 W
W4D film or 4-D film is a usually hypothetical marketing term for an entertainment presentation system combining a 3D film with physical effects that occur in the theatre in synchronization with the film. Effects simulated in a 4D film may include rain, mist, bubbles, fog or smoke, wind, temperature changes, strobe lights, scent, vibration and motion. Seats in 4D venues may vibrate or move a few centimeters during the presentations. Other common chair effects include air jets, water sprays, and leg and back ticklers. Auditorium effects may include smoke, rain, lightning, bubbles, and smell.
 W
W4DX is a 4D film format developed by CJ 4DPlex, a subsidiary of South Korean cinema chain CJ CGV. It allows films to be augmented with various practical effects, including motion seats, wind, strobe lights, simulated snow, and scents. First introduced commercially in 2009, it presents films in both 3D and traditional 2D formats.
 W
W8 mm film is a motion picture film format in which the film strip is eight millimeters wide. It exists in two main versions – the original standard 8 mm film, also known as regular 8 mm, and Super 8. Although both standard 8 mm and Super 8 are 8 mm wide, Super 8 has a larger image area because of its smaller and more widely spaced perforations.
 W
W9.5 mm film is an amateur film format introduced by Pathé in 1922 as part of the Pathé Baby amateur film system. It was conceived initially as an inexpensive format to provide copies of commercially made films to home users, although a simple camera was released shortly afterwards.
 W
W16 mm film is a historically popular and economical gauge of film. 16 mm refers to the width of the film; other common film gauges include 8 and 35 mm. It is generally used for non-theatrical film-making, or for low-budget motion pictures. It also existed as a popular amateur or home movie-making format for several decades, alongside 8 mm film and later Super 8 film. Eastman Kodak released the first 16 mm "outfit" in 1923, consisting of a camera, projector, tripod, screen and splicer, for $335. RCA-Victor introduced a 16 mm sound movie projector in 1932, and developed an optical sound-on-film 16 mm camera, released in 1935.
 W
W28 mm film was introduced by the Pathé Film Company in 1912 under the name Pathé Kok. Geared toward the home market, 28 mm utilized diacetate film stock rather than the flammable nitrate commonly used in 35 mm. The film gauge was deliberately chosen such that it would be uneconomical to slit 35 mm nitrate film.
 W
W35 mm film is a film gauge used in filmmaking, and the film standard. In motion pictures that record on film, 35 mm is the most commonly used gauge. The name of the gauge is not a direct measurement, and refers to the nominal width of the 35 mm format photographic film, which consists of strips 1.377 ± 0.001 inches (34.976 ± 0.025 mm) wide. The standard image exposure length on 35 mm for movies is four perforations per frame along both edges, which results in 16 frames per foot of film.
 W
W70 mm film is a wide high-resolution film gauge for motion picture photography, with negative area nearly 3.5 times larger than the standard 35 mm motion picture film format. As used in cameras, the film is 65 mm (2.6 in) wide. For projection, the original 65 mm film is printed on 70 mm (2.8 in) film. The additional 5 mm are for four magnetic strips holding six tracks of stereophonic sound. Although later 70 mm prints use digital sound encoding, the vast majority of existing and surviving 70 mm prints predate this technology.
 W
WThe Academy ratio of 1.375:1 is an aspect ratio of a frame of 35 mm film when used with 4-perf pulldown. It was standardized by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences as the standard film aspect ratio in 1932, although similar-sized ratios were used as early as 1928.
 W
WAnamorphic format is the cinematography technique of shooting a widescreen picture on standard 35 mm film or other visual recording media with a non-widescreen native aspect ratio. It also refers to the projection format in which a distorted image is "stretched" by an anamorphic projection lens to recreate the original aspect ratio on the viewing screen. The word anamorphic and its derivatives stem from the Greek anamorphoun, compound of morphé with the prefix aná. In the late 1990s and 2000s, anamorphic lost popularity in comparison to "flat" formats such as Super 35 with the advent of digital intermediates; however in the years since digital cinema cameras and projectors have become commonplace, anamorphic has experienced a considerable resurgence of popularity, due in large part to the higher base ISO sensitivity of digital sensors, which facilitates shooting at smaller apertures.
