 W
WBasic Interoperable Scrambling System, usually known as BISS, is a satellite signal scrambling system developed by the European Broadcasting Union and a consortium of hardware manufacturers.
 W
WA block upconverter (BUC) is used in the transmission (uplink) of satellite signals. It converts a band of frequencies from a lower frequency to a higher frequency. Modern BUCs convert from the L band to Ku band, C band and Ka band. Older BUCs convert from a 70 MHz intermediate frequency (IF) to Ku band or C band.
 W
WThe C band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies ranging from 4.0 to 8.0 gigahertz (GHz); however, this definition is the one used by radar manufacturers and users, not necessarily by microwave radio telecommunications users. The C band is used for many satellite communications transmissions, some Wi-Fi devices, some cordless telephones as well as some surveillance and weather radar systems.
 W
WCommercial use of space is the provision of goods or services of commercial value by using equipment sent into Earth orbit or outer space. This phenomenon – aka Space Economy – is accelerating cross-sector innovation processes combining the most advanced space and digital technologies to develop a broad portfolio of space-based services. The use of space technologies and of the data they collect, combined with the most advanced enabling digital technologies is generating a multitude of business opportunities that include the development of new products and services all the way to the creation of new business models, and the reconfiguration of value networks and relationships between companies. If well leveraged such technology and business opportunities can contribute to the creation of tangible and intangible value, through new forms and sources of revenue, operating efficiency and the start of new projects leading to multidimensional positive impact. Examples of the commercial use of space include satellite navigation, satellite television and commercial satellite imagery. Operators of such services typically contract the manufacturing of satellites and their launch to private or public companies, which form an integral part of the space economy. Some commercial ventures have long-term plans to exploit natural resources originating outside Earth, for example asteroid mining. Space tourism, currently an exceptional activity, could also be an area of future growth, as new businesses strive to reduce the costs and risks of human spaceflight.
 W
WA communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunications signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. There are about 2,000 communications satellites in Earth's orbit, used by both private and government organizations. Many are in geostationary orbit 22,236 miles (35,785 km) above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky, so the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track it.
 W
WDigital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the Digital Video Broadcasting Project, an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI in March 2005. The standard is based on, and improves upon DVB-S and the electronic news-gathering system, used by mobile units for sending sounds and images from remote locations worldwide back to their home television stations.
 W
WEarth exploration-satellite service is – according to Article 1.51 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A radiocommunication service between earth stations and one or more space stations, which may include links between space stations, in which: information relating to the characteristics of the Earth and its natural phenomena, including data relating to the state of the environment, is obtained from active sensors or passive sensors on Earth satellites; similar information is collected from airborne or Earth-based platforms; such information may be distributed to earth stations within the system concerned; platform interrogation may be included.
 W
WIn parabolic antennas such as satellite dishes, a feed horn is a small horn antenna used to convey radio waves between the transmitter and/or receiver and the parabolic reflector. In transmitting antennas, it is connected to the transmitter and converts the radio frequency alternating current from the transmitter to radio waves and feeds them to the rest of the antenna, which focuses them into a beam. In receiving antennas, incoming radio waves are gathered and focused by the antenna's reflector on the feed horn, which converts them to a tiny radio frequency voltage which is amplified by the receiver. Feed horns are used mainly at microwave (SHF) and higher frequencies.
 W
WFixed-satellite service is – according to article 1.21 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as A radiocommunication service between earth stations at given positions, when one or more satellites are used; the given position may be a specified fixed point or any fixed point within specified areas; in some cases this service includes satellite-to-satellite links, which may also be operated in the inter-satellite service; the fixed-satellite service may also include feeder links for other space radiocommunication services.
 W
WA focal cloud is the collection of focal points of an imperfect lens or parabolic reflector whether optical, electrostatic or electromagnetic. This includes parabolic antennas and lens-type reflective antennas of all kinds. The effect is analogous to the circle of confusion in photography.
 W
WThe footprint of a communications satellite is the ground area that its transponders offer coverage, and determines the satellite dish diameter required to receive each transponder's signal. There is usually a different map for each transponder, as each may be aimed to cover different areas.
