 W
WThe fourth USS Boston was an 18-gun sloop of war, launched on 15 October 1825 by the Boston Navy Yard and commissioned the following year, Master Commandant Beekman V. Hoffman in command.
 W
WUSS Brandywine was a wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy bearing 44 guns which had the initial task of conveying the Marquis de Lafayette back to France. She was later recommissioned a number of times for service in various theaters, such as in the Mediterranean, in China and in the South Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WUSS Columbus was a 90-gun ship of the line in the United States Navy. She was launched on 1 March 1819 by Washington Navy Yard and commissioned on 7 September 1819, Master Commandant J. H. Elton in command.
 W
WUSS Congress (1841)—the fourth United States Navy ship to carry that name—was a sailing frigate, like her predecessor, USS Congress (1799).
 W
WThe first USS Cumberland was a 50-gun sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was the first ship sunk by the ironclad CSS Virginia.
 W
WThe second USS Cyane was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the Mexican–American War.
 W
WUSS Dale (1839) was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy commissioned on 11 December 1839. Dale was involved in the Mexican–American War, the American Civil War, operations along Africa to suppress slave trade, and was used in the U.S. Coast Guard, among other activities. Dale was placed into ordinary numerous times.
 W
WUSS Decatur was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the mid-19th century. She was commissioned to protect American interests in the South Atlantic Ocean, including the interception of ships involved in the African slave trade. Decatur served in both the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.
 W
WUSS Erie was a three-masted, wooden-hulled sloop-of-war of the United States Navy in the early 19th century.
 W
WUSS Independence was a wooden-hulled, three-masted ship, originally a ship of the line and the first to be commissioned by the United States Navy. Originally a 90-gun ship, in 1836 she was cut down by one deck and re-rated as a 54-gun frigate.
 W
WThe first USS Jamestown was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.
 W
WThe first John Adams was originally built in 1799 as a frigate for the United States Navy, converted to a corvette in 1809, and later converted back to a frigate in 1830. Named for President John Adams, she fought in the Quasi-War, the First and Second Barbary Wars, the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War. At the end of her career, she participated in the Union blockade of South Carolina's ports. She then participated in a historic raid that Harriet Tubman, the former slave and Union operative, organized with Union colonel Montgomery. John Adams led three steam-powered gunboats up the Harbor River to Port Royal. The squadron relied on local black mariners to guide it past mines and fortifications. The squadron freed 750+ slaves and unsettled the Confederacy. Tubman was the first woman in U.S. history to plan and execute an armed expedition.
 W
WThe second USS Lexington was a sloop in the United States Navy built at the New York Navy Yard in Brooklyn, New York, in 1825; and commissioned on 11 June 1826, Master Commandant William B. Shubrick in command.
 W
WLibertad, meaning "liberty" in Spanish, was a merchant schooner built on the west coast of Mexico for service between Mexico and the Baja California peninsula and along the coast of Mexico. During the Mexican–American War, she was captured at Loreto, Mexico, along with the schooner Fortuna on 1 October 1846 by the United States Navy sloop-of-war USS Cyane under the command of Commander Samuel Francis Du Pont.
 W
WUSS Massachusetts (1845) was a steamer built in 1845 and acquired by the U.S. War Department in 1847. She was used by the U.S. Army as a transport during the Mexican–American War before being transferred to U.S. Navy Department in 1849. She traveled widely, including transiting Cape Horn several times as part of her official duties on both sides of the Americas. During her years of service she spent most of her time on the west coast of North America.
 W
WUSS Mississippi, a paddle frigate, was the first ship of the United States Navy to bear that name. She was named for the Mississippi River. Her sister ship was Missouri. Her keel was laid down by the Philadelphia Navy Yard in 1839; built under the personal supervision of Commodore Matthew Perry. She was commissioned on 22 December 1841, with Captain W. D. Salter in command and launched several weeks later.
 W
WUSS North Carolina was a 74-gun ship of the line in the United States Navy. One of the "nine ships to rate not less than 74 guns each" authorized by Congress on 29 April 1816, she was laid down in 1818 by the Philadelphia Navy Yard, launched on 7 September 1820, and fitted out in the Norfolk Navy Yard. Master Commandant Charles W. Morgan was assigned to North Carolina as her first commanding officer on 24 June 1824.
 W
WThe second USS Ohio was a ship of the line of the United States Navy, rated at 74 guns, although her total guns was 104. She was designed by Henry Eckford, laid down at Brooklyn Navy Yard in 1817, and launched on 30 May 1820. She went into ordinary and in the ensuing years decayed badly. Refitted for service in 1838, Ohio sailed on 16 October 1838 to join the Mediterranean Squadron under Commodore Isaac Hull. Acting as flagship for two years, she protected commerce and suppressed the slave trade off the African coast. Ohio proved to have excellent performance under sail, repeatedly making more than 12 kn. One of her officers stated, "I never supposed such a ship could be built—a ship possessing in so great a degree all the qualifications of a perfect vessel." In 1840, Ohio returned to Boston where she again went into ordinary. From 1841–1846, Ohio served as receiving ship.
