 W
WA microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer with a microprocessor as its central processing unit (CPU). It includes a microprocessor, memory and minimal input/output (I/O) circuitry mounted on a single printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive. Many microcomputers are also personal computers.
 W
W W
WThe Applix 1616 was a kit computer with a Motorola 68000 CPU, produced by a small company called Applix in Sydney, Australia, from 1986 to the early 1990s. It ran a custom multitasking multiuser operating system that was resident in ROM. A version of Minix was also ported to the 1616, as was the MGR Window System. Andrew Morton, designer of the 1616 and one of the founders of Applix, later became the maintainer of the 2.6 version of the Linux kernel.
 W
WThe C-One is a single-board computer (SBC) created in 2002 as an enhanced version of the Commodore 64, a home computer popular in the 1980s. Designed by Jeri Ellsworth, a self-taught designer, and Jens Schönfeld from Individual Computers, who manufactured the boards themselves, the C-One has been re-engineered to allow cloning of other 8-bit computers.
 W
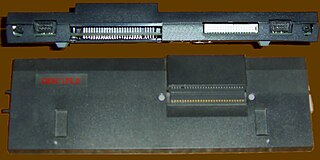
WThe Professional 325 (PRO-325), Professional 350 (PRO-350), and Professional 380 (PRO-380) were PDP-11 compatible microcomputers introduced in 1982 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as high-end competitors to the IBM PC.
 W
WThe DISCiPLE was a floppy disk interface for the Sinclair ZX Spectrum home computer. Designed by Miles Gordon Technology, it was marketed by Rockfort Products and launched in 1986.
DVK is a Soviet PDP-11-compatible personal computer.
 W
WThe Fly Pentop Computer and FLY Fusion Pentop Computer are personal electronics products manufactured by LeapFrog Enterprises Inc. They are called a "pentop" computer by its manufacturer, because they consist of a pen with a computer inside.
 W
WThe Gigatron TTL is a retro-style 8-bit microcomputer, where the CPU is implemented by a set of TTL chips instead of a single microprocessor, imitating the hardware present in early arcades. Its target is the computing enthusiasts, for studying or hobby purposes.
 W
WThe GMC-4 is the only 4-bit microcomputer to be mass-produced in the last 30 years. It was produced by Gakken, a Japanese publisher who distributed it with a magazine attached to a box containing the components required to assemble the computer.
 W
WThe Intertec Superbrain was an all-in-one commercial microcomputer that was first sold by Intertec Data Systems Corp. of Columbia, South Carolina, USA in 1979. The machine ran the operating system CP/M and was somewhat unusual in that it used dual Z80 CPUs, the second being used as a disk controller. In 1983, the basic machine sold for about $2000.
 W
WIskra Delta Partner was a computer developed by Iskra Delta in 1983.
 W
WIskradata 1680 was a computer developed by Iskradata in 1979.
 W
WA microprocessor is a computer processor that is implemented on a single integrated circuit (IC) of MOSFET construction. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic. Microprocessors operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system.
 W
WThe NDR Klein Computer, abbreviated NKC, was a do-it-yourself computer project from the early 1980s developed by Rolf-Dieter Klein (RDK) and Joachim Arendt. In 1984, the computer was featured in the educational television series NDR-Klein-Computer for NDR-Schulfernsehen. It was also broadcast on the computer television show ComputerTreff on the Bavarian TV network Bayerisches Fernsehen (BFS).
 W
WThe P8000 is a microcomputer system developed in 1987 by the VEB Elektro-Apparate-Werke Berlin-Treptow „Friedrich Ebert“ (EAW) in the German Democratic Republic. It consisted of an 8-bit and a 16-bit microprocessor and a Winchester disk controller. It was intended as a universal programming and development system for multi-user/multi-task applications. The initial list price of the P8000 was 172,125 East German marks.
 W
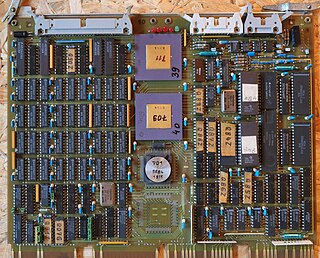
WThe RAD750 is a radiation-hardened single board computer manufactured by BAE Systems Electronics, Intelligence & Support. The successor of the RAD6000, the RAD750 is for use in high radiation environments experienced on board satellites and spacecraft. The RAD750 was released in 2001, with the first units launched into space in 2005.
 W
WThe K 1820, full name RVS K 1820, cipher in the SM EVM of the former COMECON countries SM 1720, was a workstation developed in East Germany. VEB Robotron Elektronik Dresden began development of the K 1820 in 1986 and it went into serial production in 1990.
 W
WA single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers are commonly made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.
 W
WThe SPC-1000 is a Z80-based personal computer produced by Samsung. It was developed in South Korea, but featured built-in BASIC written by Hudson Soft in Japan. The computer features a 4 MHz processor and 64 KB of RAM.
 W
WThe HP LX System Manager is the application manager and GUI for HP LX-series Palmtop computers.
 W
WA system on a module (SOM) is a board-level circuit that integrates a system function in a single module. It may integrate digital and analog functions on a single board. A typical application is in the area of embedded systems. Unlike a single-board computer, a SOM serves a special function like a system on a chip (SoC). The device integrated in the SOM typically requires a high level of interconnection for reasons such as speed, timing, bus-width etc., in a highly integrated module. There are benefits in building a SOM, as for SoC; one notable result is to reduce the cost of the base board or the main PCB. Two other major advantages of SOMs are design-reuse and that they can be integrated into many embedded computer applications.
 W
WIn computer networking, a thin client is a simple (low-performance) computer that has been optimized for establishing a remote connection with a server-based computing environment. The server does most of the work, which can include launching software programs, performing calculations, and storing data. This contrasts with a fat client or a conventional personal computer; the former is also intended for working in a client–server model but has significant local processing power, while the latter aims to perform its function mostly locally.
 W
WTIM 011 is an educational or personal computer for school microcomputer developed by Mihajlo Pupin Institute of Serbia in 1987. There were about 1200 TIM-011 computers in Serbian schools in the 1990s.
 W
WTIM-600 was an important PC computer system of the series of the TIM microcomputers, from Mihajlo Pupin Institute-Belgrade, developed 1987-1988. It was based on the Intel microprocessor types 80386 and 80387. It has word-length of 32 bits, basic cycle time of 20 MHz and operating system Unix V.3. Computer system TIM-600 was exposed at the Munich International Computer Exhibition on September 1988.
 W
WThe TRS-80 Model II was a computer system launched by Tandy in October 1979, and targeted at the small-business market.
 W
WUKNC was a Soviet PDP-11-compatible educational micro computer, aimed at teaching school informatics courses. It is also known as Elektronika MS-0511. UKNC stands for Educational Computer by Scientific Centre.
 W
WThe West PC-800 is a home computer introduced by Norwegian company West Computer AS in 1984. The computer was designed as an alarm center allowing use of several CPUs and operating systems. The company introduced an IBM PC compatible in early 1986 and the West PC-800 line was phased out.
 W
WThe Xerox 820 is an 8-bit desktop computer sold by Xerox in the early 1980s. The computer runs under the CP/M operating system and uses floppy disk drives for mass storage. The microprocessor board is a licensed variant of the Big Board computer.