 W
WAndroid is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device launched in September 2008.
 W
WBlackBerry 10 is a proprietary mobile operating system for the BlackBerry line of smartphones, both developed by BlackBerry Limited. BlackBerry 10 is based on QNX, a Unix-like operating system that was originally developed by QNX Software Systems until the company was acquired by BlackBerry in April 2010.
 W
WChrome OS is a Gentoo Linux–based operating system designed by Google. It is derived from the free software Chromium OS and uses the Google Chrome web browser as its principal user interface.
 W
WChromium OS is a free and open-source operating system designed for running web applications and browsing the World Wide Web. It is the development version of Chrome OS, a Linux distribution made by Google.
 W
WContiki is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things devices. Extant uses for Contiki include systems for street lighting, sound monitoring for smart cities, radiation monitoring, and alarms. It is open-source software released under a BSD license.
 W
WAmazon Fire OS is a mobile operating system based on Android and created by Amazon for its Fire Phone and Fire brand of tablets, Echo, and other content delivery devices like Fire TV. It is forked from the open source Android operating system and includes proprietary software, customized user interface primarily centered on content consumption, and heavy ties to content available from Amazon's own storefronts and services.
 W
WFirefox OS is a discontinued open-source operating system – made for smartphones, tablet computers and smart TVs – designed by Mozilla and external contributors. It is based on the rendering engine of the Firefox web browser, Gecko, and on the Linux kernel. It was first commercially released in 2013.
 W
WFreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular open-source BSD operating system, accounting for more than three-quarters of all installed simply, permissively licensed BSD systems.
 W
WFreeRTOS is a real-time operating system kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 35 microcontroller platforms. It is distributed under the MIT License.
 W
WGeeXboX is a free Linux distribution providing a media center software suite for personal computers. GeeXboX 2.0 and later uses XBMC for media playback and is implemented as Live USB and Live CD options. As such, the system does not need to be permanently installed to a hard drive, as most modern operating systems would. Instead, the computer can be booted with the GeeXboX CD when media playback is desired. It is based on the Debian distribution of Linux.
 W
WGenode is a free and open-source software operating system (OS) framework consisting of a microkernel abstraction layer and a set of user space components. The framework is notable as one of the few open-source operating systems not derived from a proprietary OS, such as Unix. The characteristic design philosophy is that a small trusted computing base is of primary concern in a security-oriented OS.
 W
WInferno is a distributed operating system started at Bell Labs and now developed and maintained by Vita Nuova Holdings as free software. Inferno was based on the experience gained with Plan 9 from Bell Labs, and the further research of Bell Labs into operating systems, languages, on-the-fly compilers, graphics, security, networking and portability. The name of the operating system and many of its associated programs, as well as that of the current company, were inspired by Dante Alighieri's Divine Comedy. In Italian, Inferno means "hell" — of which there are nine circles in Dante's Divine Comedy.
 W
WKaiOS is a mobile operating system based on Linux, developed by KaiOS Technologies Limited, a company based in Kowloon, Hong Kong, for keypad devices with largest shareholder being Chinese multinational electronics conglomerate TCL Corporation. It is forked from B2G OS, an open source community-driven fork of Firefox OS, which was discontinued by Mozilla in 2016.
 W
WKali Linux is a Debian-derived Linux distribution designed for digital forensics and penetration testing. It is maintained and funded by Offensive Security.
 W
WKali NetHunter is a free and open-source mobile penetration testing platform for Android devices, based on Kali Linux. Kali NetHunter is available for un-rooted devices, for rooted devices that have a custom recovery, and for rooted devices with custom recovery for which a NetHunter specific kernel is available (NetHunter). Official images are published by Offensive Security on their download page and are updated every quarter. NetHunter images with custom kernels are published for the most popular supported devices, such as Google Nexus, Samsung Galaxy and OnePlus. Many more models are supported, and images not published by Offensive Security can be generated using NetHunter build scripts. Kali NetHunter is maintained by a community of volunteers, and is funded by Offensive Security.
 W
WLibreELEC is a non-profit fork of OpenELEC as an open source software appliance, a just enough Linux distribution for Kodi. This fork of OpenELEC announced in March 2016 as a split from the OpenELEC team after "creative differences", taking most of its active developers at the time to join the new LibreELEC project. This is a conservative fork of the OpenELEC project with a stronger focus on pre-release testing and post-release change management.
