 W
WAutomatic number-plate recognition is a technology that uses optical character recognition on images to read vehicle registration plates to create vehicle location data. It can use existing closed-circuit television, road-rule enforcement cameras, or cameras specifically designed for the task. ANPR is used by police forces around the world for law enforcement purposes, including to check if a vehicle is registered or licensed. It is also used for electronic toll collection on pay-per-use roads and as a method of cataloguing the movements of traffic, for example by highways agencies.
 W
WA biometric passport is a traditional passport that has an embedded electronic microprocessor chip which contains biometric information that can be used to authenticate the identity of the passport holder. It uses contactless smart card technology, including a microprocessor chip and antenna embedded in the front or back cover, or centre page, of the passport. The passport's critical information is printed on the data page of the passport, repeated on the machine readable lines and stored in the chip. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to authenticate the data stored electronically in the passport chip, making it expensive and difficult to forge when all security mechanisms are fully and correctly implemented.
 W
WA copy detection pattern (CDP), secure graphic or graphical code is a small random or pseudo-random digital image which is printed on documents, labels or products for counterfeit detection. Authentication is made by scanning the printed CDP using an image scanner or mobile phone camera.
 W
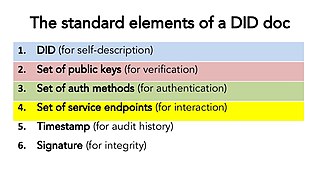
WDecentralized identifiers (DIDs) are a type of identifier that enables a verifiable, decentralized digital identity. They are based on the Self-sovereign identity paradigm. A DID identifies any subject that the controller of the DID decides that it identifies. These identifiers are designed to enable the controller of a DID to prove control over it and to be implemented independently of any centralized registry, identity provider, or certificate authority. DIDs are URLs that associate a DID subject with a DID document allowing trustable interactions associated with that subject. Each DID document can express cryptographic material, verification methods, or service endpoints, which provide a set of mechanisms enabling a DID controller to prove control of the DID. Service endpoints enable trusted interactions associated with the DID subject. A DID document might contain semantics about the subject that it identifies. A DID document might contain the DID subject itself.
 W
WA digital watermark is a kind of marker covertly embedded in a noise-tolerant signal such as audio, video or image data. It is typically used to identify ownership of the copyright of such signal. "Watermarking" is the process of hiding digital information in a carrier signal; the hidden information should, but does not need to, contain a relation to the carrier signal. Digital watermarks may be used to verify the authenticity or integrity of the carrier signal or to show the identity of its owners. It is prominently used for tracing copyright infringements and for banknote authentication.
 W
WeIDAS is an EU regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Single Market. It was established in EU Regulation 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and repeals directive 1999/93/EC from 13 December 1999.
 W
WThe European identity card is an electronic identity document intended to replace and standardise the various identity card styles currently in use in the member states of the European Union and the European Economic Area. It was created by Regulation (EU) 2019/1157 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2019 on strengthening the security of identity cards of Union citizens and of residence documents issued to Union citizens and their family members exercising their right of free movement, which is scheduled to enter into force on 2 August 2021.
 W
WSince the 1980s, member states of the European Union have started to harmonise aspects of the designs of their ordinary passports, as well as common security features and biometrics.
 W
WExpertization is the process of authentication of an object, usually of a sort that is collected, by an individual authority or a committee of authorities. The expert, or expert committee, examines the collectible and issues a certificate typically including:A statement of: Whether or not the item is authentic Identification of any damage to the item Identification of any repairs to the item Identification of any forgery or faked parts of the item A photo of the item
 W
WFace ID is a facial recognition system designed and developed by Apple Inc. for the iPhone and iPad Pro. A successor to Touch ID, the system allows biometric authentication for unlocking a device, making payments, and accessing sensitive data, as well as providing detailed facial expression tracking for Animoji and other features. Initially released in November 2017 with the iPhone X, it has since been updated and introduced to most new iPhone models, and all iPad Pro models.
 W
WThe FIDO Alliance is an open industry association launched in February 2013 whose mission is to develop and promote authentication standards that help reduce the world’s over-reliance on passwords. FIDO addresses the lack of interoperability among strong authentication devices and reduces the problems users face creating and remembering multiple usernames and passwords.
