 W
WComputer security, cybersecurity or information technology security is the protection of computer systems and networks from the theft of or damage to their hardware, software, or electronic data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the services they provide.
 W
WIn the fields of physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the selective restriction of access to a place or other resource while access management describes the process. The act of accessing may mean consuming, entering, or using. Permission to access a resource is called authorization.
 W
WThe American Innovation and Competitiveness Act ("AICA") is a United States federal law enacted in 2017.
 W
WIdaho National Laboratory ran the Aurora Generator Test in 2007 to demonstrate how a cyberattack could destroy physical components of the electric grid. The experiment used a computer program to rapidly open and close a diesel generator's circuit breakers out of phase from the rest of the grid and cause it to explode. This vulnerability is referred to as the Aurora Vulnerability.
 W
WA biometric device is a security identification and authentication device. Such devices use automated methods of verifying or recognising the identity of a living person based on a physiological or behavioral characteristic. These characteristics include fingerprints, facial images, iris and voice recognition.
 W
WIn computing, a blacklist or a blocklist or a denylist is a basic access control mechanism that allows through all elements, except those explicitly mentioned. Those items on the list are denied access. The opposite is a whitelist which means only items on the list are let through whatever gate is being used. A greylist contains items that are temporarily blocked until an additional step is performed.
 W
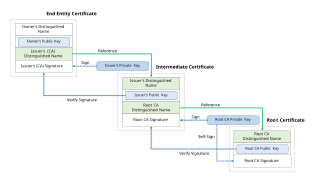
WIn computer security, a chain of trust is established by validating each component of hardware and software from the end entity up to the root certificate. It is intended to ensure that only trusted software and hardware can be used while still retaining flexibility.
 W
WCheckmarx is a global software security company headquartered in Ramat Gan, Israel. Founded in 2006, Checkmarx integrates automated software security technologies into DevOps. Checkmarx provides static and interactive application security testing, software composition analysis (SCA), and application security and training development (Codebashing).
 W
WCommon Criteria Evaluation and Validation Scheme (CCEVS) is a United States Government program administered by the National Information Assurance Partnership (NIAP) to evaluate security functionality of an information technology with conformance to the Common Criteria international standard. The new standard uses Protection Profiles and the Common Criteria Standards to certify the product. This change happened in 2009. Their stated goal in making the change was to ensure achievable, repeatable and testable evaluations.
 W
WThe Computer Law & Security Review is a journal accessible to a wide range of professional legal and IT practitioners, businesses, academics, researchers, libraries and organisations in both the public and private sectors, the Computer Law and Security Review regularly covers:CLSR Briefing with special emphasis on UK/US developments European Union update National news from 10 European jurisdictions Pacific rim news column Refereed practitioner and academic papers on topics such as Web 2.0, IT security, Identity management, ID cards, RFID, interference with privacy, Internet law, telecoms regulation, online broadcasting, intellectual property, software law, e-commerce, outsourcing, data protection and freedom of information and many other topics.
 W
WThe Cyber and Information Domain Service is the youngest branch of Germany's military the Bundeswehr. The decision to form a new military branch was presented by Defense Minister Ursula von der Leyen on 26 April 2016, becoming operational on 5 April 2017. The headquarter of the Cyber and Information Domain Service is Bonn.
 W
WThe Cyber Intelligence Sharing and Protection Act was a proposed law in the United States which would allow for the sharing of Internet traffic information between the U.S. government and technology and manufacturing companies. The stated aim of the bill is to help the U.S. government investigate cyber threats and ensure the security of networks against cyberattacks.
 W
WCyberPatriot is a national youth cyber education program created in the United States to help direct students toward careers in cybersecurity or other science, technology, engineering, and mathematics disciplines. The program was created by the Air Force Association (AFA). It features the annual National Youth Cyber Defense Competition for high school and middle school students. It is similar to its collegiate counterpart, the Collegiate Cyber Defense Competition (CCDC), especially at the CyberPatriot National Finals Competition.
 W
WThe Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act is a United States federal law designed to "improve cybersecurity in the United States through enhanced sharing of information about cybersecurity threats, and for other purposes". The law allows the sharing of Internet traffic information between the U.S. government and technology and manufacturing companies. The bill was introduced in the U.S. Senate on July 10, 2014, and passed in the Senate October 27, 2015. Opponents question CISA's value, believing it will move responsibility from private businesses to the government, thereby increasing vulnerability of personal private information, as well as dispersing personal private information across seven government agencies, including the NSA and local police.
 W
WDomain fronting is a technique for internet censorship circumvention that uses different domain names in different communication layers of an HTTPS connection to discreetly connect to a different target domain than is discernable to third parties monitoring the requests and connections.
 W
WEnCase is the shared technology within a suite of digital investigations products by Guidance Software. The software comes in several products designed for forensic, cyber security, security analytics, and e-discovery use. Encase is traditionally used in forensics to recover evidence from seized hard drives. Encase allows the investigator to conduct in depth analysis of user files to collect evidence such as documents, pictures, internet history and Windows Registry information.
