 W
WWi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access. Wi‑Fi is a trademark of the non-profit Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term Wi-Fi Certified to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. As of 2017, the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from around the world. As of 2019, over 3.05 billion Wi-Fi enabled devices are shipped globally each year. Devices that can use Wi-Fi technologies include personal computer desktops and laptops, smartphones and tablets, smart TVs, printers, smart speakers, cars, and drones.
 W
WAirPlay is a proprietary protocol stack/suite developed by Apple Inc. that allows wireless streaming between devices of audio, video, device screens, and photos, together with related metadata. Originally implemented only in Apple's software and devices, it was called AirTunes and used for audio only. Apple has since licensed the AirPlay protocol stack as a third-party software component technology to manufacturers that build products compatible with Apple's devices.
 W
WAirPort is the name given to a series of products by Apple Inc. using the Wi-Fi protocols. These products comprise a number of wireless routers and wireless cards. The AirPort Extreme name was originally intended to signify the addition of the 802.11g protocol to these products.
 W
WAlterGeo, formerly known as Wi2Geo, is a Russian IT company specializing in the development of a global hybrid positioning system which combines Wi-Fi, WiMAX, GSM, GPS, LTE, IP address and network environment approaches. It also created cross-platform location-based services Gvidi and AlterGeo, and hyperlocal banner ad system Local Hero.
 W
WRonald Hugh Barker FIEE was an Irish physicist and inventor of Barker code for digital synchronisation. He was a member of the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) for 70 years. Born in Dublin, Ireland, Barker had an erratic education but excelled in mathematics, becoming keen on electronics. He is best known for his ground-breaking work on synchronising digital communication systems and framing of received data, using digital codes. These digital codes are known as Barker code. The method was initially researched at SRDE Royal Signals Research Establishment, just after World War II for use in radar, rocket telemetry and digital speech. In 1952, Barker found 7 Barker sequences up to a length of 13 useful for correlation. These sequences are widely used in most data transmissions today. Examples of applications are radar, mobile phone technology, telemetry, digital speech, ultrasound imaging and testing, GPS and WiFi, etc.
 W
WFujitsu Ltd. v. Netgear Inc., 620 F.3d 1321, was a patent infringement case centered on three patents claimed to be required for full compliance of the IEEE 802.11 (WiFi) standard and the WiFi Alliance Wireless Multimedia Extensions (WMM) Specification. US patents 4,975,952, 6,018,642, and 6,469,993 were owned by Philips Electronics, Fujitsu, and LG Electronics respectively, and placed in the Via Licensing pool. The Via Licensing pool claimed to hold all patents required for a complete WiFi/WMM implementation. Netgear did not enter an agreement with Via Licensing but produced a series of products that conform to the WiFi standard and WMM Specification. Philips Electronics, Fujitsu, and LG Electronics sued Netgear for patent infringement claiming a complete implementation of the WiFi standard implied violating patents held by Via Licensing pool. When tried in United States District Court for the Western District of Wisconsin, the court granted summary judgment of non-infringement by Netgear for all three patents thus plaintiffs appealed. The United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit confirmed non-infringement for two of the three patent and found infringement of the third patent in four of Netgear's products.
 W
WA home network or home area network (HAN) is a type of computer network that facilitates communication among devices within the close vicinity of a home. Devices capable of participating in this network, for example, smart devices such as network printers and handheld mobile computers, often gain enhanced emergent capabilities through their ability to interact. These additional capabilities can be used to increase the quality of life inside the home in a variety of ways, such as automation of repetitive tasks, increased personal productivity, enhanced home security, and easier access to entertainment.
 W
WA hotspot is a physical location where people may obtain Internet access, typically using Wi-Fi technology, via a wireless local-area network (WLAN) using a router connected to an Internet service provider.
 W
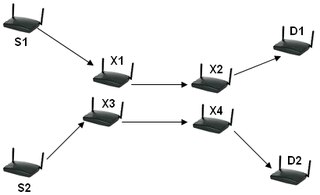
WIn wireless routing, inter-flow interference refers to the interference between neighboring routers competing for the same busy channel.
 W
WIntra-flow interference is interference between intermediate routers sharing the same flow path.
 W
WKRACK is a replay attack on the Wi-Fi Protected Access protocol that secures Wi-Fi connections. It was discovered in 2016 by the Belgian researchers Mathy Vanhoef and Frank Piessens of the University of Leuven. Vanhoef's research group published details of the attack in October 2017. By repeatedly resetting the nonce transmitted in the third step of the WPA2 handshake, an attacker can gradually match encrypted packets seen before and learn the full keychain used to encrypt the traffic.
 W
WLibreCMC is a GNU/Linux-libre distribution for computers with minimal resources, such as the Ben NanoNote, ath9k-based Wi-Fi routers, and other hardware with emphasis on free software. Based on OpenWrt, the project's goal is to aim for compliance with the GNU Free System Distribution Guidelines and ensure that the project continues to meet these requirements set forth by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). LibreCMC does not support ac or ax due to a lack of free chipsets.