 W
WThe Chronophone is an apparatus patented by Léon Gaumont in 1902 to synchronise the Cinématographe (Chrono-Bioscope) with a disc Phonograph (Cyclophone) using a "Conductor" or "Switchboard". This sound-on-disc display was used as an experiment from 1902 to 1910. In January 1911, the industrial exploitation started at the Olympia. Chronophone would show Phonoscènes and Filmparlants almost every week from 1911 until 1917 at the Gaumont Palace, "the Greatest Cinema Theatre in the World", previously known as the Paris Hippodrome.
 W
WCinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen movies that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by Spyros P. Skouras, the president of 20th Century Fox, marked the beginning of the modern anamorphic format in both principal 2.66:1, almost twice as wide as the previously common Academy format's 1.37:1 ratio. Although the technology behind the CinemaScope lens system was made obsolete by later developments, primarily advanced by Panavision, CinemaScope's anamorphic format has continued to this day. In film-industry jargon, the shortened form, 'Scope, is still widely used by both filmmakers and projectionists, although today it generally refers to any 2.35:1, 2.39:1, 2.40:1, or 2.55:1 presentation or, sometimes, the use of anamorphic lensing or projection in general. Bausch & Lomb won a 1954 Oscar for its development of the CinemaScope lens.
 W
WCinemiracle was a widescreen cinema format competing with Cinerama developed in the 1950s. It was ultimately unsuccessful, with only a single film produced and released in the format. Like Cinerama it used 3 cameras to capture a 2.59:1 image. Cinemiracle used two mirrors to give the left and right cameras the same optical center as the middle camera. This made the joins between the projected images much less obvious than with Cinerama.
 W
WCinerama is a widescreen process that originally projected images simultaneously from three synchronized 35mm projectors onto a huge, deeply curved screen, subtending 146° of arc. The trademarked process was marketed by the Cinerama corporation. It was the first of a number of novel processes introduced during the 1950s, when the movie industry was reacting to competition from television. Cinerama was presented to the public as a theatrical event, with reserved seating and printed programs, and audience members often dressed in their best attire for the evening.
 W
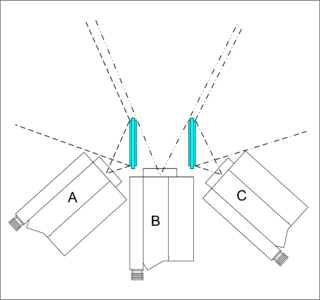
WCircle-Vision 360° is a film technique, refined by The Walt Disney Company, that uses nine cameras for nine big screens arranged in a circle. The cameras are usually mounted on top of an automobile for scenes through cities and highways, while films such as The Timekeeper use a static camera and many CGI effects. The first film was America the Beautiful in the Circarama theater, which had 11 projectors using 16mm film. And would become Circle-Vision in 1967, which has 9 projectors using 35mm film. Both the original 11-lens camera and the subsequent 9-lens camera, as well as their projection systems, were designed by longtime Disney animator and visual effects pioneer, Ub Iwerks.
 W
WDolby 3D is a marketing name for a system from Dolby Laboratories, Inc. to show three-dimensional motion pictures in a digital cinema.
 W
WThe history of film technology traces the development of techniques for the recording, construction and presentation of motion pictures. When the film medium came about in the 19th century, there already was a centuries old tradition of screening moving images through shadow play and the magic lantern that were very popular with audiences in many parts of the world. Especially the magic lantern influenced much of the projection technology, exhibition practices and cultural implementation of film. Between 1825 and 1840, the relevant technologies of stroboscopic animation, photography and stereoscopy were introduced. For much of the rest of the century, many engineers and inventors tried to combine all these new technologies and the much older technique of projection to create a complete illusion or a complete documentation of reality. Colour photography was usually included in these ambitions and the introduction of the phonograph seemed to promise the addition of synchronized sound recordings. Between 1887 to 1894, the first successful short cinematographic presentations were established. The biggest popular breakthrough of the technology came in 1895 with the first projected movies that lasted longer than 10 seconds. Initially, motion pictures lasted about 50 seconds, lacked synchronized sound and natural colour, and were mainly exhibited as novelty attractions. During the 20th century, movies grew much longer and the medium quickly developed into one of the most important tools of communication and entertainment. The breakthrough of synchronized sound occurred at the end of the 1920s and that of full color motion picture film in the 1930s. By the start of the 21st century, physical film stock was being replaced with digital film technologies at both ends of the production chain by digital image sensors and projectors.
