 W
WA Manufacturing Language (AML) is a robot programming language created by IBM in the 1970s and 80s, for its RS 1 robot and other robots in its Robot Manufacturing System product line. The systems were used in factory automation by customers such as Plessey and Northern Telecom. They are no longer listed as available from IBM, but robots and parts can occasionally be found in used condition on auction sites, and are refurbished by hobbyists.
 W
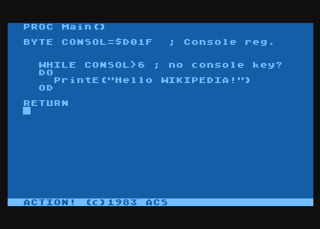
WAction! is a procedural programming language similar to ALGOL that is intended to produce high-performance programs for the Atari 8-bit family. The language was written by Clinton Parker and distributed on ROM cartridge by Optimized Systems Software (OSS) starting in 1983. It was one of the first of OSS's bank switching "Super Cartridges", with a total of 16 kB of code.
 W
WAda is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, extended from Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design by contract (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). As of 2020, the standard, called Ada 2012 informally, is ISO/IEC 8652:2012.
 W
WAgda is a dependently typed functional programming language originally developed by Ulf Norell at Chalmers University of Technology with implementation described in his PhD thesis. The original Agda system was developed at Chalmers by Catarina Coquand in 1999. The current version, originally known as Agda 2, is a full rewrite, which should be considered a new language that shares a name and tradition.
 W
WC++ is a general-purpose programming language created by Bjarne Stroustrup as an extension of the C programming language, or "C with Classes". The language has expanded significantly over time, and modern C++ now has object-oriented, generic, and functional features in addition to facilities for low-level memory manipulation. It is almost always implemented as a compiled language, and many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Oracle, and IBM, so it is available on many platforms.
 W
WC is a general-purpose, procedural computer programming language supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. By design, C provides constructs that map efficiently to typical machine instructions. It has found lasting use in applications previously coded in assembly language. Such applications include operating systems and various application software for computer architectures that range from supercomputers to PLCs and embedded systems.
 W
WC# is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm programming language encompassing static typing, strong typing, lexically scoped, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines.
 W
WCOBOL is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is imperative, procedural and, since 2002, object-oriented. COBOL is primarily used in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments. COBOL is still widely used in applications deployed on mainframe computers, such as large-scale batch and transaction processing jobs. However, due to its declining popularity and the retirement of experienced COBOL programmers, programs are being migrated to new platforms, rewritten in modern languages or replaced with software packages. Most programming in COBOL is now purely to maintain existing applications; however, many large financial institutions were still developing new systems in COBOL in 2006 due to the mainframe processing speed.
 W
WCrystal is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language, designed and developed by Ary Borenszweig, Juan Wajnerman, Brian Cardiff and more than 300 contributors. With syntax inspired by the language Ruby, it is a compiled language with static type-checking, but specifying the types of variables or method arguments is generally unneeded. Types are resolved by an advanced global type inference algorithm. Crystal is currently in active development. It is released as free and open-source software under the Apache License version 2.0.
 W
WCuneiform is an open-source workflow language for large-scale scientific data analysis. It is a statically typed functional programming language promoting parallel computing. It features a versatile foreign function interface allowing users to integrate software from many external programming languages. At the organizational level Cuneiform provides facilities like conditional branching and general recursion making it Turing-complete. In this, Cuneiform is the attempt to close the gap between scientific workflow systems like Taverna, KNIME, or Galaxy and large-scale data analysis programming models like MapReduce or Pig Latin while offering the generality of a functional programming language.
 W
WD, also known as Dlang, is a multi-paradigm system programming language created by Walter Bright at Digital Mars and released in 2001. Andrei Alexandrescu joined the design and development effort in 2007. Though it originated as a re-engineering of C++, D is a distinct language. It has redesigned some core C++ features, while also sharing characteristics of other languages, notably Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and Eiffel.
 W
WElm is a domain-specific programming language for declaratively creating web browser-based graphical user interfaces. Elm is purely functional, and is developed with emphasis on usability, performance, and robustness. It advertises "no runtime exceptions in practice", made possible by the Elm compiler's static type checking.