 W
WA fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers.
 W
WFreeOTP is a free and open-source software token that can be used for two-factor authentication. It provides implementations of HOTP and TOTP. Tokens can be added by scanning a QR code or by manually entering in the token configuration. It is maintained by Red Hat under the Apache 2.0 license, and supports Android and iOS.
 W
WA great seal is a seal used by a head of state, or someone authorised to do so on their behalf, to confirm formal documents, such as laws, treaties, appointments and letters of dispatch. It was and is used as a guarantee of the authenticity of the most important and solemn records and documents.
 W
WA guksae or oksae (국새,옥새) is an official seal made for used in lieu of signatures in personal documents, office paperwork, contracts, art, or any item requiring acknowledgment or authorship in South Korea. Guksae is carved with characters called injang. With the establishment of the South Korean state in 1948, its government created a new state seal, or guksae. It is used in promulgation of constitution, designation of cabinet members and ambassadors, conference of national orders and important diplomatic documents.
 W
WHandwritten biometric recognition is the process of identifying the author of a given text from the handwriting style. Handwritten biometric recognition belongs to behavioural biometric systems because it is based on something that the user has learned to do.
 W
WIdentification, friend or foe (IFF) is a radar-based identification system designed for command and control. It uses a transponder that listens for an interrogation signal and then sends a response that identifies the broadcaster. It enables military and civilian air traffic control interrogation systems to identify aircraft, vehicles or forces as friendly and to determine their bearing and range from the interrogator. IFF may be used by both military and civilian aircraft. IFF was first developed during World War II, with the arrival of radar, and several friendly fire incidents.
 W
WThe security features governing the security of an identity can be divided into three levels of security, i.e. Level 1 Security (L1S) (Overt), Level 2 Security (L2S) (Covert) and Level 3 Security (L3S) (Forensic). The three levels of security, in combination, provide comprehensive security coverage for identities and related documents to ensure their validity and authenticity. These are typically used to protect identity information on crucial documents such as identity cards, driving licenses and passports to ensure originality and accuracy of the identities they represent. The diagram below illustrates the different levels of security and how they ensure complete security coverage of an identity.
 W
WA kaō or huāyā is a stylized signature or a mark used in East Asia in place of a true signature.
 W
WIn computer security, logging in is the process by which an individual gains access to a computer system by identifying and authenticating themselves. The user credentials are typically some form of "username" and a matching "password", and these credentials themselves are sometimes referred to as a login. In practice, modern secure systems often require a second factor such as email or SMS confirmation for extra security.
 W
WManu propria, abbreviated to m.p. or mppria is a phrase sometimes used at the end of typewritten or printed documents when there is no handwritten signature. It is typically found just after the name(s) of the person(s) who would have signed the document if it had not been printed or typewritten.
 W
WMicroprinting is the production of recognizable patterns or characters in a printed medium at a scale that requires magnification to read with the naked eye. To the unaided eye, the text may appear as a solid line. Attempts to reproduce by methods of photocopy, image scanning, or pantograph typically translate as a dotted or solid line, unless the reproduction method can identify and recreate patterns to such scale. Microprint is predominantly used as an anti-counterfeiting technique, due to its inability to be easily reproduced by widespread digital methods.
 W
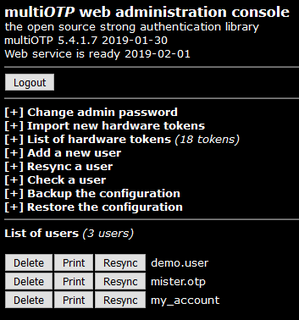
WmultiOTP is an open source PHP class, a command line tool and a web interface that can be used to provide an operating system independent strong authentication system. multiOTP is OATH certified since version 4.1.0 and is developed under the LGPL license. Starting with version 4.3.2.5, multiOTP open source is also available as a virtual appliance - as a standard OVA file, a customized OVA file with open-vm-tools, and also as an Hyper-V downloadable file.
 W
WNational identity cards are issued to their citizens by the governments of all European Economic Area (EEA) member states except Denmark, Iceland, Ireland and the United Kingdom. The various identity card styles currently in use are intended to be standardized and replaced by the European identity card from 2 August 2021.