 W
WKeller-Dorian cinematography was a French technique from the 1920s for filming movies in color, using a lenticular process to separate red, green and blue colors and record them on a single frame of black-and-white film. Keller-Dorian was primarily a manufacturer of paper and aluminum foil. It was granted 38 patents. While researching how to create dies to color aluminum foil, they accidentally stumbled on this cinematography technique. This additive color system differs from other systems, for example Technicolor, which divided the colors into more than one frame on one or more pieces of film.
 W
WKinemacolor was the first successful colour motion picture process, used commercially from 1908 to 1914. It was invented by George Albert Smith in 1906. He was influenced by the work of William Norman Lascelles Davidson and, more directly, Edward Raymond Turner. It was launched by Charles Urban's Urban Trading Co. of London in 1908. From 1909 on, the process was known and trademarked as Kinemacolor. It was a two-colour additive colour process, photographing and projecting a black-and-white film behind alternating red and green filters.
 W
WMasterImage 3D is a company that develops stereoscopic 3D systems for theaters, and auto-stereoscopic 3D displays for mobile devices.
 W
WThe Movietone sound system is an optical sound-on-film method of recording sound for motion pictures that guarantees synchronization between sound and picture. It achieves this by recording the sound as a variable-density optical track on the same strip of film that records the pictures. The initial version was capable of a frequency response of 8500 Hz. Although sound films today use variable-area tracks, any modern motion picture theater can play a Movietone film without modification to the projector. Movietone was one of four motion picture sound systems under development in the U.S. during the 1920s, the others being DeForest Phonofilm, Warner Brothers' Vitaphone, and RCA Photophone, though Phonofilm was primarily an early version of Movietone.
 W
WMulticolor is a subtractive natural color motion picture process. Multicolor, introduced to the motion picture industry in 1929, was based on the earlier Prizma Color process, and was the forerunner of Cinecolor.
 W
WThe Phonoscène was an antecedent of music video and was regarded by Michel Chion, Noël Burch and Richard Abel as a forerunner of sound film. The first Phonoscènes were presented by Léon Gaumont in 1902 in France. The first official presentation in the United Kingdom took place at Buckingham Palace in 1907. The last phonoscène was presented in 1917.
 W
WThe Prizma Color system was a color motion picture process, invented in 1913 by William Van Doren Kelley and Charles Raleigh. Initially, it was a two-color additive color system, similar to its predecessor, Kinemacolor. However, Kelley eventually transformed Prizma into a bi-pack color system that itself became the predecessor for future color processes such as Multicolor and Cinecolor.
 W
WScreenX is a panoramic film format which presents films with an expanded, dual-sided, 270-degree screens projected on the walls in a theater. First introduced in 2012, it is created by CJ 4DPLEX, a subsidiary of the CJ CGV group which also created the 4DX motion-theater technology, which, in fact, uses a similar logo and combines both formats, known as "4DX Screen". Co-developed by KAIST, it is considered a "sideways" version of IMAX and a presumed competitor to streaming platforms such as Netflix. In addition to films, the ScreenX theater also shows advertisements filmed or converted for the format.
 W
WSingle-8 is a motion picture film format introduced by Fujifilm of Japan in 1965 as an alternative to the Kodak Super 8 format. The company Konan claims in its history page to have developed the Single-8 system in 1959.
 W
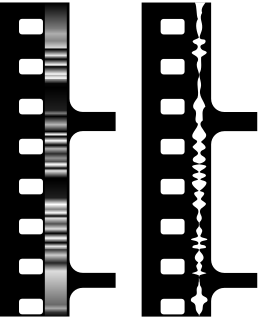
WSound-on-film is a class of sound film processes where the sound accompanying a picture is recorded onto photographic film, usually, but not always, the same strip of film carrying the picture. Sound-on-film processes can either record an analog sound track or digital sound track, and may record the signal either optically or magnetically. Earlier technologies were sound-on-disc, meaning the film's soundtrack would be on a separate phonograph record.
 W
WStandard 8 mm film, also known as Regular 8 mm film, Double 8 mm film, Double Regular 8 mm film, or simply as Standard-8 or Regular-8, is a film format originally developed by the Eastman Kodak company and released onto the market in 1932.
