 W
WThe 30 cm Wurfkörper 42 Spreng was an unguided spin-stabilized artillery rocket developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Abwehrflammenwerfer 42 was a German static defensive flamethrower, flame fougasse or flame mine used during the Second World War. The design was copied from Russian FOG-1 mines that were encountered in 1941 during Operation Barbarossa. These were usually buried at intervals of 12 to 30 yards covering road blocks, landing beaches, harbour walls and other obstacles. They were normally mixed in with other mines or emplaced behind barbed wire and could be command detonated or triggered by tripwires or other devices.
 W
WThe B-Stabmine (Behelfs-Stabmine) or Makeshift Stickmine in English was an anti-tank mine that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Blendkörper 1H was a non-lethal smoke grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Blendkörper 2H was a non-lethal smoke grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
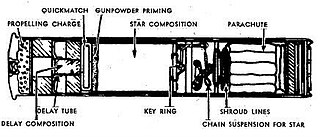
WThe Fallschirm Leuchtpatrone or "parachute light cartridge" in English was a non-lethal star shell that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Fallschirm Leuchtpatrone was designed to be fired from a Kampfpistole flare gun.
 W
WThe German nuclear weapons program was an unsuccessful scientific effort led by Germany to research and develop atomic weapons during World War II. It went through several phases of work, but in the words of a historian, it was ultimately "frozen at the laboratory level" with the "modest goal" to "build a nuclear reactor which could sustain a nuclear fission chain reaction for a significant amount of time and to achieve the complete separation of at least tiny amount of the uranium isotopes." Scholarly consensus is that it failed to achieve these goals.
 W
WThe Gewehr-Granatpatrone 40 or GGP/40 for short was a shaped charge rifle grenade used by German forces during the Second World War. It was originally developed for Luftwaffe Fallschirmjäger units to provide them with a light and portable anti-tank weapon.
 W
WThe Gewehr-Panzergranate was a shaped charge rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Gewehr-Sprenggranate was a high-explosive rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Große Gewehr-Panzergranate was a shaped charge rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Grosse Panzergranate 46 & 61 were shaped charge rifle grenades that were developed by Germany and used by the Waffen-SS during World War II.
 W
WThe Henschel Hs 297 Föhn or 7.3 cm Raketen Sprenggranate was a small German surface-to-air rocket of the Second World War. The associated multiple rocket launcher was known as the 7.3 cm Föhn-Gerät.
 W
WHitlers Bombe is a nonfiction book by the German historian Rainer Karlsch published in March 2005, which claims to have evidence concerning the development and testing of a possible "nuclear weapon" by Nazi Germany in 1945. The "weapon" in question is not alleged to be a standard nuclear weapon powered by nuclear fission, but something closer to either a radiological weapon or a hybrid-nuclear fusion weapon. Its new evidence is concerned primarily with the parts of the German nuclear energy project under Kurt Diebner.
 W
WThe Holzmine 42 was an anti-tank mine that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Kampfpistole or "struggle or combat pistol" in English was a flare gun introduced into German service during 1939 and served throughout World War II.
 W
WThe Leuchtpistole 34 or flare gun in English was introduced into German service before World War II and served throughout World War II.
 W
WThe Leuchtpistole 42 or flare gun in English was introduced into German service in 1943 and served throughout World War II.
 W
WThe Multi-Star Signal Cartridge was a non-lethal signal flare that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Multi-Star Signal Cartridge was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.