 W
WLuneOS is a mobile operating system (OS) based on the Linux kernel and currently developed by WebOS Ports community. With a user interface based on direct manipulation, LuneOS is designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. The OS uses touch inputs that loosely correspond to real-world actions, like swiping, tapping, pinching, and reverse pinching to manipulate on-screen objects, and a virtual keyboard.
 W
WMaemo is a software platform originally developed by Nokia, now developed by the community, for smartphones and Internet tablets. The platform comprises both the Maemo operating system and SDK.
 W
WMeeGo is a discontinued Linux distribution hosted by the Linux Foundation, using source code from the operating systems Moblin and Maemo. Primarily targeted at mobile devices and information appliances in the consumer electronics market, MeeGo was designed to act as an operating system for hardware platforms such as netbooks, entry-level desktops, nettops, tablet computers, mobile computing and communications devices, in-vehicle infotainment devices, SmartTV / ConnectedTV, IPTV-boxes, smart phones, and other embedded systems.
 W
WMer was a free and open-source software distribution, targeted at hardware vendors to serve as a middleware for Linux kernel-based mobile-oriented operating systems. It is a fork of MeeGo.
 W
WMinix is a POSIX-compliant, Unix-like operating system based on a microkernel architecture.
 W
WNetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was forked. It continues to be actively developed and is available for many platforms, including servers, desktops, handheld devices, and embedded systems.
 W
WNewton OS is a discontinued operating system for the Apple Newton PDAs produced by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1993–1997. It was written entirely in C++ and trimmed to be low power consuming and use the available memory efficiently. Many applications were pre-installed in the ROM of the Newton and to save on RAM and flash memory storage for user applications.
 W
WThe Nokia Asha platform is a mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for low-end borderline smartphones, based on software from Smarterphone which was acquired by Nokia. The platform inherits UI similarities mostly from MeeGo "Harmattan", and replaces Series 40 on Nokia's low-end devices. The user interface design team was headed by Peter Skillman, who had worked previously on webOS and the design of MeeGo for the Nokia N9.
 W
WOpenComRTOS is a commercial network-centric, formally developed real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market.
 W
WPalm OS is a discontinued mobile operating system initially developed by Palm, Inc., for personal digital assistants (PDAs) in 1996. Palm OS was designed for ease of use with a touchscreen-based graphical user interface. It is provided with a suite of basic applications for personal information management. Later versions of the OS have been extended to support smartphones. Several other licensees have manufactured devices powered by Palm OS.
 W
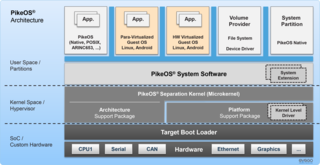
WPikeOS is a commercial, hard real-time operating system (RTOS) that offers a separation kernel based hypervisor with multiple logical partition types for many other operating systems and applications. It enables users to build certifiable smart devices for the Internet of things according to the high quality, safety and security standards of different industries.
 W
WPlan 9 from Bell Labs is a distributed operating system, originating in the Computing Science Research Center (CSRC) at Bell Labs in the mid-1980s, and building on UNIX concepts first developed there in the late 1960s. The final official release was in early 2015.
 W
WPureOS is a Linux distribution focusing on privacy and security, using the GNOME desktop environment. It is maintained by Purism for use in the company's Librem laptop computers as well as the Librem 5 smartphone.
 W
WQNX is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market. QNX was one of the first commercially successful microkernel operating systems. As of 2020, it is used in a variety of devices including cars and mobile phones.
 W
WRaspberry Pi OS is a Debian-based operating system for Raspberry Pi. Since 2015 it has been officially provided by the Raspberry Pi Foundation as the primary operating system for the Raspberry Pi family of compact single-board computers. The original Raspbian OS was created by Mike Thompson and Peter Green as an independent project. The initial build was completed in June 2012.
 W
WRIOT is a small operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It is open-source software, released under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
 W
WRISC iX is a discontinued Unix operating system designed to run on a series of workstations based on the Acorn Archimedes microcomputer. Heavily based on 4.3BSD, it was initially completed in 1988 – a year after Arthur but prior to RISC OS. It was introduced in the ARM2-based R140 workstation in 1989, followed up by the ARM3-based R200-series workstations in 1990.
 W
WRISC OS is a computer operating system originally designed by Acorn Computers Ltd in Cambridge, England. First released in 1987, it was designed to run on the ARM chipset, which Acorn had designed concurrently for use in its new line of Archimedes personal computers. RISC OS takes its name from the reduced instruction set computer (RISC) architecture it supports.
