 W
WAn anvil is a metalworking tool consisting of a large block of metal, with a flattened top surface, upon which another object is struck.
 W
WAn arbor press is a small hand-operated press. It is typically used to perform smaller jobs, such as staking, riveting, installing, configuring and removing bearings and other press fit work. Punches, inserters, or other tools/dies may be added to the end of the ram depending on the desired task. Arbor presses are usually rated by the ideal force that the leverage bar can apply. Typically common are presses with a leverage of 1–5 tons. This leverage is achieved when a force is applied to the lever arm or wheel.
 W
WA bending machine is a forming machine tool. Its purpose is to assemble a bend on a workpiece. A bend is manufactured by using a bending tool during a linear or rotating move. The detailed classification can be done with the help of the kinematics.
 W
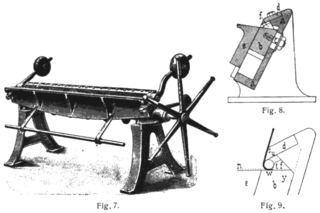
WA brake is a metalworking machine that allows the bending of sheet metal. A cornice brake only allows for simple bends and creases, while a box-and-pan brake also allows one to form box and pan shapes. It is also known as a bending machine or bending brake or in Britain as a sheet metal folder or just a folder.
 W
WCemented carbide is a hard material used extensively as cutting tool material, as well as other industrial applications. It consists of fine particles of carbide cemented into a composite by a binder metal. Cemented carbides commonly use tungsten carbide (WC), titanium carbide (TiC), or tantalum carbide (TaC) as the aggregate. Mentions of "carbide" or "tungsten carbide" in industrial contexts usually refer to these cemented composites.
 W
WA fixture is a work-holding or support device used in the manufacturing industry. Fixtures are used to securely locate and support the work, ensuring that all parts produced using the fixture will maintain conformity and interchangeability. Using a fixture improves the economy of production by allowing smooth operation and quick transition from part to part, reducing the requirement for skilled labor by simplifying how workpieces are mounted, and increasing conformity across a production run.
 W
WA fuller is a rounded or beveled longitudinal groove or slot along the flat side of a blade that is made using a blacksmithing tool called a spring swage or, like the groove, a fuller. A fuller is often used to lighten the blade. When combined with proper distal tapers, heat treatment and blade tempering, a fullered blade can be 20% to 35% lighter than a non-fullered blade with minimal sacrifice of strength or blade integrity. This effect lessens as the blade is reduced in length. A blade is said to be "fullered" after introduction of the groove.
 W
WA grinding wheel is a wheel composed of an abrasive compound and used for various grinding and abrasive machining operations. Such wheels are used in grinding machines.
 W
WA hammer is a tool consisting of a weighted "head" fixed to a long handle that is swung to deliver an impact to a small area of an object. This can be, for example, to drive nails into wood, to shape metal, or to crush rock. Hammers are used for a wide range of driving, shaping, and breaking applications.
 W
WA hydraulic press is a machine press using a hydraulic cylinder to generate a compressive force. It uses the hydraulic equivalent of a mechanical lever, and was also known as a Bramah press after the inventor, Joseph Bramah, of England. He invented and was issued a patent on this press in 1795. As Bramah installed toilets, he studied the existing literature on the motion of fluids and put this knowledge into the development of the press.
 W
WA jig is a type of custom-made tool used to control the location and/or motion of parts or other tools.
 W
WA metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of applications, and a broad range of materials. In machining jargon, where the larger context is already understood, they are usually simply called lathes, or else referred to by more-specific subtype names. These rigid machine tools remove material from a rotating workpiece via the movements of various cutting tools, such as tool bits and drill bits.
 W
WThe Mästermyr chest is a Viking Age (793–1066) tool chest found in the Mästermyr mire west of Hemse on the island of Gotland, Sweden. It is the largest tool find from that era in Europe.
 W
WA parts washer is a piece of equipment used to remove contaminants or debris, such as dirt, grime, carbon, oil, grease, metal chips, cutting fluids, mold release agents, ink, paint, and corrosion from workpieces. Parts washers are used in new manufacturing and remanufacturing processes; they are designed to clean, degrease and dry bulk loads of small or large parts in preparation for assembly, inspection, surface treatment, packaging and distribution. Parts washers may be as simple as the manual "sink-on-a-drum" common to many auto repair shops, or they may be very complex, multi-stage units with pass-through parts handling systems. Parts washers are essential in maintenance, repair and remanufacturing operations as well, from cleaning fasteners, nuts, bolts and screws to diesel engine blocks and related parts, rail bearings, wind turbine gears boxes and automotive assemblies.
 W
WPower hammers are mechanical forging hammers that use a non-muscular power source to raise the hammer preparatory to striking, and accelerate it onto the work being hammered. Also called "Open Die Power Forging Hammers." They have been used by blacksmiths, bladesmiths, metalworkers, and manufacturers since the late 1880s, having replaced trip hammers.
 W
WA press brake is a machine pressing tool for bending sheet and plate material, most commonly sheet metal. It forms predetermined bends by clamping the workpiece between a matching punch and die.
 W
WA propane torch is a tool normally used for the application of flame or heat which uses propane, a hydrocarbon gas, for its fuel. Propane is one of a group of by-products of the natural gas and petroleum industries known as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Propane and other fuel torches are most commonly used in the manufacturing, construction and metal-working industries.