 W
WA Super 8mm camera is a motion picture camera specifically manufactured to use the Super 8mm motion picture format. Super 8mm film cameras were first manufactured in 1965 by Kodak for their newly introduced amateur film format, which replaced the Standard 8 mm film format. Manufacture continued until the rise in popularity of video cameras in the mid 1970s. In 2014 the first new Super 8mm camera in 30 years was introduced by the Danish company Logmar Camera Solutions. Most other cameras readily available are from the 1960s through the 1980s.
 W
WSuper 8mm film is a motion picture film format released in 1965 by Eastman Kodak as an improvement over the older "Double" or "Regular" 8 mm home movie format.
 W
WTechnicolor is a series of color motion picture processes, the first version dating to 1916, and followed by improved versions over several decades.
 W
WTechnirama is a screen process that has been used by some film production houses as an alternative to CinemaScope. It was first used in 1957 but fell into disuse in the mid-1960s. The process was invented by Technicolor and is an anamorphic process with a screen ratio the same as revised CinemaScope (2.35:1), but it's actually 2.25:1 on the negative.
 W
WTechniscope or 2-perf is a 35 mm motion picture camera film format introduced by Technicolor Italia in 1960. The Techniscope format uses a two film-perforation negative pulldown per frame, instead of the standard four-perforation frame usually exposed in 35 mm film photography. Techniscope's 2.33:1 aspect ratio is easily cropped to the 2.39:1 widescreen ratio, because it uses half the amount of 35 mm film stock and standard spherical lenses. Thus, Techniscope release prints are made by anamorphosizing and enlarging each frame by a factor of two.
 W
WTeleview was a system for projecting stereoscopic motion pictures invented by Laurens Hammond, best known as the inventor of the Hammond organ. It made its public debut on 27 December 1922 at the Selwyn Theatre in New York City, the only theater ever equipped with the system. The program included several short films, a live presentation of projected 3D shadows, and the 95-minute feature film M.A.R.S., later re-released in 2D as Radio-Mania.
 W
WTodd-AO is an American post-production company founded in 1953 by Mike Todd and Robert Naify, providing sound-related services to the motion picture and television industries. For more than five decades, it became the worldwide leader in theater sound. The company operates three facilities in the Los Angeles area.
 W
WUltra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were, from 1957 to 1966, the marketing brands that identified motion pictures photographed with Panavision's anamorphic movie camera lenses on 65 mm film. Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were shot at 24 frames per second (fps) using anamorphic camera lenses. Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65's anamorphic lenses compressed the image 1.25 times, yielding an extremely wide aspect ratio of 2.76:1.
 W
WUnivisium is a proposed universal film format created by cinematographer Vittorio Storaro, ASC, AIC and his son, Fabrizio, to unify all future theatrical and television movies into one respective aspect ratio of 2:1. The proposed format also includes new standards for projection to maximize the efficiencies of the Univisium format.
 W
WVistaVision is a higher resolution, widescreen variant of the 35 mm motion picture film format which was created by engineers at Paramount Pictures in 1954.
 W
WVitaphone was a sound film system used for feature films and nearly 1,000 short subjects made by Warner Bros. and its sister studio First National from 1926 to 1931. Vitaphone was the last major analog sound-on-disc system and the only one which was widely used and commercially successful. The soundtrack was not printed on the film itself, but issued separately on phonograph records. The discs, recorded at 33 1⁄3 rpm and typically 16 inches (41 cm) in diameter, would be played on a turntable physically coupled to the projector motor while the film was being projected. It had a frequency response of 4300 Hz. Many early talkies, such as The Jazz Singer (1927), used the Vitaphone system. The name "Vitaphone" derived from the Latin and Greek words, respectively, for "living" and "sound".
 W
WVitasound was an experimental sound system developed by Warner Brothers in 1939. It was intended to provide a wider sound source and greater dynamic range for music and effects than standard soundtracks of the period. But unlike the near-contemporary Fantasound system used for the roadshow release of Walt Disney's 'Fantasia' it was not a stereophonic system.
 W
WXPAND 3D developed active-shutter 3D solutions for multiple purposes. The company was founded by Maria Costeira and Ami Dror in 1995 as X6D Limited. The company deployed over 15,000 cinemas worldwide.