 W
WRodos is a real-time operating system for embedded systems and was designed for application domains demanding high dependability.
 W
WReal-Time Executive for Multiprocessor Systems (RTEMS), formerly Real-Time Executive for Missile Systems, and then Real-Time Executive for Military Systems, is a real-time operating system (RTOS) designed for embedded systems. It is free open-source software.
 W
WSailfish OS is a Linux-based operating system based on open source projects such as Mer and including a closed source UI. The project is being developed by the Finnish company Jolla.
 W
WSymbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. Symbian was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for PDAs in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian OS is a descendant of Psion's EPOC, and was released exclusively on ARM processors, although an unreleased x86 port existed. Symbian was used by many major mobile phone brands, like Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, and above all by Nokia. It was also prevalent in Japan by brands including Fujitsu, Sharp and Mitsubishi. As a pioneer that established the smartphone industry, it was the most popular smartphone OS on a worldwide average until the end of 2010—at a time when smartphones were in limited use—when it was overtaken by iOS and Android. It was notably not as popular in North America.
 W
WTizen is a Linux-based mobile operating system backed by the Linux Foundation but developed and used primarily by Samsung Electronics.
 W
WμClinux is a variation of the Linux kernel, previously maintained as a fork, that targets microcontrollers without a memory management unit (MMU). It was integrated into the mainline of development as of 2.5.46; the project continues to develop patches and tools for microcontrollers. The homepage lists Linux kernel releases for 2.0, 2.4 and 2.6.
 W
WVxWorks is a real-time operating system (RTOS) developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a wholly owned subsidiary of TPG Capital, US. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and, in many cases, safety and security certification, for industries, such as aerospace and defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.
 W
WwebOS, also known as LG webOS and previously known as Open webOS, HP webOS and Palm webOS, is a Linux kernel-based multitasking operating system for smart devices such as smart TVs that has also been used as a mobile operating system. Initially developed by Palm, Inc., HP made the platform open source, at which point it became Open webOS.
 W
WWindows 10 is a series of operating systems developed by Microsoft and released as part of its Windows NT family of operating systems. It is the successor to Windows 8.1, released nearly two years earlier, and was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and broadly released for the general public on July 29, 2015. Windows 10 was made available for download via MSDN and Technet, and as a free upgrade for retail copies of Windows 8 via the Windows Store. Windows 10 receives new builds on an ongoing basis, which are available at no additional cost to users, in addition to additional test builds of Windows 10, which are available to Windows Insiders. Devices in enterprise environments can receive these updates at a slower pace, or use long-term support milestones that only receive critical updates, such as security patches, over their ten-year lifespan of extended support.
 W
WWindows 10 Mobile is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Microsoft. First released in 2015, it is a successor to Windows Phone 8.1, but was marketed by Microsoft as being an edition of its PC operating system Windows 10.
 W
WWindows IoT, formerly Windows Embedded, is a family of operating systems from Microsoft designed for use in embedded systems. Microsoft currently has three different subfamilies of operating systems for embedded devices targeting a wide market, ranging from small-footprint, real-time devices to point of sale (POS) devices like kiosks. Windows Embedded operating systems are available to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), who make it available to end users preloaded with their hardware, in addition to volume license customers in some cases.
Windows Mobile is a discontinued family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.
 W
WWindows Phone (WP) is a discontinued family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones as the replacement successor to Windows Mobile and Zune. Windows Phone featured a new user interface derived from Metro design language. Unlike Windows Mobile, it was primarily aimed at the consumer market rather than the enterprise market.
 W
WWindows Phone 8.1 is the third generation of Microsoft's Windows Phone mobile operating system, succeeding Windows Phone 8. Rolled out at Microsoft's Build Conference in San Francisco, California, on April 2, 2014, it was released in final form to Windows Phone developers on April 14, 2014 and reached general availability on August 4, 2014. All Windows Phones running Windows Phone 8 can be upgraded to Windows Phone 8.1, with release dependent on carrier rollout dates.
 W
WZephyr is a small real-time operating system for connected, resource-constrained and embedded devices supporting multiple architectures and released under the Apache License 2.0. Beyond its kernel, Zephyr includes all the components and libraries needed to develop a full application such as device drivers, protocol stacks, file systems, and firmware updates.