 W
WApache Mynewt is a modular real-time operating system for connected Internet of things (IoT) devices that must operate for long times under power, memory, and storage constraints. It is free and open-source software incubating under the Apache Software Foundation, with source code distributed under the Apache License 2.0, a permissive license that is conducive to commercial adoption of open-source software.
 W
WBlackBerry 10 is a proprietary mobile operating system for the BlackBerry line of smartphones, both developed by BlackBerry Limited. BlackBerry 10 is based on QNX, a Unix-like operating system that was originally developed by QNX Software Systems until the company was acquired by BlackBerry in April 2010.
 W
WMultiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
 W
WMultiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
 W
WMultiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
 W
WMultiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
 W
WMultiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
 W
WFreeRTOS is a real-time operating system kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 35 microcontroller platforms. It is distributed under the MIT License.
 W
WFuchsia is an open-source capability-based operating system currently being developed by Google. It first became known to the public when the project appeared on a self hosted form of git in August 2016 without any official announcement. The name means "Pink + Purple = Fuchsia ", which is a reference to Pink and Purple. In contrast to prior Google-developed operating systems such as Chrome OS and Android, which are based on the Linux kernel, Fuchsia is based on a new kernel called Zircon.
 W
WInferno is a distributed operating system started at Bell Labs and now developed and maintained by Vita Nuova Holdings as free software. Inferno was based on the experience gained with Plan 9 from Bell Labs, and the further research of Bell Labs into operating systems, languages, on-the-fly compilers, graphics, security, networking and portability. The name of the operating system and many of its associated programs, as well as that of the current company, were inspired by Dante Alighieri's Divine Comedy. In Italian, Inferno means "hell" — of which there are nine circles in Dante's Divine Comedy.
 W
WMultiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers.
 W
WOpenComRTOS is a commercial network-centric, formally developed real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market.
 W
WBaget RTOS is a real-time operating system developed by the Scientific Research Institute of System Development of the Russian Academy of Sciences for a MIPS and Intel BSPs. Baget is intended for software execution in a hard real-time embedded systems (firmware).
 W
WPhantom OS is an operating system mostly made by Russian programmers. Phantom OS is based on a concept of persistent virtual memory, and is managed-code oriented. Phantom OS is one of a few OSes that are not based on classical concepts of Unix-like systems. Its primary goal is to achieve simplicity and effectiveness in both the operating system and applications at the same time.
 W
WPhoenix-RTOS is a real-time operating system designed for Internet of Things appliances. The main goal of the system is to facilitate the creation of "Software Defined Solutions".
 W
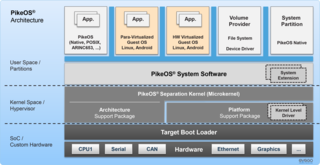
WPikeOS is a commercial, hard real-time operating system (RTOS) that offers a separation kernel based hypervisor with multiple logical partition types for many other operating systems and applications. It enables users to build certifiable smart devices for the Internet of things according to the high quality, safety and security standards of different industries.
 W
WQNX is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market. QNX was one of the first commercially successful microkernel operating systems. As of 2020, it is used in a variety of devices including cars and mobile phones.
 W
WQP is a family of lightweight, open source software frameworks for building responsive and modular real-time embedded applications as systems of cooperating, event-driven active objects (actors).
 W
WRIOT is a small operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It is open-source software, released under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
 W
WRSX-11 is a discontinued family of multi-user real-time operating systems for PDP-11 computers created by Digital Equipment Corporation. In widespread use through the late 1970s and early 1980s, RSX-11 was influential in the development of later operating systems such as VMS and Windows NT.
 W
WReal-time application interface (RTAI) is a real-time extension for the Linux kernel, which lets users write applications with strict timing constraints for Linux. Like Linux itself the RTAI software is a community effort. RTAI provides deterministic response to interrupts, POSIX-compliant and native RTAI real-time tasks. RTAI supports several architectures, including IA-32, x86-64, PowerPC, ARM, and MIPS.
 W
WReal-Time Executive for Multiprocessor Systems (RTEMS), formerly Real-Time Executive for Missile Systems, and then Real-Time Executive for Military Systems, is a real-time operating system (RTOS) designed for embedded systems. It is free open-source software.
 W
WRTX is a line of real-time operating system (RTOS) extensions by the firm IntervalZero. They are a software extension or abstraction layer that converts Microsoft Windows operating system into a RTOS. It was the first Windows real-time solution on the market.
 W
WNEC V60 was a CISC microprocessor manufactured by NEC starting in 1986. It has a memory management unit (MMU), and real-time operating system (RTOS) support for both Unix-based user-application-oriented systems and for I‑TRON–based hardware-control-oriented embedded systems. This article also describes the V70 and V80, as these share the same instruction set architecture (ISA) with the V60. In addition, a dedicated co-FPP, multi-cpu lockstep fault-tolerant mechanism named FRM, development tools including Ada certified system MV‑4000, and in-circuit emulator (ICE) are described. Their successor, the V800 Series product families, are briefly introduced.
 W
WNEC V60 was a CISC microprocessor manufactured by NEC starting in 1986. It has a memory management unit (MMU), and real-time operating system (RTOS) support for both Unix-based user-application-oriented systems and for I‑TRON–based hardware-control-oriented embedded systems. This article also describes the V70 and V80, as these share the same instruction set architecture (ISA) with the V60. In addition, a dedicated co-FPP, multi-cpu lockstep fault-tolerant mechanism named FRM, development tools including Ada certified system MV‑4000, and in-circuit emulator (ICE) are described. Their successor, the V800 Series product families, are briefly introduced.
 W
WSymbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. Symbian was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for PDAs in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian OS is a descendant of Psion's EPOC, and was released exclusively on ARM processors, although an unreleased x86 port existed. Symbian was used by many major mobile phone brands, like Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, and above all by Nokia. It was also prevalent in Japan by brands including Fujitsu, Sharp and Mitsubishi. As a pioneer that established the smartphone industry, it was the most popular smartphone OS on a worldwide average until the end of 2010—at a time when smartphones were in limited use—when it was overtaken by iOS and Android. It was notably not as popular in North America.
 W
WTransaction Processing Facility (TPF) is an IBM real-time operating system for mainframe computers descended from the IBM System/360 family, including zSeries and System z9.
 W
WVenix is a discontinued version of the Unix operating system for low-end computers, developed by VenturCom, a "company that specialises in the skinniest implementations of Unix".
 W
WVxWorks is a real-time operating system (RTOS) developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a wholly owned subsidiary of TPG Capital, US. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and, in many cases, safety and security certification, for industries, such as aerospace and defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.
 W
WWindows Embedded Compact 7 is the seventh major release of the Windows Embedded CE operating system, released on March 1, 2011. Windows Embedded Compact 7 is a real-time OS, separate from the Windows NT line, and is designed to target enterprise specific tools such as industrial controllers and consumer electronics devices such as digital cameras, GPS systems and also automotive infotainment systems. Windows Embedded Compact is designed to run on multiple CPU architectures and supports x86, SH and ARM.
 W
WXenomai is a real-time development framework cooperating with the Linux kernel to provide pervasive, interface-agnostic, hard real-time support to user space applications seamlessly integrated into the Linux environment.
 W
WZephyr is a small real-time operating system for connected, resource-constrained and embedded devices supporting multiple architectures and released under the Apache License 2.0. Beyond its kernel, Zephyr includes all the components and libraries needed to develop a full application such as device drivers, protocol stacks, file systems, and firmware updates.