 W
WThe Nahverteidigungswaffe was a roof mounted, breech-loaded, single shot, multi-purpose, 360° rotating grenade launcher that could fire a variety of ammunition. It was typically found on German tanks such as the Panzer IV, Panther I, Tiger I, and Tiger II from 1944 until the end of the war and was intended to replace three previous devices: the Nebelwurfgerät, the Minenabwurfvorrichtung, and pistol ports. The Nahverteidigungswaffe was a simple breech-loaded launcher tube oriented at a 50° angle and fitted in a traversable mounting on the turret roof. Unlike the previous externally mounted launchers, it was not exposed to enemy fire, being reloaded from within the vehicle through a hinged breech. The Nahverteidigungswaffe was designed to mate with the standard 26 millimetres (1 in) Kampfpistole and could be sealed by an armored plug when not in use. Aiming was by periscopes located on the turret and cupola. The device could fire the Schnellnebelkerze 39 smoke grenade for the purpose of concealment, the Rauchsichtzeichen Orange 350 smoke signal for identification to friendly aircraft, the Leuchtgeschoss R flare and the Sprenggranatpatrone 326 Lp anti-personnel explosive to defend the vehicle against infantry attack. The Sprenggranatpatrone 326 Lp had a range of 7 to 10 meters with a blast point of 0.5 to 2 meters above the ground. It splintered to a circumferential distance of 100 meters (328 ft) after an initial delay time of one second. All turret hatches and openings were to be closed when this round was fired. The Nahverteidigungswaffe was first mounted in March 1944 on the Panther tank and equipped a variety of late-war vehicles, including the Sturmtiger and the Maus tank.
 W
WThe Nebelpatrone or "fog cartridge" in English was a non-lethal smoke grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Nebelpatrone was designed to be fired from a Kampfpistole flare gun.
 W
WThe Nebelwurfgerät was a turret mounted launcher used to disperse the Schnellnebelkertze 39 smoke grenade. It was typically found on German tanks from 1942 through 1943. The Nebelwurfgerät was mounted in two sets of three, one on each forward side wall of the turret with each launcher being 9 centimetres (3.5 in) in calibre by 15 centimetres (6 in) in length. The uppermost launcher tubes were oriented forward and angled slightly outwards while the middle and lower tubes were set on a progressively lower elevation but increasing angle. Six smoke grenades were carried, one in each launcher tube. They were ejected out of each tube by Zündschraube C 23 primer which was electrically fired from six push-buttons labeled Nebelkerzen, these buttons being grouped in two sets of three, located in the turret to the left and right of the commander's position and forward of his cupola. No spare smoke grenades, primers or launcher tubes were carried. Starting in August 1942, Wegmann prepared turrets for installation by welding mounting brackets to the turret sides and drilling holes for the wiring so that the troops could mount the device by themselves. Complete Nebelwurfgerät were mounted by the assembly plants starting in October 1942. During a reported action in February 1943, enemy small arms fire had inadvertently set off the smoke grenades inside their launcher tubes resulting in the temporary blinding and incapacitation of the tank crew. Because of this hazard, the Nebelwurfgerät was no longer mounted after June 1943 and this device was eventually supplanted by the Nahverteidigungswaffe.
 W
WThe Panzer-Stabmine 43 was a German anti-tank mine, together with the Hohl-Sprung mine 4672 it was the first mine to combine a shaped charge warhead with a tilt-rod fuze. The mine was developed during the Second World War. The mine consisted of a wine glass shaped metal main body mounted on a wooden post, with a tilt rod holding arm projecting to one side. It used a 125 mm diameter warhead with 1.6 kg of explosive, and a combination pressure/tilt fuze.
 W
WPanzerblitz is a German anti-tank unguided aerial rocket developed during the Second World War.
 W
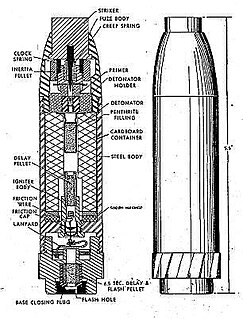
WThe Panzergranate 39 or Pzgr. 39 was a German armor-piercing shell used during World War II. It was manufactured in various calibers and was the most common anti-tank shell used in German tank and anti-tank guns of 37 to 88 mm caliber.
 W
WThe Panzerwurfkörper 42 was a HEAT grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Panzerwurfkörper 42 was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.
