the P5 Pentium processor. It works with multiple 82492 Cache SRAMs.
 W
WAccounts & SSO, accounts-sso, or lately gSSO is a single sign-on framework for computers.
 W
WIntel Active Management Technology (AMT) is hardware and firmware for remote out-of-band management of select business computers, running on the Intel Management Engine, a separate microprocessor not exposed to the user, in order to monitor, maintain, update, upgrade, and repair them. Out-of-band (OOB) or hardware-based management is different from software-based management and software management agents.
 W
WCentrino is a brand name of Intel Corporation which represents its Wi-Fi and WiMAX wireless computer networking adapters. Previously the same brand name was used by the company as a platform-marketing initiative. The change of the meaning of the brandname occurred on January 7, 2010.
 W
WIntel High Definition Audio (IHDA) is a specification for the audio sub-system of personal computers. It was released by Intel in 2004 as successor to its AC'97 PC audio standard.
 W
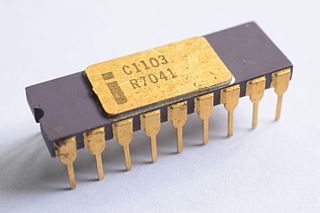
WThe 1103 is a dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) integrated circuit (IC) developed and fabricated by Intel. Introduced in October 1970, the 1103 was the first commercially available DRAM IC; and due to its small physical size and low price relative to magnetic-core memory, it replaced the latter in many applications. When it was introduced in 1970, initial production yields were poor, and it was not until the fifth stepping of the production masks that it became available in large quantities during 1971.
 W
WThe Intel Edison is a computer-on-module that was offered by Intel as a development system for wearable devices and Internet of Things devices. The system was initially announced to be the same size and shape as an SD card and containing a dual-core Intel Quark x86 CPU at 400 MHz communicating via Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. A later announcement changed the CPU to a 500 MHz Silvermont dual-core Intel Atom CPU, and in September 2014 a second version of Edison was shown at IDF, which was bigger and thicker than a standard SD card.
 W
WIntel Galileo is the first in a line of Arduino-certified development boards based on Intel x86 architecture and is designed for the maker and education communities. Intel released two versions of Galileo, referred to as Gen 1 and Gen 2. These development boards are sometimes called "Breakout boards".
 W
WThe Intel Paragon is a discontinued series of massively parallel supercomputers that was produced by Intel in the 1990s. The Paragon XP/S is a productized version of the experimental Touchstone Delta system that was built at Caltech, launched in 1992. The Paragon superseded Intel's earlier iPSC/860 system, to which it is closely related.
 W
WThe Core 2 brand refers to Intel's x86/x86-64 microprocessors with the Core microarchitecture targeted at the consumer and business markets above Pentium. The Core 2 solo branch covered single-core CPUs for notebook computers, Core 2 Duo – dual-core CPUs for both desktop and notebook computers, Core 2 Quad – quad-core CPUs for both desktop and notebook computers, and Core 2 Extreme – dual-core and quad-core CPUs for both desktop and notebook computers.
 W
WThe Intel Upgrade Service was a relatively short-lived and controversial program of Intel that allowed some low-end processors to have additional features unlocked by paying a fee and obtaining an activation code that was then entered in a software program, which ran on Windows 7.
 W
WThe Intellec computers were a series of early microcomputers Intel produced in the 1970s as a development platform for their processors. The Intellec computers were among the first microcomputers ever sold, predating the Altair 8800 by at least two years.
 W
WInTru3D is a brand that identifies content that may be viewed in stereoscopic 3D. Motion pictures or other visual media bearing the brand are developed through animation technology developed by Intel Corporation in partnership with DreamWorks Animation in 2008. InTru3D enables animators to author films directly in 3D for what is described as "a more realistic 3D experience." Animated films authored with InTru3D are shown in theaters using 3D stereoscopic projection technology such as that provided by Real D Cinema and IMAX 3D which both require polarized glasses to view the 3D films.
 W
WThe Intel Personal SuperComputer was a product line of parallel computers in the 1980s and 1990s. The iPSC/1 was superseded by the Intel iPSC/2, and then the Intel iPSC/860.
 W
WOn September 8, 2008, Intel began shipping its first mainstream solid-state drives (SSDs), the X18-M and X25-M with 80 GB and 160 GB storage capacities. Reviews measured high performance with these MLC-based drives. Intel released its SLC-based Enterprise X25-E Extreme SSDs on October 15 that same year in capacities of 32GB and 64GB.