 W
WUSS Perry (1843) was a brig commissioned by the United States Navy prior to the American Civil War. She was tasked by the Navy for various missions, including those related to diplomatic tensions with Paraguay, the Mexican–American War, the slave trade, and the American Civil War. She was probably named after Commodore Oliver Hazard Perry.
 W
WThe second USS Porpoise was a 224-ton Dolphin-class brigantine. Porpoise was later re-rigged as a brig. She was based on the same plans as Dolphin.
 W
WThe second USS Portsmouth was a wooden sloop-of-war in the United States Navy in service during the mid-to-late 19th century. She was designed by Josiah Barker on the lines of a French-built privateer, and built at the Portsmouth Navy Yard, directly across the Piscataqua River from Portsmouth, New Hampshire. She was described as an improvement over USS Saratoga built in the same shipyard a year earlier. Portsmouth was launched on 23 October 1843 and commissioned on 10 November 1844, with Commander John Berrien Montgomery in command.
 W
WUSS Preble was a United States Navy sloop-of-war with 16 guns, built by the Portsmouth Navy Yard, Kittery, Maine, launched June 13, 1839 and commissioned in 1840. She was named after Commodore Edward Preble (1761–1807).
 W
WThe first USS Raritan was a wooden-hulled, three-masted sailing frigate of the United States Navy built at the Philadelphia Navy Yard, laid down in 1820, but not launched until 13 June 1843, sponsored by Commodore Frederick Engle. She was one of the last sailing frigates of the United States Navy.
 W
WUSS Saranac was a sloop-of-war of the United States Navy. The ship laid down in 1847 during the Mexican–American War; however, by the time she completed sea trials, the war was over. She was commissioned in 1850 and saw service protecting American interests in the Atlantic Ocean as well as the Pacific Ocean.
 W
WUSS Saratoga, a sloop-of-war, was the third ship of the United States Navy to be named for the Battle of Saratoga of the American Revolutionary War. Her keel was laid down in the summer of 1841 by the Portsmouth Navy Yard. She was launched on 26 July 1842 and commissioned on 4 January 1843 with Commander Josiah Tattnall in command.
 W
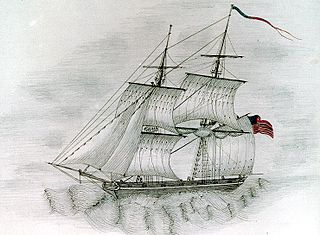
WThe second USS Savannah was a frigate in the United States Navy. She was named after the city of Savannah, Georgia.
 W
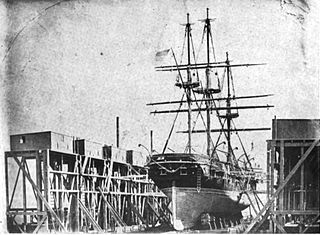
WThe second USS Somers was a brig in the United States Navy during the John Tyler administration which became infamous for being the only U.S. Navy ship to undergo a mutiny which led to executions.
 W
WThe second USS St. Mary's was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy.
 W
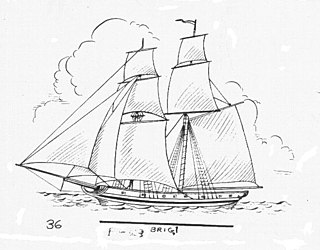
WThe first USS Supply was a ship-rigged sailing vessel which served as a stores ship in the United States Navy. She saw service in the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.
 W
WThe first USS Truxtun was a brig in the United States Navy. She was named for Commodore Thomas Truxtun, and was an active participant in the Mexican–American War.
 W
WThe first Vandalia was an 18-gun sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the Second Seminole War and the American Civil War. She was named for the city of Vandalia, Illinois.
 W
WUSS Vincennes (1826) was a 703-ton Boston-class sloop of war in the United States Navy from 1826 to 1865. During her service, Vincennes patrolled the Pacific, explored the Antarctic, and blockaded the Confederate Gulf coast in the Civil War. Named for the Revolutionary War Battle of Vincennes, she was the first U.S. warship to circumnavigate the globe.
 W
WThe third USS Vixen was a steamboat in the United States Navy during the Mexican–American War.
 W
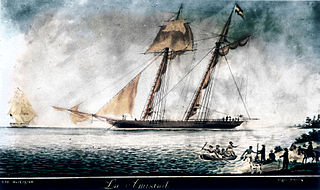
WWashington was a revenue cutter that served in the United States Revenue Cutter Service and in the United States Navy. She discovered, boarded and captured La Amistad after the slaves onboard had seized control of that schooner in an 1839 mutiny.