 W
WThe Pappmine or Cardboard Mine in English was an anti-tank mine that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Propaganda-Gewehrgranate was a non-lethal rifle grenade designed to deliver propaganda leaflets that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Riegel mine 43 or is a German steel cased anti-tank bar mine used during the Second World War. The mine is a long thin rectangle. It consists of a lower and upper metal tray, and an internal metal-cased explosive block. It uses two ZZ42 fuzes inserted into either end of the internal block, although it can be used with an additional pressure fuze on the top. The mine is similar to the Italian B-2 mine. A variant, the Riegel mine 44 was also produced with a different fuze. Approximately 3,051,400 were produced between 1943 and 1945.
 W
WThe Schü-mine 42, also known as the Schützenmine 42, was a German anti-personnel mine used during the Second World War. It consisted of a simple wooden box with a hinged lid containing a 200-gram (7.1 oz) block of cast TNT and a ZZ-42 type detonator. A slot in the lid pressed down on the striker retaining pin, sufficient pressure on the lid caused the pin to move, releasing the striker which triggered the detonator.
 W
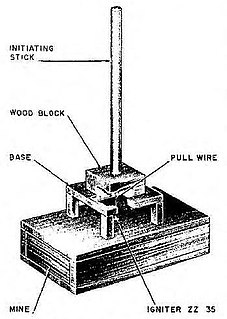
WThe stock mine was a German anti-personnel stake mine used during the Second World War. It consisted of a cylindrical concrete main body on top of a short wooden stake. The concrete head contained a small TNT bursting charge, and was embedded with a number of metal fragments. A fuze is fitted to a central fuze well on the top of the mine. It could be used with a range of fuzes including the ZZ 35, ZZ 42 and ZU ZZ 35 that would trigger on either a tripwire pull or release.
 W
WThe Shaving Stick Grenade was an offensive grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Sprengpatrone or "explosive cartridge" in English was a rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Sprengpatrone was designed to be fired from a Kampfpistole flare gun.
 W
WThe Stielgranate 41 was a German shaped charge, fin-stabilized shell, used with the 3.7 cm Pak 36 anti-tank gun to give it better anti-tank performance.
 W
WThe Stielgranate 42 was a German fin-stabilized demolition charge, used with the 15 cm SIG 33 heavy infantry gun and armored vehicles armed with the SIG 33 during World War II. The primary purpose of the Stielgranate 42 was the demolition of concrete fortifications and for the clearing of minefields and barbed wire. Unlike the Stielgranate 41 it was not a shaped charge anti-tank weapon. In an emergency, the Stielgranate 42 could be used in an anti-tank role to great effect but due to its short range and poor accuracy the gun crew would be dangerously exposed to enemy fire.
 W
WThe Tellermine 29 is a round, metal-cased German anti-tank blast landmine. It first entered service in 1929, and the initial German defence plan was to purchase 6,000 a year, but in January 1931 it was decided to speed up the purchase process, and 61,418 were ordered. By 1937, with the introduction of the Tellermine 35, it was being used for training, and the majority were sent to warehouses.
 W
WThe Topfmines were a series of German circular minimum metal anti-tank blast mines that entered service with the German army in 1944, during the Second World War.
 W
WThe Werfer-Granate 21 rocket launcher, also known as the BR 21 in official Luftwaffe manuals, was a weapon used by the German Luftwaffe during World War II and was the first on-board rocket placed into service by the Luftwaffe, first introduced in mid 1943. The weapon was developed by Rheinmetall-Borsig under the leadership of Dipl.-Ing. Rudolf Nebel, who had pioneered German use of wing-mounted offensive rocketry in World War I with the Luftstreitkräfte.
 W
WWunderwaffe is German for "Miracle weapon" and was a term assigned during World War II by Nazi Germany's propaganda ministry to some revolutionary "superweapons". Most of these weapons however remained prototypes, which either never reached the combat theater, or if they did, were too late or in too insignificant numbers to have a military effect.
 W
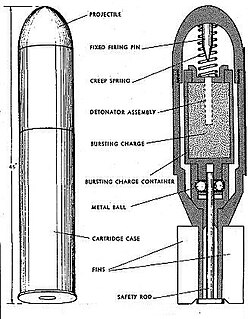
WThe Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was a small grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.
 W
WThe Wurfkörper 361 was a grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Wurfkörper 361 was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.