 W
WA Reducing Machine was a type of pantograph lathe used until the 21st century to manufacture coin dies. Prior to the machine's introduction, designs were cut by hand into metal dies by a specialist engraver. The reducing machine changed this by allowing artists to create designs on a larger surface area and then have them scaled down and cut into a die automatically. The most successful version of the machine, created by Victor Janvier, was used by mints all around the world including the US Mint who operated one as late as 2008 when it was replaced by CNC milling machines.
 W
WA rivet gun, also known as a rivet hammer or a pneumatic hammer, is a type of tool used to drive rivets. The rivet gun is used on rivet's factory head, and a bucking bar is used to support the tail of the rivet. The energy from the hammer in the rivet gun drives the work and the rivet against the bucking bar. As a result, the tail of the rivet is compressed and work-hardened. At the same time the work is tightly drawn together and retained between the rivet head and the flattened tail. Nearly all rivet guns are pneumatically powered. Those rivet guns used to drive rivets in structural steel are quite large while those used in aircraft assembly are easily held in one hand. A rivet gun differs from an air hammer in the precision of the driving force.
 W
WA riveting machine is used to automatically set (squeeze) rivets in order to join materials together. The riveting machine offers greater consistency, productivity, and lower cost when compared to manual riveting.
 W
WA roll bender is a mechanical jig having three rollers used to bend a metal bar into a circular arc. The rollers freely rotate about three parallel axes, which are arranged with uniform horizontal spacing. Two outer rollers, usually immobile, cradle the bottom of the material while the inner roller, whose position is adjustable, presses on the topside of the material.
 W
WA sand rammer is a piece of equipment used in foundry sand testing to make test specimen of molding sand by compacting bulk material by free fixed height drop of fixed weight for 3 times. It is also used to determine compactibility of sands by using special specimen tubes and a linear scale.
 W
WA sander is a power tool used to smooth surfaces by abrasion with sandpaper. Sanders have a means to attach the sandpaper and a mechanism to move it rapidly contained within a housing with means to hand-hold it or fix it to a workbench. Woodworking sanders are usually powered electrically, and those used in auto-body repair work by compressed air. There are many different types of sanders for different purposes. Multi-purpose power tools and electric drills may have sander attachments.
 W
WA screw press is a type of machine press in which the ram is driven up and down by a screw. The screw shaft can be driven by a handle or a wheel. It works by using a coarse screw to convert the rotation of the handle or drive-wheel into a small downward movement of greater force. The overhead handle usually incorporates balls as flyweights. The weights helps to maintain the momentum and thrust of the tool to make it easier to operate.
 W
WA shaper is a type of machine tool that uses linear relative motion between the workpiece and a single-point cutting tool to machine a linear toolpath. Its cut is analogous to that of a lathe, except that it is (archetypally) linear instead of helical.
 W
WA Snarling iron is a metal worker's tool used to drive the walls of metal vessels. "A snarler... is a worker in teapots, and may... be compared with the leaf bumper who bumps up the leaves commonly seen in metalwork". Examples have come to light in different historical contexts, as in Chanhudaro, Indus valley civilization.
 W
WA stamping press is a metalworking machine tool used to shape or cut metal by deforming it with a die. In simple terms, a stamping press is the modern day equivalent of a hammer and anvil. The difference is that a stamping press uses precision-made male and female dies to dictate the shape of the final product.
 W
WA steam hammer, also called a drop hammer, is an industrial power hammer driven by steam that is used for tasks such as shaping forgings and driving piles. Typically the hammer is attached to a piston that slides within a fixed cylinder, but in some designs the hammer is attached to a cylinder that slides along a fixed piston.
 W
WA stop block is a simple reusable jig used in metalworking and woodworking to locate a common edge of a workpiece so that multiple workpieces can get the same operation performed quickly. Common applications are table saws and manual milling machines, but they are also used on miter saws, band saws, radial arm saws, and abrasive saws.
 W
WA swage block is a large, heavy block of cast iron or steel used in smithing, with variously-sized holes in its face and usually with forms on the sides.
 W
WA tombstone, also known as a pedestal-type fixture, tooling tower, tooling column or fixture block, is a fixture of two or more sides, onto which are mounted parts to be manufactured. Tombstones are typically used in automated systems; parts are loaded onto the tombstone so that robots may operate on one part, flip the tombstone, and operate on the next part until all processes are completed, then transport the entire tombstone to the next station.
 W
WA trip hammer, also known as a tilt hammer or helve hammer, is a massive powered hammer. Traditional uses of trip hammers include pounding, decorticating and polishing of grain in agriculture. In mining, trip hammers were used for crushing metal ores into small pieces, although a stamp mill was more usual for this. In finery forges they were used for drawing out blooms made from wrought iron into more workable bar iron. They were also used for fabricating various articles of wrought iron, latten, steel and other metals.
 W
WTube bending is any metal forming processes used to permanently form pipes or tubing. Tube bending may be form-bound or use freeform-bending procedures, and it may use heat supported or cold forming procedures.
 W
WA turret punch or turret press is a type of punch press used for metal forming by punching.
 W
WA turret punch or turret press is a type of punch press used for metal forming by punching.
 W
WA wire brush is a tool consisting of a brush whose bristles are made of wire, most often steel wire. The steel used is generally a medium- to high-carbon variety and very hard and springy. Other wire brushes feature bristles made from brass or stainless steel, depending on application. Wires in a wire brush can be held together by epoxy, staples, or other binding. Wire brushes usually either have a handle of wood or plastic or are formed into a wheel for use on angle grinders, bench grinders, pistol-grip drill motors, or other power tools.