 W
WThe Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 is a United States federal law enacted in 2002 as Title III of the E-Government Act of 2002. The act recognized the importance of information security to the economic and national security interests of the United States. The act requires each federal agency to develop, document, and implement an agency-wide program to provide information security for the information and information systems that support the operations and assets of the agency, including those provided or managed by another agency, contractor, or other source.
 W
WThe Federal Information Security Modernization Act of 2014 was signed into federal law by President Barack Obama on December 18, 2014. Passed as a response to the increasing amount of cyber attacks on the federal government, it amended existing laws to enable the federal government to better respond to cyber attacks on departments and agencies.
 W
WFidelis Cybersecurity is a cybersecurity company focused on threat detection, hunting, and targeted response of advanced threats and data breaches. Among its customers includes IBM, the United States Army and the United States Department of Commerce.
 W
WThe Gordon–Loeb model is a mathematical economic model analyzing the optimal investment level in information security.
 W
Whackers.mu is a group of developers from Mauritius who are focused on computer security, IETF standards and Linux and Open Source Software adoption. They have worked on implementing TLS 1.3 in Linux and Open Source Software during the IETF 100 Hackathon as part of the TLS Working Group. They have also prepared high school students for Google Code-in in 2016 which marked the first time that Mauritius participated. In 2017, they trained another batch of high school students and this would lead to the first Grand Prize Winner for Mauritius. During IETF 101, hackers.mu acted as TLS 1.3 champions, and continued to work on application integration support. In June 2018, hackers.mu organized a hackathon with codename "Operation JASK" to fix sigspoof3 in a number of open source projects. In July 2018, hackers.mu participated in IETF 102 hackathon as TLS 1.3 champions to work on inter-operability and applications support and http 451. Additionally, they have been active in authoring IETF Standards such as RFC 8270.
 W
WIASME Governance is an Information Assurance standard that is designed to be simple and affordable to help improve the cyber security of Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
 W
WAn information security operations center is a facility where enterprise information systems are monitored, assessed, and defended.
 W
WThe INOC-DBA hotline phone system is a global voice telephony network deployed and managed by Packet Clearing House that connects the network operations centers and security incident response teams of critical Internet infrastructure providers such as backbone carriers, Internet service providers, and Internet exchanges as well as critical individuals within the policy, regulatory, Internet governance, security and vendor communities.
 W
WAn insider threat is a malicious threat to an organization that comes from people within the organization, such as employees, former employees, contractors or business associates, who have inside information concerning the organization's security practices, data and computer systems. The threat may involve fraud, the theft of confidential or commercially valuable information, the theft of intellectual property, or the sabotage of computer systems. The insider threat comes in three categories:Malicious insiders, which are people who take advantage of their access to inflict harm on an organization; Negligent insiders, which are people who make errors and disregard policies, which place their organizations at risk; and Infiltrators, who are external actors that obtain legitimate access credentials without authorization.
 W
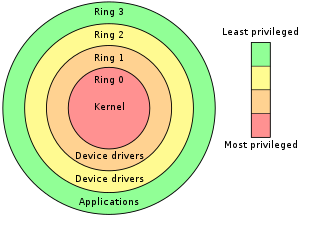
WThe Intel Management Engine (ME), also known as the Intel Manageability Engine, is an autonomous subsystem that has been incorporated in virtually all of Intel's processor chipsets since 2008. It is located in the Platform Controller Hub of modern Intel motherboards.
 W
WIT Risk Management is the application of risk management methods to information technology in order to manage IT risk, i.e.:The business risk associated with the use, ownership, operation, involvement, influence and adoption of IT within an enterprise or organization
 W
WKon-Boot is a software utility that allows users to bypass Microsoft Windows passwords and Apple macOS passwords without lasting or persistent changes to system on which it is executed. It is also the first reported tool capable of bypassing Windows 10 online (live) passwords and supporting both Windows and macOS systems. It is also a widely used tool in computer security, especially in penetration testing. Since version 3.5 Kon-Boot is also able to bypass SecureBoot feature.
 W
WA list of cyber attack threat trends is presented in alphabetical order. These methods were used between the 1990s and 2015.Analysis of vulnerabilities in compiled software without source code Anti-forensic techniques Automated probes and scans Automated widespread attacks Cyber-threats & bullying Distributed attack tools Email propagation of malicious code Executable code attacks Fully undetectable (FUD) GUI intrusion tools Industrial espionage Internet social engineering attacks Network sniffers Packet spoofing Session-hijacking Sophisticated botnet command and control attacks "Stealth" and other advanced scanning techniques Targeting of specific users Widespread attacks on DNS infrastructure Widespread attacks using NNTP to distribute attack Wide-scale trojan distribution Wide-scale use of worms Widespread, distributed denial-of-service attacks Windows-based remote access trojans
 W
WMISP Threat Sharing (MISP) is an open source threat intelligence platform. The project develops utilities and documentation for more effective threat intelligence, by sharing indicators of compromise. There are several organizations who run MISP instances, who are listed on the website.
