 W
WDVD is a digital optical disc data storage format invented and developed in 1995 and released in late 1996. The medium can store any kind of digital data and was widely used for software and other computer files as well as video programs watched using DVD players. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than compact discs while having the same dimensions.
AnyDVD is a device driver for Microsoft Windows which allows decryption of DVDs on the fly, as well as targeted removal of copy preventions and user operation prohibitions (UOPs). With an upgrade, it will also do the same for HD DVD and Blu-ray Disc. The AnyDVD program runs in the background, making discs unrestricted and region-free. In addition to removing digital restrictions, AnyDVD will also defeat Macrovision analog copy prevention. Analog prevention distorts the video signal to prevent high quality copying from the output. AnyDVD is also able to remove copy-prevention from audio CDs.
 W
WDVD-Audio is a digital format for delivering high-fidelity audio content on a DVD. DVD-Audio uses most of the storage on the disc for high-quality audio and is not intended to be a video delivery format.
 W
WIn computing, the burst cutting area (BCA) or narrow burst cutting area (NBCA) refers to the circular area near the center of a DVD, HD DVD or Blu-ray Disc, where a barcode can be written for additional information such as ID codes, manufacturing information, and serial numbers. The BCA can be written during mastering and will be common for all discs from that master or, more usually, will be written using a YAG laser to "cut" the barcode into the aluminum reflective layer of the finished disc, potentially adding a unique barcode to each manufactured disc.
 W
WA compressed audio optical disc, MP3 CD, or MP3 CD-ROM or MP3 DVD is an optical disc that contains digital audio in the MP3 file format. Discs are written in the "Yellow Book" standard data format, as opposed to the Red Book standard audio format.
 W
WDualDisc was a type of double-sided optical disc product developed by a group of record companies including MJJ Productions Inc., EMI Music, Universal Music Group, Sony BMG Music Entertainment, Warner Music Group, and 5.1 Entertainment Group and later under the aegis of the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). It featured an audio layer intended to be compatible with CD players on one side and a standard DVD layer on the other. In this respect it was similar to, but distinct from, the DVDplus developed in Europe by Dieter Dierks and covered by European patents.
 W
WDVD-Video is a consumer video format used to store digital video on DVD discs. DVD-Video was the dominant consumer home video format in Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia in the 2000s until it was supplanted by the high-definition Blu-ray Disc. Discs using the DVD-Video specification require a DVD drive and an MPEG-2 decoder. Commercial DVD movies are encoded using a combination MPEG-2 compressed video and audio of varying formats. Typically, the data rate for DVD movies ranges from 3 Mbit/s to 9.5 Mbit/s, and the bit rate is usually adaptive. DVD-Video was first available in Japan on November 1, 1996, followed by a release on March 24, 1997 in the United States—to line up with the 69th Academy Awards that same day.
 W
WDVD authoring is the process of creating a DVD video capable of playing on a DVD player. DVD authoring software must conform to the specifications set by the DVD Forum.
 W
WA DVD card, also called Business Card DVD, is a DVD with the size and shape of a business card. Much like a traditional DVD, is an optical based media whose primary function is DVD-video playback and data storage. In recent years, the DVD card format has been used in the retail market to distribute sports and entertainment titles. However, leveraging its affinity with business, loyalty and payment cards, the DVD Card has also been used for promotional and marketing purposes.
 W
WDVD+R DL also called DVD+R9, is a derivative of the DVD+R format created by the DVD+RW Alliance. Its use was first demonstrated in October 2003. DVD+R DL discs employ two recordable dye layers, each capable of storing nearly the 4.7 GB capacity of a single-layer disc, almost doubling the total disc capacity to 8.5 GB. Discs can be read in many DVD devices and can only be created using DVD+R DL and Super Multi drives. DL drives started appearing on the market during mid-2004, at prices comparable to those of existing single-layer drives. As of March 2011 DL media is up to twice as expensive as single-layer media. The latest DL drives write double layer discs at a slower rate than current single-layer discs.
