 W
WA Manufacturing Language (AML) is a robot programming language created by IBM in the 1970s and 80s, for its RS 1 robot and other robots in its Robot Manufacturing System product line. The systems were used in factory automation by customers such as Plessey and Northern Telecom. They are no longer listed as available from IBM, but robots and parts can occasionally be found in used condition on auction sites, and are refurbished by hobbyists.
 W
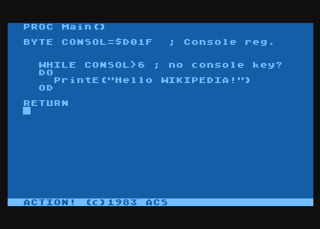
WAction! is a procedural programming language similar to ALGOL that is intended to produce high-performance programs for the Atari 8-bit family. The language was written by Clinton Parker and distributed on ROM cartridge by Optimized Systems Software (OSS) starting in 1983. It was one of the first of OSS's bank switching "Super Cartridges", with a total of 16 kB of code.
 W
WALGOL is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in textbooks and academic sources until object-oriented languages came around, for more than thirty years.
 W
WALGOL 68 is an imperative programming language that was conceived as a successor to the ALGOL 60 programming language, designed with the goal of a much wider scope of application and more rigorously defined syntax and semantics.
 W
WC is a general-purpose, procedural computer programming language supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. By design, C provides constructs that map efficiently to typical machine instructions. It has found lasting use in applications previously coded in assembly language. Such applications include operating systems and various application software for computer architectures that range from supercomputers to PLCs and embedded systems.
 W
WCOBOL is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is imperative, procedural and, since 2002, object-oriented. COBOL is primarily used in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments. COBOL is still widely used in applications deployed on mainframe computers, such as large-scale batch and transaction processing jobs. However, due to its declining popularity and the retirement of experienced COBOL programmers, programs are being migrated to new platforms, rewritten in modern languages or replaced with software packages. Most programming in COBOL is now purely to maintain existing applications; however, many large financial institutions were still developing new systems in COBOL in 2006 due to the mainframe processing speed.
 W
WD, also known as Dlang, is a multi-paradigm system programming language created by Walter Bright at Digital Mars and released in 2001. Andrei Alexandrescu joined the design and development effort in 2007. Though it originated as a re-engineering of C++, D is a distinct language. It has redesigned some core C++ features, while also sharing characteristics of other languages, notably Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and Eiffel.
 W
WEzhil, in Tamil language script, is a compact, open source, interpreted, programming language, originally designed to enable native-Tamil speaking students, K-12 age-group to learn computer programming, and enable learning numeracy and computing, outside of linguistic expertise in predominately English language-based computer systems.
 W
WFortran is a general-purpose, compiled imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing.
 W
WFoxPro was a text-based procedurally oriented programming language and database management system (DBMS), and it was also an object-oriented programming language, originally published by Fox Software and later by Microsoft, for MS-DOS, Windows, Macintosh, and UNIX. The final published release of FoxPro was 2.6. Development continued under the Visual FoxPro label, which in turn was discontinued in 2007.
 W
WGambas is the name of an object-oriented dialect of the BASIC programming language, as well as the integrated development environment that accompanies it. Designed to run on Linux and other Unix-like computer operating systems, its name is a recursive acronym for Gambas Almost Means Basic. Gambas is also the word for prawns in the Spanish, French, and Portuguese languages, from which the project's logos are derived.
 W
WGNU Pascal (GPC) is a Pascal compiler composed of a frontend to GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), similar to the way Fortran and other languages were added to GCC. GNU Pascal is ISO 7185 compatible, and it implements "most" of the ISO 10206 Extended Pascal standard.
 W
WGo is a statically typed, compiled programming language designed at Google by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson. Go is syntactically similar to C, but with memory safety, garbage collection, structural typing, and CSP-style concurrency. The language is often referred to as Golang because of its domain name, golang.org, but the proper name is Go.
 W
WHollywood is a commercially distributed programming language developed by Andreas Falkenhahn which mainly focuses on the creation of multimedia-oriented applications. Hollywood is available for AmigaOS, MorphOS, WarpOS, AROS, Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. Hollywood has an inbuilt cross compiler that can automatically save executables for all platforms supported by the software. The generated executables are completely stand-alone and do not have any external dependencies, so they can also be started from a USB flash drive. An optional add-on also allows users to compile projects into APK files.