 W
WThe Norwegian identity card, commonly referred to as the national identity card in Norway, is a non-compulsory biometric identity document issued since 30 November 2020. It is one of two official identity documents issued by the Norwegian Police Service, the other being the Norwegian passport. It is only issued to Norwegian citizens, and may indicate citizenship so that it can be used as a travel document facilitating freedom of movement in the European Economic Area, Switzerland and the UK. For travel within the Nordic countries no identity documentation is legally required for Nordic citizens due to the Nordic Passport Union.
 W
WPARAFE is a passport verification program operated by France's Direction centrale de la police aux frontières. PARAFE, incorporating automated self-service barriers operated by DCPAF, is located at immigration checkpoints in the arrival and departure halls at the Paris, Marseille, Nice and Lyon airports and at London St. Pancras train station, offering an alternative to using desks staffed by immigration officers. The gates use facial recognition technology to verify the user's identity against the data stored in the chip in their biometric passport.
 W
WPassports of the EFTA member states are passports issued by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. EFTA is in this article used as a common name for these countries.
 W
WprivacyIDEA is a Two Factor Authentication System which is multi-tenency- and multi-instance-capable. It is opensource, written in Python and hosted at GitHub.
 W
WPASS is a government-backed scheme in the UK that gives young people a valid and accepted form of proof of age identification. The scheme is supported by the Home Office, the Chartered Trading Standards Institute (CTSI) and the National Police Chiefs’ Council (NPCC). It acts as an umbrella system: it does not itself issue identification cards, but various proof of age card schemes operate under the PASS umbrella, and issue cards which bear a PASS hologram as proof of authenticity and validity.
 W
WA qualified website authentication certificate is a qualified digital certificate under the trust services defined in the eIDAS Regulation.
 W
WA seal, in an East and Southeast Asian context, is a general name for printing stamps and impressions thereof which are used in lieu of signatures in personal documents, office paperwork, contracts, art, or any item requiring acknowledgement or authorship. In the western world they were traditionally known by traders as chop marks or simply chops. The process started in China and soon spread across East Asia. China, Japan and Korea currently use a mixture of seals and hand signatures, and, increasingly, electronic signatures.
 W
WA seal is a device for making an impression in wax, clay, paper, or some other medium, including an embossment on paper, and is also the impression thus made. The original purpose was to authenticate a document, a wrapper for one such as a modern envelope, or the cover of a container or package holding valuables or other objects.
 W
WSealing wax is a wax material of a seal which, after melting, hardens quickly forming a bond that is difficult to separate without noticeable tampering. Wax is used to verify something such as a document is unopened, to verify the sender's identity, for example with a signet ring, and as decoration. Sealing wax can be used to take impressions of other seals. Wax was used to seal letters close and later, from about the 16th century, envelopes. Before sealing wax, the Romans used bitumen for this purpose.
 W
WSecurity holograms are labels with a hologram printed onto it for sale security reasons. Holograms on security labels are very difficult to forge because they are replicated from a master hologram which requires expensive, specialized and technologically advanced equipment. They are used widely in several banknotes around the world, in particular those that are of high denominations. They are also used in passports, credit and bank cards as well as quality products. Herman Lopata, the President of the New York-based Automatic Toll Systems, Inc., received a patent in 1987 for the credit card security hologram as part of his early work on high speed highway toll collection—the predecessor of the modern EZ Pass type equipment.
 W
WSecurity printing is the field of the printing industry that deals with the printing of items such as banknotes, cheques, passports, tamper-evident labels, security tapes, product authentication, stock certificates, postage stamps and identity cards. The main goal of security printing is to prevent forgery, tampering, or counterfeiting. More recently many of the techniques used to protect these high-value documents have become more available to commercial printers, whether they are using the more traditional offset and flexographic presses or the newer digital platforms. Businesses are protecting their lesser-value documents such as transcripts, coupons and prescription pads by incorporating some of the features listed below to ensure that they cannot be forged or that alteration of the data cannot occur undetected.