 W
WMiFi is a brand name used to describe a wireless router that acts as mobile Wi-Fi hotspot. In many countries, including the United States, Canada, and Mexico, Inseego Corp owns a registered trademark on the "MiFi" brand name; in the United Kingdom mobile operator Hutchison 3G owns the "MiFi" trademark. Novatel Wireless has never offered an official explanation for the origin of the name "MiFi"; it is believed to be short for "My Wi-Fi". In September 2016 Novatel Wireless announced that it agreed to sell the MiFi brand to TCL Industries Holdings of Hong Kong; the sale was expected to close in early 2017, pending approval from shareholders and regulators.
 W
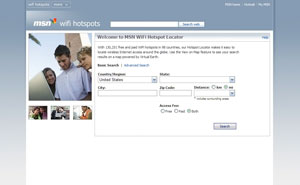
WMSN WiFi Hotspots, previously Windows Live WiFi Hotspot Locator, was a website that helped users to locate wireless Internet hotspots worldwide and view their positions on a map using Live Search Maps.
 W
WA municipal wireless network is a citywide wireless network. This usually works by providing municipal broadband via Wi-Fi to large parts or all of a municipal area by deploying a wireless mesh network. The typical deployment design uses hundreds of wireless access points deployed outdoors, often on poles. The operator of the network acts as a wireless internet service provider.
 W
WNintendo Wi-Fi Connection was an online multiplayer gaming service run by Nintendo to provide free online play in compatible Nintendo DS and Wii games. The service included the company's Wii Shop Channel and DSi Shop game download services. It also ran features for the Wii and Nintendo DS systems.
 W
WThe Nintendo Wi-Fi USB Connector is a wireless game adapter, developed jointly by Nintendo and Buffalo Technology, which allows Nintendo DSi and Wii users without a Wi-Fi connection or compatible Wi-Fi network to establish one via a broadband-connected PC. Inserted into the host PC's USB port, the connector functions with the Nintendo DS, Wii, and DSi, permitting the user to connect to the Internet to play Nintendo Wi-Fi Connection games and access various other online functionality. The product was the best selling Nintendo accessory to date, according to the official Nintendo site on 15 November 2007, but was discontinued in the same month until further notice. On September 8, 2008, Nintendo announced the Nintendo Wi-Fi Network Adapter, an 802.11g wireless router/bridge which serves a similar purpose.
 W
WDHI Telecom, LLC is a US commercial Internet service provider (ISP) that operates on U.S. and NATO bases in the Middle East including Iraq, Kuwait, and Afghanistan. DHI provides wired, fiber-optic cable, mobile Wi-Fi, and wireless commercial Internet access to US, coalition armed forces, direct-hire DoD, Department of the Army and State Department civilians, authorized civilian contractors, and international businesses participating in Operation New Dawn and Operation Enduring Freedom. DHI has additional operations in the UAE, Jordan, The Congo, Poland and Romania.
 W
WUMA Today is an international consortium of companies joined together to lead the adoption of 3GPP UMA technology around the world.
 W
WWarchalking is the drawing of symbols in public places to advertise an open Wi-Fi network. Inspired by hobo symbols, the warchalking marks were conceived by a group of friends in June 2002 and publicised by Matt Jones who designed the set of icons and produced a downloadable document containing them. Within days of Jones publishing a blog entry about warchalking, articles appeared in dozens of publications and stories appeared on several major television news programs around the world.
 W
WThe Wi-Fi Alliance owns the Wi-Fi trademark. Manufacturers may use the trademark to brand certified products that have been tested for interoperability.
 W
WWireless Display (WiDi) is technology developed by Intel that enables users to stream music, movies, photos, videos and apps without wires from a compatible computer to a compatible HDTV or through the use of an adapter with other HDTVs or monitors. Intel WiDi supports HD 1080p video quality, 5.1 surround sound, and low latency for interacting with applications sent to the TV from a PC.
 W
WWi-Fi Protected Setup is a network security standard to create a secure wireless home network.
 W
WWireless USB is a short-range, high-bandwidth wireless radio communication protocol created by the Wireless USB Promoter Group which intends to further increase the availability of general USB-based technologies. In large, IPv6 was a key of this technology. It is maintained by the WiMedia Alliance and the current revision is 1.0, which was approved in 2005. Wireless USB is sometimes abbreviated as "WUSB", although the USB Implementers Forum discouraged this practice and instead prefers to call the technology Certified Wireless USB to distinguish it from the competing UWB standard.
 W
WWokFi is a slang term for a style of homemade Wi-Fi antenna consisting of a crude parabolic antenna made with a low-cost Asian kitchen wok, spider skimmer or similar household metallic dish. The dish forms a directional antenna which is pointed at the wireless access point antenna, allowing reception of the wireless signal at greater distances than standard omnidirectional Wi-Fi antennas.
 W
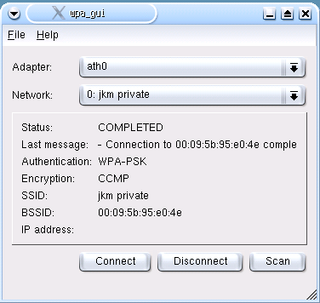
Wwpa_supplicant is a free software implementation of an IEEE 802.11i supplicant for Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, QNX, AROS, Microsoft Windows, Solaris, OS/2 and Haiku. In addition to being a fully featured WPA2 supplicant, it also implements WPA and older wireless LAN security protocols.