 W
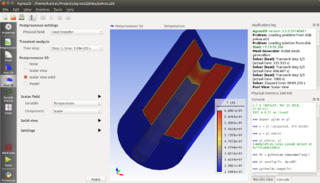
WAgros2D is an open-source code for numerical solutions of 2D coupled problems in technical disciplines. Its principal part is a user interface serving for complete preprocessing and postprocessing of the tasks. The processor is based on the library Hermes containing the most advanced numerical algorithms for monolithic and fully adaptive solution of systems of generally nonlinear and nonstationary partial differential equations (PDEs) based on hp-FEM. Both parts of the code are written in C++.
 W
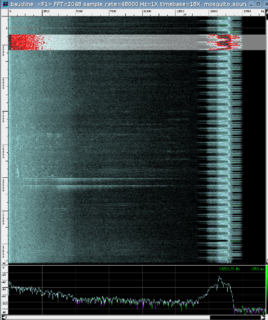
WThe baudline time-frequency browser is a signal analysis tool designed for scientific visualization. It runs on several Unix-like operating systems under the X Window System. Baudline is useful for real-time spectral monitoring, collected signals analysis, generating test signals, making distortion measurements, and playing back audio files.
 W
WElmer is computational tool for multi-physics problems. It has been developed by CSC in collaboration with Finnish universities, research laboratories and industry. Elmer FEM solver is free and open-source software, subject to the requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2 or any later.
 W
WFinite-difference time-domain (FDTD) or Yee's method is a numerical analysis technique used for modeling computational electrodynamics. Since it is a time-domain method, FDTD solutions can cover a wide frequency range with a single simulation run, and treat nonlinear material properties in a natural way.
 W
WFlexPro is a software package for analysis and presentation of scientific and technical data, produced by Weisang GmbH. It runs on Microsoft Windows and is available in English, German, Japanese, Chinese and French. FlexPro has its roots in the test and measurement domain and supports different binary file formats of data acquisition instruments and software. In particular, FlexPro can analyze large amounts of data with high sampling rates.
 W
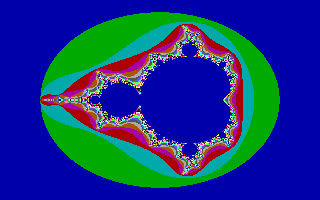
WFractint is a freeware computer program to render and display many kinds of fractals. The program originated on MS-DOS, then ported to the Atari ST, Linux, and Macintosh. During the early 1990s, Fractint was the definitive fractal generating program for personal computers.
 W
WGraphBLAS is an API specification that defines standard building blocks for graph algorithms in the language of linear algebra. GraphBLAS is built upon the notion that a sparse matrix can be used to represent graphs as either an adjacency matrix or an incidence matrix. The GraphBLAS specification describes how graph operations can be efficiently implemented via linear algebraic methods over different semirings.
 W
Wgretl is an open-source statistical package, mainly for econometrics. The name is an acronym for Gnu Regression, Econometrics and Time-series Library.
 W
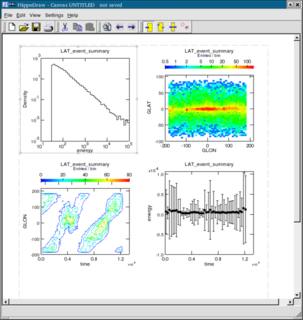
WHippoDraw is a powerful object-oriented statistical data analysis package written in C++, with user interaction via a Qt-based GUI and a Python-scriptable interface. It is being developed by Paul Kunz at SLAC, primarily for the analysis and presentation of particle physics and astrophysics data, but can be equally well used in other fields where data handling is important.
 W
WLaboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench (LabVIEW) is a system-design platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments.
 W
WLAPACK is a standard software library for numerical linear algebra. It provides routines for solving systems of linear equations and linear least squares, eigenvalue problems, and singular value decomposition. It also includes routines to implement the associated matrix factorizations such as LU, QR, Cholesky and Schur decomposition. LAPACK was originally written in FORTRAN 77, but moved to Fortran 90 in version 3.2 (2008). The routines handle both real and complex matrices in both single and double precision.
 W
WMaple is a symbolic and numeric computing environment as well as a multi-paradigm programming language. It covers several areas of technical computing, such as symbolic mathematics, numerical analysis, data processing, visualization, and others. A toolbox, MapleSim, adds functionality for multidomain physical modeling and code generation.
 W
WMathcad is computer software primarily intended for the verification, validation, documentation and re-use of engineering calculations. First introduced in 1986 on DOS, it was the first to introduce live editing of typeset mathematical notation, combined with its automatic computations.