 W
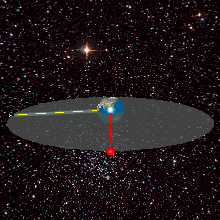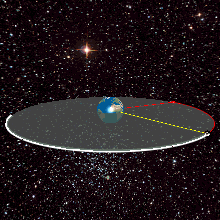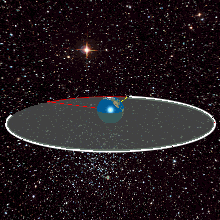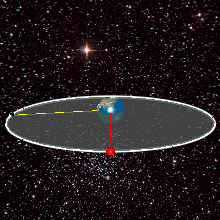
WA geosynchronous orbit is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds. The synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that, for an observer on Earth's surface, an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period of one sidereal day. Over the course of a day, the object's position in the sky may remain still or trace out a path, typically in a figure-8 form, whose precise characteristics depend on the orbit's inclination and eccentricity. A circular geosynchronous orbit has a constant altitude of 35,786 km (22,236 mi), and all geosynchronous orbits share that semi-major axis.
 W
WA geosynchronous satellite is a satellite in geosynchronous orbit, with an orbital period the same as the Earth's rotation period. Such a satellite returns to the same position in the sky after each sidereal day, and over the course of a day traces out a path in the sky that is typically some form of analemma. A special case of geosynchronous satellite is the geostationary satellite, which has a geostationary orbit – a circular geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator. Another type of geosynchronous orbit used by satellites is the Tundra elliptical orbit.
 W
WA ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft, or reception of radio waves from astronomical radio sources. Ground stations may be located either on the surface of the Earth, or in its atmosphere. Earth stations communicate with spacecraft by transmitting and receiving radio waves in the super high frequency (SHF) or extremely high frequency (EHF) bands. When a ground station successfully transmits radio waves to a spacecraft, it establishes a telecommunications link. A principal telecommunications device of the ground station is the parabolic antenna.
 W
WWeather satellite pictures are often broadcast as high-resolution picture transmissions (HRPTs), color high-resolution picture transmissions (CHRPTs) for Chinese weather satellite transmissions, or advanced high-resolution picture transmissions (AHRPTs) for EUMETSAT weather satellite transmissions. HRPT transmissions are available around the world and are available from both polar and geostationary weather satellites. The polar satellites rotate in orbits that allow each location on earth to be covered by the weather satellite twice per day while the geostationary satellites remain in one location at the equator taking weather images of the earth from that location over the equator. The sensor on weather satellites that picks up the data transmitted in HRPT is referred to as an Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR).
 W
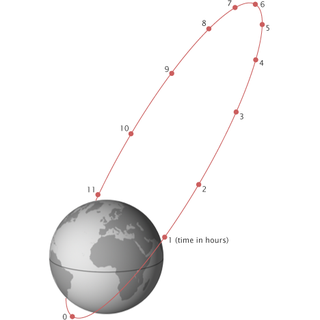
WA highly elliptical orbit (HEO) is an elliptic orbit with high eccentricity, usually referring to one around Earth. Examples of inclined HEO orbits include Molniya orbits, named after the Molniya Soviet communication satellites which used them, and Tundra orbits.
 W
WA low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is the receiving device mounted on satellite dishes used for satellite TV reception, which collects the radio waves from the dish and converts them to a signal which is sent through a cable to the receiver inside the building. Also called a low-noise block, low-noise converter (LNC), or even low-noise downconverter (LND), the device is sometimes inaccurately called a low-noise amplifier (LNA).
 W
WMeteorological-satellite service is – according to Article 1.52 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as « An earth exploration-satellite service for meteorological purposes.»
 W
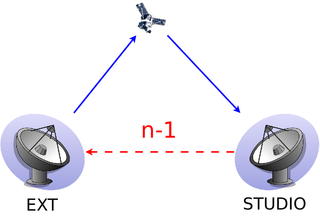
WIn audio engineering, a mix-minus or clean feed is a particular setup of a mixing console or matrix mixer, such that an output of the mixer contains everything except a designated input. Mix-minus is often used to prevent echoes or feedback in broadcast or sound reinforcement systems.
 W
WA Molniya orbit is a type of satellite orbit designed to provide communications and remote sensing coverage over high latitudes. It is a highly elliptical orbit with an inclination of 63.4 degrees, an argument of perigee of 270 degrees, and an orbital period of approximately half a sidereal day. The name comes from the Molniya satellites, a series of Soviet/Russian civilian and military communications satellites which have used this type of orbit since the mid-1960s.