 W
WSecurity tape is a type of adhesive tape used to help reduce shipping losses due to pilfering and reduce tampering or product adulteration. Often it is a pressure sensitive tape or label with special tamper resistant or tamper evident features. It can be used as a ‘’security seal’’ in addition to a container closure or can be used as a security label. They are sometimes used as or with authentication products and can be an anti-pilferage seal.
 W
WSelf-sovereign identity (SSI) is a concept in the digital movement that only the user should own their identity data fully without intervention from outside administration. With SSI, the individual identity holders can fully create and control their verifiable credentials, without being forced to request permission of an intermediary or centralized authority and gives control over how their personal data is shared and used. The individual has a means of generating and controlling unique identifiers as well as some facility to store identity data.
 W
WA shibboleth is any custom or tradition, usually a choice of phrasing or even a single word, that distinguishes one group of people from another. Shibboleths have been used throughout history in many societies as passwords, simple ways of self-identification, signaling loyalty and affinity, maintaining traditional segregation, or protecting from real or perceived threats.
 W
WA smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card is a physical electronic authorization device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, mobile phones (SIM), public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations.
 W
WSproxil is an American venture capital-backed for-profit company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts that provides a consumer product verification service to help consumers avoid purchasing counterfeit products. The service was the first Mobile Authentication Service (MAS) to launch in Nigeria. The ISO 27001 and ISO 9001 certified company also offers supply chain protection solutions, mobile-based loyalty and marketing programs, and advisory services.
 W
WSQRL or Secure, Quick, Reliable Login is a draft open standard for secure website login and authentication. The software typically uses a link of the scheme sqrl:// or optionally a QR code, where a user identifies via a pseudonymous zero-knowledge proof rather than providing a user ID and password. This method is thought to be impervious to a brute force password attack or data breach. It shifts the burden of security away from the party requesting the authentication and closer to the operating system implementation of what is possible on the hardware, as well as to the user. SQRL was proposed by Steve Gibson of Gibson Research Corporation in October 2013 as a way to simplify the process of authentication without the risk of revelation of information about the transaction to a third party.
 W
WA ticket punch is a hand tool for permanently marking admission tickets and similar items of paper or card stock. It makes a perforation and a corresponding chad. A ticket punch resembles a hole punch, differing in that the ticket punch has a longer jaw and the option of having a distinctive die shape. A ticket punch resembles a needle punch in that it makes a distinctive pattern in the item punched, but differs in that it makes a chad.
 W
WTouch ID is an electronic fingerprint recognition feature, designed and released by Apple Inc., that allows users to unlock devices, make purchases in the various Apple digital media stores, and authenticate Apple Pay online or in apps. It can also be used to lock and unlock password-protected notes on iPhone and iPad. Touch ID was first introduced in iPhones with 2013's iPhone 5S, and has been included on every subsequent iPhone until it was replaced with Face ID on the iPhone X. Following the iPhone X, Apple released the iPhone SE in 2020, which includes Touch ID in a design similar to the iPhone 8. Touch ID has been used on all iPads since the iPad Air 2 was introduced in 2014, until it was discontinued in favor of Face ID for iPad Pro. In 2020, with the removal of the home button on the newest iPad Air, Apple implemented Touch ID into the top sleep/wake button of the iPad Air (2020). It is the first Touch ID sensor on an iOS/iPadOS device that is not embedded within the home button.
 W
WWeb Authentication (WebAuthn) is a web standard published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). WebAuthn is a core component of the FIDO2 Project under the guidance of the FIDO Alliance. The goal of the project is to standardize an interface for authenticating users to web-based applications and services using public-key cryptography.
 W
WThe YubiKey is a hardware authentication device manufactured by Yubico to protect access to computers, networks, and online services that supports one-time passwords, public-key cryptography, and authentication, and the Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) and FIDO2 protocols developed by the FIDO Alliance. It allows users to securely log into their accounts by emitting one-time passwords or using a FIDO-based public/private key pair generated by the device. YubiKey also allows for storing static passwords for use at sites that do not support one-time passwords. Facebook uses YubiKey for employee credentials. Google supports it for both employees and users. Some password managers support YubiKey. Yubico also manufactures the Security Key, a device similar to the YubiKey, but focused on public-key authentication.