 W
WMATLAB is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numerical computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages.
 W
WMultiple Precision Integers and Rationals (MPIR) is an open-source software multiprecision integer library forked from the GNU Multiple Precision Arithmetic Library (GMP) project. It consists of much code from past GMP releases, and some original contributed code.
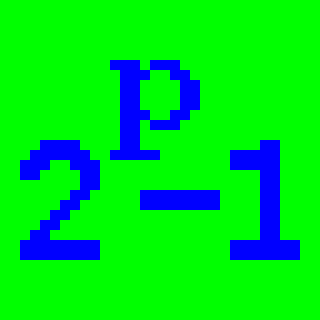 W
WPrime95, also distributed as a command-line utility mprime under FreeBSD and Linux, is a freeware application written by George Woltman. It is used by Great Internet Mersenne Prime Search (GIMPS), a distributed computing project dedicated to Mersenne prime hunting. In overclocking circles, it is commonly used for stability testing.
 W
WNetworkX is a Python library for studying graphs and networks. NetworkX is free software released under the BSD-new license.
 W
WNumerical Recipes is the generic title of a series of books on algorithms and numerical analysis by William H. Press, Saul A. Teukolsky, William T. Vetterling and Brian P. Flannery. In various editions, the books have been in print since 1986. The most recent edition was published in 2007. In 2015 Numerical Recipes sold its historic two-letter domain name nr.com and became numerical.recipes instead.
 W
WOrange is an open-source data visualization, machine learning and data mining toolkit. It features a visual programming front-end for explorative rapid qualitative data analysis and interactive data visualization.
 W
WRange Software is finite element analysis software package.
 W
WROOT is an object-oriented program and library developed by CERN. It was originally designed for particle physics data analysis and contains several features specific to this field, but it is also used in other applications such as astronomy and data mining. The latest release is 6.22.00, as of 2020-07-02.
 W
WSAS is a statistical software suite developed by SAS Institute for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, criminal investigation, and predictive analytics.
 W
WSimcenter Amesim is a commercial simulation software for the modeling and analysis of multi-domain systems. It is part of systems engineering domain and falls into the mechatronic engineering field.
 W
WSimcenter STAR-CCM+ is a commercial Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) based simulation software developed by Siemens Digital Industries Software. Simcenter STAR-CCM+ allows the modeling and analysis of a range of engineering problems involving fluid flow, heat transfer, stress, particulate flow, electromagnetics and related phenomena.
 W
WSimulink is a MATLAB-based graphical programming environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing multidomain dynamical systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool and a customizable set of block libraries. It offers tight integration with the rest of the MATLAB environment and can either drive MATLAB or be scripted from it. Simulink is widely used in automatic control and digital signal processing for multidomain simulation and model-based design.
 W
WSnapPea is free software designed to help mathematicians, in particular low-dimensional topologists, study hyperbolic 3-manifolds. The primary developer is Jeffrey Weeks, who created the first version as part of his doctoral thesis, supervised by William Thurston. It is not to be confused with the unrelated android malware with the same name.
 W
WSOFA Statistics is an open-source statistical package. The name stands for Statistics Open For All. It has a graphical user interface and can connect directly to MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, MS Access (mdb), and Microsoft SQL Server. Data can also be imported from CSV and Tab-Separated files or spreadsheets. The main statistical tests available are Independent and Paired t-tests, Wilcoxon signed ranks, Mann–Whitney U, Pearson's chi squared, Kruskal Wallis H, one-way ANOVA, Spearman's R, and Pearson's R. Nested tables can be produced with row and column percentages, totals, sd, mean, median, lower and upper quartiles, and sum.
 W
WWolfram Mathematica is a modern technical computing system spanning most areas of technical computing — including neural networks, machine learning, image processing, geometry, data science, visualizations, and others. The system is used in many technical, scientific, engineering, mathematical, and computing fields. It was conceived by Stephen Wolfram and is developed by Wolfram Research of Champaign, Illinois. The Wolfram Language is the programming language used in Mathematica.
 W
WWORHP ( "warp"), also referred to as eNLP by ESA, is a mathematical software library for solving continuous large scale nonlinear optimization problems numerically. The acronym WORHP is sometimes spelled out as "We Optimize Really Huge Problems", its primary intended application. WORHP is a hybrid Fortran and C implementation and can be used from C/C++ and Fortran programs using different interfaces of varying complexity and flexibility. In addition interfaces for the modelling environments MATLAB, CasADi and AMPL exist.