 W
WDVD-Ds, also referred to as disposable DVDs, are a type of digital versatile disc/digital video disc that is designed to be used for a maximum 48 hours after the containing package is opened. After this time, the DVDs become unreadable to DVD players because they contain a chemical that, after the set period of time, will prevent the underlying data from being read by DVD drives. The medium in itself is copy protection neutral and does not require additional Digital Rights Management types of applications to be installed for the content to be accessible. The technology used for DVD-Ds is different from that for earlier disposable DVDs. DVD-D has a reservoir in the central area of the disc which contains the chemical agent. When the disc spins for the first time the chemical agent moves and gets in contact with the reflective layer of the disc. After approximately 48 hours, the reflective layer becomes unreadable as the laser cannot reflect on the layer.
 W
WDVD-R DS is also called DVD-10 or DVD-18, it is a sub category of DVD-R. A DVD-R DS has a storage capacity of 8.75 GB (DVD-10) or 15.9 GB (DVD-18).
 W
WDVD-R DL, also called DVD-R9, is a derivative of the DVD-R format standard. DVD-R DL discs hold 8.5 GB by utilizing two recordable dye layers, each capable of storing a little less than the 4.7 gigabyte (GB) of a single layer disc, almost doubling the total disc capacity. Discs can be read in many DVD devices and can only be written using DVD-R DL compatible recorders. It is part of optical disc recording technologies for digital recording to optical disc.
 W
WDVD-RAM is a DVD-based disc specification presented in 1996 by the DVD Forum, which specifies rewritable DVD-RAM media and the appropriate DVD writers. DVD-RAM media have been used in computers as well as camcorders and personal video recorders since 1998.
 W
WDVD+R DS a sub category of DVD+R. It can only be written once.
 W
WAn EcoDisc is a patented type of DVD which is thinner than a conventional DVD because it is made from a single layer of polycarbonate instead of two layers glued together. Because it contains less material, its manufacture produces only around half of the carbon dioxide of a conventional DVD, and the absence of a non-biodegradable toxic glue layer makes it easier to recycle. Ecodiscs are prone to breakage since they are, as of May 2011, much less stiff than regular discs.
 W
WThe Farmiloe Building is a Grade II listed building in Clerkenwell, London, in the London Borough of Islington.
 W
WFlexplay is a trademark for a discontinued DVD-compatible optical video disc format with a time-limited playback. They are often described as "self-destructing", although the disc merely turns black or dark red and does not physically disintegrate. The technology launched in August 2003 as a joint-venture with Disney's Buena Vista Home Entertainment under the name eZ-D. The Flexplay concept was invented by two professors, Yannis Bakos and Erik Brynjolfsson, who founded Flexplay Technologies in 1999. The technology was developed by Flexplay Technologies and General Electric.
 W
WHD DVD is an obsolete high-density optical disc format for storing data and playback of high-definition video. Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format.
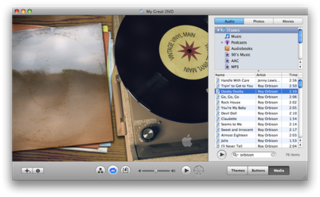 W
WiDVD is a discontinued DVD-creation application for Mac OS X produced by Apple Inc. iDVD allows the user to burn QuickTime movies, MP3 music, and digital photos to a DVD that can then be played on a commercial DVD player. It was often considered the last step of Apple's iLife suite, bringing together the results of all of the other iLife apps onto a removable medium.
 W
WA keep case or poly-box is a type of packaging, most commonly used with DVDs.
 W
WLayer Jump Recording (LJR) is a writing method used for DVD-R DL.
 W
WLightScribe is an optical disc recording technology that was created by the Hewlett-Packard Company. It uses specially coated recordable CD and DVD media to produce laser-etched labels with text or graphics, as opposed to stick-on labels and printable discs. Although HP is no longer developing the technology, it is still maintained and supported by a number of independent enthusiasts.
 W
WThe following applications can be used to create playable DVDs.
 W
WM-DISC is a write-once optical disc technology introduced in 2009 by Millenniata, Inc. and available as DVD and Blu-ray discs.