 W
WAn offset dish antenna or off-axis dish antenna is a type of parabolic antenna. It is so called because the antenna feed is offset to the side of the reflector, in contrast to the common "front-feed" parabolic antenna where the feed antenna is suspended in front of the dish, on its axis. As in a front-fed parabolic dish, the feed is located at the focal point of the reflector, but the reflector is an asymmetric segment of a paraboloid, so the focus is located to the side.
 W
WAn orthomode transducer (OMT) is a waveguide component. It is commonly referred to as a polarisation duplexer. Orthomode transducers serve either to combine or to separate two orthogonally polarized microwave signal paths. One of the paths forms the uplink, which is transmitted over the same waveguide as the received signal path, or downlink path. Such a device may be part of a VSAT antenna feed or a terrestrial microwave radio feed; for example, OMTs are often used with a feed horn to isolate orthogonal polarizations of a signal and to transfer transmit and receive signals to different ports.
 W
WA parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct the radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type. In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used, so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave (SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently-sized reflectors can be used.
 W
WAn antenna reflector is a device that reflects electromagnetic waves. Antenna reflectors can exist as a standalone device for redirecting radio frequency (RF) energy, or can be integrated as part of an antenna assembly.
 W
WA satellite finder is a satellite signal meter used to accurately point satellite dishes at communications satellites in geostationary orbit.
 W
WSAT>IP specifies an IP-based client–server communication protocol for a TV gateway in which SAT>IP servers, connected to one or more DVB broadcast sources, send the program selected and requested by an SAT>IP client over an IP based local area network in either unicast for the one requesting client or multicast in one datastream for several SAT>IP clients.
 W
WA communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunications signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. There are about 2,000 communications satellites in Earth's orbit, used by both private and government organizations. Many are in geostationary orbit 22,236 miles (35,785 km) above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky, so the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track it.
 W
WA satellite dish is a dish-shaped type of parabolic antenna designed to receive or transmit information by radio waves to or from a communication satellite. The term most commonly means a dish used by consumers to receive direct-broadcast satellite television from a direct broadcast satellite in geostationary orbit.
 W
WA set-top box (STB), also colloquially known as a cable box, is an information appliance device that generally contains a TV-tuner input and displays output to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the source signal into content in a form that can then be displayed on the television screen or other display device. They are used in cable television, satellite television, and over-the-air television systems as well as other uses. A computer that connects to your television. Allows you to use telephone line or cable connection do you browse the Internet and exchange electronic mail on your television.
 W
WSolar conjunction occurs when a planet or other solar system object is on the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth. From an Earth reference, the Sun will pass between the Earth and the object. Communication with any spacecraft in solar conjunction will be severely limited due to the Sun's interference on radio transmissions from the spacecraft.
 W
WIn astronomy, a solar transit is a movement of any object passing between the Sun and the Earth. This mainly includes the planets Mercury and Venus. A solar eclipse is also a solar transit of the Moon, but technically only if it does not cover the entire disc of the Sun, as "transit" counts only objects that are smaller than what they are passing in front of. Solar transit is only one of several types of astronomical transit.
 W
WThe space segment of an artificial satellite system is one of its three operational components. It comprises the satellite or satellite constellation and the uplink and downlink satellite links.
 W
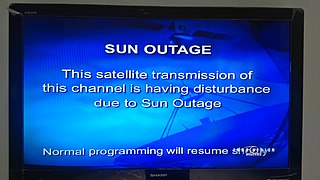
WA Sun outage, Sun transit, or Sun fade is an interruption in or distortion of geostationary satellite signals caused by interference of the sun when it falls directly behind a satellite which an earth station is trying to receive data from or transmit data to. It usually occurs briefly to such satellites twice per year and such earth stations install temporary or permanent guards to their receiving systems to prevent equipment damage.
 W
WA Tundra orbit is a highly elliptical geosynchronous orbit with a high inclination, an orbital period of one sidereal day, and a typical eccentricity between 0.2 and 0.3. A satellite placed in this orbit spends most of its time over a chosen area of the Earth, a phenomenon known as apogee dwell, which makes them particularly well suited for communications satellites serving high latitude regions. The ground track of a satellite in a Tundra orbit is a closed figure 8 with a smaller loop over either the northern or southern hemisphere. This differentiates them from Molniya orbits designed to service high-latitude regions, which have the same inclination but half the period and do not loiter over a single region.