 W
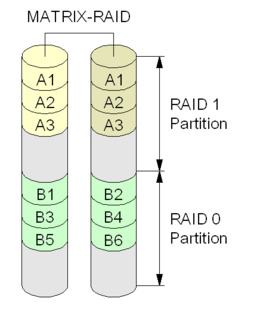
WIntel Rapid Storage Technology (RST), until 2010 called Matrix RAID, is a firmware-based RAID solution built into a wide range of Intel chipsets. As of 2020, it includes a RAID system capable of RAID levels 0, 1, 5, and 10, a block level SSD caching accelerator with support for write-back and write-through modes for speed or data protection of any disk or RAID array, and support for intelligent caching, speedy recovery from certain issues, and for PCI Express based drives. Intel RST comes in two variants, RST for desktops, and RSTe for enterprise scenarios, although for many chipsets, the user can choose as both variants will operate correctly.
 W
WMobile Module Connector 1 (MMC-1) is a 280-pin microprocessor cartridge developed by Intel for used by their mobile Pentium, Pentium MMX, Pentium II and Celeron processors. It contains the microprocessor and its associated L2 cache, a 430TX for the Pentium or a 443BX for the Pentium II northbridge, and a voltage regulator.
 W
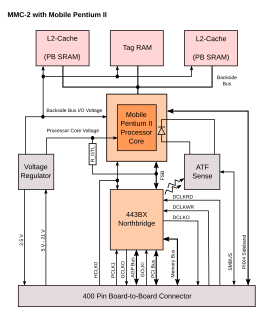
WMobile Module Connector 2 (MMC-2) is Intel's 400 pin processor cartridge used with Pentium II, Celeron and Pentium III mobile processors. It contains CPU, 443BX Northbridge, off-die L2 cache and voltage regulator. It is the successor of MMC-1, main differences being AGP interface and 100 MHz FSB for the Pentium III. This processor cartridge was widely used on laptops from the late 1990s to early 2000s.
 W
WNext Unit of Computing (NUC) is a line of small-form-factor barebone computer kits designed by Intel. It was previewed in 2012 and launched in early 2013. The NUC has developed over ten generations, spanning from Sandy Bridge-based Celeron CPUs in the first generation through Ivy Bridge-based Core i3 and i5 CPUs in the second generation to Gemini Lake-based Pentium and Celeron CPUs and Kaby Lake-based Core i3, i5, and i7 CPUs in the seventh and eighth generations. The NUC motherboard usually measures approximately 4 × 4 inches (10.16 × 10.16 cm), although some models have had different dimensions.
 W
WThe Platform Controller Hub (PCH) is a family of Intel's single-chip chipsets, first introduced in 2009. It is the successor to the Intel Hub Architecture, which used two chips - a northbridge and southbridge instead, and first appeared in the Intel 5 Series.
 W
WUltrabook is an Intel specification and trademark for a line of high-end subnotebook computers featuring reduced bulk without compromising battery life. Ultrabooks use low-power Intel Core processors, solid-state drives, and a unibody chassis to help meet these criteria. Due to their limited size, Ultrabooks may omit traditional laptop features such as optical disc drives, Ethernet ports, and in some models, audio connectors.
 W
WViiv was a platform initiative from Intel similar to Intel's Centrino and vPro. Initially, it was a collection of computer technologies with a particular combination of Intel ingredients to support a "media PC" concept. Intel also provided the Media Server as the core software stack on the PC to support "media" distribution through the home.
 W
WWireless Display (WiDi) is technology developed by Intel that enables users to stream music, movies, photos, videos and apps without wires from a compatible computer to a compatible HDTV or through the use of an adapter with other HDTVs or monitors. Intel WiDi supports HD 1080p video quality, 5.1 surround sound, and low latency for interacting with applications sent to the TV from a PC.
 W
WThe Intel X25-M was a line of Serial ATA interface solid-state drives developed by Intel for personal computers, announced in late 2008. The SSD was a multi-level-cell solid-state drive available in a 2.5" form factor, came in 80 GB and 160 GB capacities and utilized NAND flash memory on a 50 nm process. The second-generation SSD which was called the "X25-M G2". The X25-M G2 was also available in a 2.5" form factor and 80 GB and 160 GB capacities, but with NAND flash memory on a more efficient 34 nm process.
 W
Wx86 is a family of instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel based on the Intel 8086 microprocessor and its 8088 variant. The 8086 was introduced in 1978 as a fully 16-bit extension of Intel's 8-bit 8080 microprocessor, with memory segmentation as a solution for addressing more memory than can be covered by a plain 16-bit address. The term "x86" came into being because the names of several successors to Intel's 8086 processor end in "86", including the 80186, 80286, 80386 and 80486 processors.