 W
WF# is a functional-first, general purpose, strongly typed, multi-paradigm programming language that encompasses functional, imperative, and object-oriented programming methods. F# is most often used as a cross-platform Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) language on .NET Core, but it can also generate JavaScript and graphics processing unit (GPU) code.
 W
WFortran is a general-purpose, compiled imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing.
 W
WGNU Pascal (GPC) is a Pascal compiler composed of a frontend to GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), similar to the way Fortran and other languages were added to GCC. GNU Pascal is ISO 7185 compatible, and it implements "most" of the ISO 10206 Extended Pascal standard.
 W
WGo is a statically typed, compiled programming language designed at Google by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson. Go is syntactically similar to C, but with memory safety, garbage collection, structural typing, and CSP-style concurrency. The language is often referred to as Golang because of its domain name, golang.org, but the proper name is Go.
 W
WHaxe is an open source high-level cross-platform programming language and compiler that can produce applications and source code, for many different computing platforms from one code-base. It is free and open-source software, released under the MIT License. The compiler, written in OCaml, is released under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2.
 W
WJava is a class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let application developers write once, run anywhere (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need for recompilation. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. As of 2019, Java was one of the most popular programming languages in use according to GitHub, particularly for client-server web applications, with a reported 9 million developers.
 W
WNim is an imperative, general-purpose, multi-paradigm, statically typed, systems, compiled programming language designed and developed by Andreas Rumpf. It is designed to be "efficient, expressive, and elegant", supporting metaprogramming, functional, message passing, procedural, and object-oriented programming styles by providing several features such as compile time code generation, algebraic data types, a foreign function interface (FFI) with C, C++, Objective-C, and JavaScript, as well as supporting compiling to C, C++, Objective-C, and JavaScript.
 W
WOberon is a general-purpose programming language first published in 1987 by Niklaus Wirth and the latest member of the Wirthian family of ALGOL-like languages. Oberon was the result of a concentrated effort to increase the power of Modula-2, the direct successor of Pascal, and simultaneously to reduce its complexity. Its principal new feature is the concept of type extension of record types: It permits the construction of new data types on the basis of existing ones and to relate them, deviating from the dogma of strictly static data typing. Type extension is Wirth's way of inheritance reflecting the viewpoint of the parent site. Oberon was developed as part of the implementation of the Oberon operating system at ETH Zurich in Switzerland. The name is from the moon of Uranus, Oberon.
 W
WPureScript is a strongly-typed, purely-functional programming language that compiles to JavaScript. It can be used to develop web applications, server side apps, and also desktop applications with use of Electron. Its syntax is mostly comparable to that of Haskell. In addition, it introduces row polymorphism and extensible records. Also, contrary to Haskell, PureScript adheres to a strict evaluation strategy.
 W
WRust is a multi-paradigm programming language designed for performance and safety, especially safe concurrency. Rust is syntactically similar to C++, but can guarantee memory safety by using a borrow checker to validate references. Rust achieves memory safety without garbage collection, and reference counting is optional.
 W
WScala is a general-purpose programming language providing support for both object-oriented programming and functional programming. The language has a strong static type system. Designed to be concise, many of Scala's design decisions are aimed to address criticisms of Java.
 W
WTuring is a Pascal-like programming language developed in 1982 by Ric Holt and James Cordy, then of University of Toronto, in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Turing is a descendant of Euclid, Pascal and SP/k that features a clean syntax and precise machine-independent semantics.
 W
WUmple is a language for both object-oriented programming and modelling with class diagrams and state diagrams. The name Umple is a portmanteau of "UML", "ample" and "Simple", indicating that it is designed to provide ample features to extend programming languages with UML capabilities.
 W
WVala is an object-oriented programming language with a self-hosting compiler that generates C code and uses the GObject system.
 W
WVisual Prolog, formerly known as PDC Prolog and Turbo Prolog, is a strongly typed object-oriented extension of Prolog. As Turbo Prolog, it was marketed by Borland but it is now developed and marketed by the Danish firm Prolog Development Center (PDC) that originally developed it. Visual Prolog can build Microsoft Windows GUI-applications, console applications, DLLs, and CGI-programs. It can also link to COM components and to databases by means of ODBC.