 W
WNCP Engineering is Nuremberg-based company produces software for remote access, industrial Internet of things security and information security. NCP's products use virtual private network (VPN) and other technologies like encryption, personal firewalls and electronic certificates in a public key infrastructure (PKI) to secure data communication.
 W
WOperations security (OPSEC) is a process that identifies critical information to determine if friendly actions can be observed by enemy intelligence, determines if information obtained by adversaries could be interpreted to be useful to them, and then executes selected measures that eliminate or reduce adversary exploitation of friendly critical information.
 W
WEverykey designs and builds a patented universal smart key that can unlock devices and log into online accounts on those devices. The idea began as an entrepreneurship class project at Case Western Reserve University.
 W
WThe Pwnie Awards recognize both excellence and incompetence in the field of information security. Winners are selected by a committee of security industry professionals from nominations collected from the information security community. The awards are presented yearly at the Black Hat Security Conference.
 W
WRiskIQ is a cyber security company based in San Francisco, California. It provides cloud-based software as a service (SaaS) for organizations to detect phishing, fraud, malware, and other online security threats.
 W
WSecurity awareness is the knowledge and attitude members of an organization possess regarding the protection of the physical, and especially informational, assets of that organization. Many organizations require formal security awareness training for all workers when they join the organization and periodically thereafter, usually annually.
 W
WA smart meter is an electronic device that records information such as consumption of electric energy, voltage levels, current, and power factor. Smart meters communicate the information to the consumer for greater clarity of consumption behavior, and electricity suppliers for system monitoring and customer billing. Smart meters typically record energy near real-time, and report regularly, short intervals throughout the day. Smart meters enable two-way communication between the meter and the central system. Such an advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) differs from automatic meter reading (AMR) in that it enables two-way communication between the meter and the supplier. Communications from the meter to the network may be wireless, or via fixed wired connections such as power line carrier (PLC). Wireless communication options in common use include cellular communications, Wi-Fi, wireless ad hoc networks over Wi-Fi, wireless mesh networks, low power long-range wireless (LoRa), ZigBee, and Wi-SUN.
 W
Wsecurity.txt is a proposed standard for websites' security information that is meant to allow security researchers to easily report security vulnerabilities. The standard prescribes a text file called "security.txt" that is similar to robots.txt but intended to be read by humans wishing to contact a website's owner about security issues. security.txt files have been adopted by Google, GitHub, LinkedIn, and Facebook.
 W
WShamoon, also known as W32.DistTrack, is a modular computer virus that was discovered in 2012, targeting then-recent 32-bit NT kernel versions of Microsoft Windows. The virus was notable due to the destructive nature of the attack and the cost of recovery. Shamoon can spread from an infected machine to other computers on the network. Once a system is infected, the virus continues to compile a list of files from specific locations on the system, upload them to the attacker, and erase them. Finally the virus overwrites the master boot record of the infected computer, making it unusable.
 W
WThe Spanish Cybersecurity Research Conference, is a scientific congress that works as a meeting point where different actors working in the field of cybersecurity research can exchange knowledge and experience with the shared goal of strengthening research in the Cybersecurity field at the national level.
 W
WA thermal attack is an approach that exploits heat traces to uncover the entered credentials. These attacks rely on the phenomenon of heat transfer from one object to another. During authentication, heat transfers from the users' hands to the surface they are interacting with, leaving heat traces behind that can be analyzed using thermal cameras that operate in the far-infrared spectrum. These traces can be recovered and used to reconstruct the passwords. In some cases, the attack can be successful even 30 seconds after the user has authenticated.
 W
WTitan Rain was a series of coordinated attacks on computer systems in the United States since 2003; they were known to have been ongoing for at least three years. The attacks originated in Guangdong, China. The activity is believed to be associated with a state-sponsored advanced persistent threat. It was given the designation Titan Rain by the federal government of the United States.
 W
WAn application for employment is a standard business document that is prepared with questions deemed relevant by employers. It is used to determine the best candidate to fill a specific role within the company. Most companies provide such forms to anyone upon request, at which point it becomes the responsibility of the applicant to complete the form and return it to the employer for consideration. The completed and returned document notifies the company of the applicant's availability and desire to be employed as well as their qualifications and background so that a determination can be made as to the candidate's suitability to the position.
 W
WVirus Bulletin is a magazine about the prevention, detection and removal of malware and spam. It regularly features analyses of the latest virus threats, articles exploring new developments in the fight against viruses, interviews with anti-virus experts, and evaluations of current anti-malware products.
 W
WVPN blocking is a technique used to block the encrypted protocol tunneling communications methods used by virtual private network (VPN) systems. Often used by large organizations such as national governments or corporations, it can act as a tool for computer security or Internet censorship by preventing the use of VPNs to bypass network firewall systems.
 W
W W
W