 W
WMeridian Lossless Packing, also known as Packed PCM (PPCM), is a lossless compression technique for compressing PCM audio data developed by Meridian Audio, Ltd. MLP is the standard lossless compression method for DVD-Audio content and typically provides about 1.5:1 compression on most music material. All DVD-Audio players are equipped with MLP decoding, while its use on the discs themselves is at their producers' discretion.
 W
WMiniDVD is a DVD disc which is 8 centimetres (3.15 in) in diameter. Most MiniDVDs hold 1.4 GB of data, but there are variants that hold up to 5.2 GB. The MiniDVD is also known as a "3 inch DVD", referring to its approximate diameter in inches.
 W
WNintendo optical discs are physical media used to distribute video games on three of Nintendo's consoles that followed the Nintendo 64. These are the GameCube Game Disc, Wii Optical Disc, and Wii U Optical Disc. The physical size of a GameCube Game Disc is that of a miniDVD; the Wii and Wii U Optical Discs are the size of a DVD, a CD, and a Blu-ray. To maintain backward compatibility between generations of game consoles, GameCube discs are compatible with the first model of the Wii, and Wii Optical Discs are compatible with the Wii U. A burst cutting area is located at the inner ring of the disc surface.
 W
WNuon is a technology developed by VM Labs that adds features to a DVD player. In addition to viewing DVDs, one can play 3D video games and use enhanced DVD navigational tools such as zoom and smooth scanning of DVD playback. One could also play CDs while the Nuon graphics processor generates synchronized graphics on the screen. There were plans to provide Internet access capability in the next generation of Nuon-equipped DVD players.
 W
WIn computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc (OD) is a flat, usually circular disc that encodes binary data (bits) in the form of pits and lands on a special material on one of its flat surfaces.
 W
WA DVD player is a device that plays DVDs produced under both the DVD-Video and DVD-Audio technical standards, two different and incompatible standards. Some DVD players will also play audio CDs. DVD players are connected to a television to watch the DVD content, which could be a movie, a recorded TV show, or other content.
 W
WA portable DVD player is a mobile, battery powered DVD player in the format of a mobile device. Many recent players play files from USB flash drives and SD cards.
 W
WDVD recordable and DVD rewritable are optical disc recording technologies. Both terms describe DVD optical discs that can be written to by a DVD recorder, whereas only 'rewritable' discs are able to erase and rewrite data. Data is written ('burned') to the disc by a laser, rather than the data being 'pressed' onto the disc during manufacture, like a DVD-ROM. Pressing is used in mass production, primarily for the distribution of home video.
 W
WDVD region codes are a digital rights management technique designed to allow rights holders to control the international distribution of a DVD release, including its content, release date, and price, all according to the appropriate region. This is achieved by way of region-locked DVD players, which will play back only DVDs encoded to their region. The American DVD Copy Control Association also requires that DVD player manufacturers incorporate the regional-playback control (RPC) system. However, region-free DVD players, which ignore region coding, are also commercially available, and many DVD players can be modified to be region-free, allowing playback of all discs. DVDs may use one code, multiple codes (multi-region), or all codes.
 W
WA snap case is a type of optical disc packaging, used for DVDs and CDs, also known as a paperback case, Ivy Hill Snapper, "snapper case", or FLP case.
 W
WThe Stacked Volumetric Optical Disc is an optical disc format developed by Hitachi/Maxell, which uses an array of wafer-thin optical discs to allow data storage.
 W
WSuper Audio CD (SACD) is a read-only optical disc format for audio storage, introduced in 1999. It was developed jointly by Sony and Philips Electronics, and intended to be the successor to the Compact Disc (CD) format.
 W
WApple's SuperDrive is a CD/DVD reader/writer, introduced in 2001. It was previously a high-density floppy disk drive from 1988 to 1999, capable of reading all major 3.5″ disk formats.
 W
WTVShowsOnDVD.com was a website dedicated to cataloging, campaigning for, and reporting news about Region 1 television series releases on DVD and region A Blu-ray. The site's slogan asked "Is YOUR Favorite Show On DVD?"
 W
WVCDHD is an optical disc standard, similar to CD or DVD. The technology for VCDHD was invented with in: Japan, the Netherlands and Poland. Since the name of the technology is similar to the arbitrarily inferior VCD, it's also marketed using the name DVHD.
 W
W