 W
WJulia is a high-level, high-performance, dynamic programming language. While it is a general-purpose language and can be used to write any application, many of its features are well suited for numerical analysis and computational science.
 W
WKarel is an educational programming language for beginners, created by Richard E. Pattis in his book Karel The Robot: A Gentle Introduction to the Art of Programming. Pattis used the language in his courses at Stanford University, California. The language is named after Karel Čapek, a Czech writer who introduced the word robot in his play R.U.R.
 W
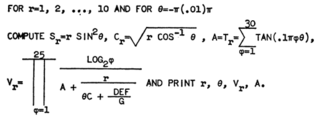
WThe Klerer–May System is a programming language developed in the mid-1960s, oriented to numerical scientific programming, whose most notable feature is its two-dimensional syntax based on traditional mathematical notation.
 W
WNim is an imperative, general-purpose, multi-paradigm, statically typed, systems, compiled programming language designed and developed by Andreas Rumpf. It is designed to be "efficient, expressive, and elegant", supporting metaprogramming, functional, message passing, procedural, and object-oriented programming styles by providing several features such as compile time code generation, algebraic data types, a foreign function interface (FFI) with C, C++, Objective-C, and JavaScript, as well as supporting compiling to C, C++, Objective-C, and JavaScript.
 W
WOberon is a general-purpose programming language first published in 1987 by Niklaus Wirth and the latest member of the Wirthian family of ALGOL-like languages. Oberon was the result of a concentrated effort to increase the power of Modula-2, the direct successor of Pascal, and simultaneously to reduce its complexity. Its principal new feature is the concept of type extension of record types: It permits the construction of new data types on the basis of existing ones and to relate them, deviating from the dogma of strictly static data typing. Type extension is Wirth's way of inheritance reflecting the viewpoint of the parent site. Oberon was developed as part of the implementation of the Oberon operating system at ETH Zurich in Switzerland. The name is from the moon of Uranus, Oberon.
 W
WParallel Specification and Implementation Language (ParaSail) is an object-oriented parallel programming language. Its design and ongoing implementation is described in a blog and on its official website.
 W
WParser is a scripting language developed by Art. Lebedev Studio used for web development and server-side scripting.
 W
WPerl is a family of two high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming languages. "Perl" refers to Perl 5, but from 2000 to 2019 it also referred to its redesigned "sister language", Perl 6, before the latter's name was officially changed to Raku in October 2019.
 W
WPowerShell is a task automation and configuration management framework from Microsoft, consisting of a command-line shell and the associated scripting language. Initially a Windows component only, known as Windows PowerShell, it was made open-source and cross-platform on 18 August 2016 with the introduction of PowerShell Core. The former is built on the .NET Framework, the latter on .NET Core.
 W
Wrc is the command line interpreter for Version 10 Unix and Plan 9 from Bell Labs operating systems. It resembles the Bourne shell, but its syntax is somewhat simpler. It was created by Tom Duff, who is better known for an unusual C programming language construct.
 W
WRust is a multi-paradigm programming language designed for performance and safety, especially safe concurrency. Rust is syntactically similar to C++, but can guarantee memory safety by using a borrow checker to validate references. Rust achieves memory safety without garbage collection, and reference counting is optional.
 W
WVisual Basic is a third-generation event-driven programming language from Microsoft known for its Component Object Model (COM) programming model first released in 1991 and declared legacy during 2008. Microsoft intended Visual Basic to be relatively easy to learn and use. Visual Basic was derived from BASIC and enables the rapid application development (RAD) of graphical user interface (GUI) applications, access to databases using Data Access Objects, Remote Data Objects, or ActiveX Data Objects, and creation of ActiveX controls and objects.
 W
WVisual FoxPro is a Microsoft data-centric procedural programming language that subsequently became object-oriented.
 W
WIn computer programming, Yoix is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. The Yoix interpreter is implemented using standard Java technology without any add-on packages and requires only a Sun-compliant JVM to operate. Initially developed by AT&T Labs researchers for internal use, it has been available as free and open source software since late 2000.