 W
WIn computing, an expansion card, also known as an expansion board, adapter card or accessory card, is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot, on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.
 W
WAn adapter in regard to computing can be either a hardware component (device) or software that allows two or more incompatible devices to be linked together for the purpose of transmitting and receiving data. Given an input, an adapter alters it in order to provide a compatible connection between the components of a system. Both software and hardware adapters are used in many different devices such as mobile phones, personal computers, servers and telecommunications networks for a wide range of purposes. Some adapters are built into devices, while the others can be installed on a computer's motherboard or connected as external devices.
 W
WA computer keyboard is a typewriter-style device which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. Replacing early punched cards and paper tape technology, interaction via teleprinter-style keyboards have been the main input method for computers since the 1970s, supplemented by the computer mouse since the 1980s.
 W
WA computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial form. A monitor usually comprises the visual display, circuitry, casing, and power supply. The display device in modern monitors is typically a thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) with LED backlighting having replaced cold-cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL) backlighting. Older monitors used a cathode ray tube (CRT). Monitors are connected to the computer via VGA, Digital Visual Interface (DVI), HDMI, DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) or other proprietary connectors and signals.
 W
WComputer speakers, or multimedia speakers, are speakers sold for use with computers, although usually capable of other audio uses, e.g. for an MP3 player. Most such speakers have an internal amplifier and consequently require a power source, which may be by a mains power supply often via an AC adapter, batteries, or a USB port. The signal input connector is often a 3.5 mm jack plug ; RCA connectors are sometimes used, and a USB port may supply both signal and power. Battery-powered wireless Bluetooth speakers require no connections at all. Most computers have speakers of low power and quality built in; when external speakers are connected they disable the built-in speakers. Altec Lansing claims to have created the computer speaker market in 1990.
 W
WThe Wave Blaster was an add-on MIDI-synthesizer for Creative Sound Blaster 16 and Sound Blaster AWE32 family of PC soundcards. It was a sample-based synthesis General MIDI compliant synthesizer. For General MIDI scores, the Wave Blaster's wavetable-engine produced more realistic instrumental music than the SB16's onboard Yamaha-OPL3.
 W
WCygwin is a POSIX-compatible programming and runtime environment that runs natively on Microsoft Windows. Under Cygwin, source code designed for Unix-like operating systems may be compiled and run natively with minimal modification.
 W
WA dial box is a computer peripheral for direct 3D manipulation e.g. to interactively input the rotation and torsion angles of a model displayed on a computer screen. Dial boxes were common input tools in the first years of interactive 3D graphics and they were available for Silicon Graphics (SGI) or Sun Microsystems and sold with their workstations. Currently they have been replaced by standard computer mouse interaction techniques.
 W
WA digital pen is an input device which captures the handwriting or brush strokes of a user and converts handwritten analog information created using "pen and paper" into digital data, enabling the data to be utilized in various applications. This type of pen is usually used in conjunction with a digital notebook, although the data can also be used for different applications or simply as a graphic.
 W
WDisplay Control Channel (DCC) is an advanced method of implementing an on-screen display (OSD) technology on KVM switches.
 W
WA dongle is a small piece of computer hardware that connects to a port on another device to provide it with additional functionality, or enable a pass-through to such a device that adds functionality.
 W
WA drive bay is a standard-sized area for adding hardware to a computer. Most drive bays are fixed to the inside of a case, but some can be removed.
 W
WIn computer data storage, drive letter assignment is the process of assigning alphabetical identifiers to volumes. Unlike the concept of UNIX mount points, where volumes are named and located arbitrarily in a single hierarchical namespace, drive letter assignment allows multiple highest-level namespaces. Drive letter assignment is thus a process of using letters to name the roots of the "forest" representing the file system; each volume holds an independent "tree".
 W
WDust-Off is a brand of dust cleaner. The product usually contains difluoroethane; although some use tetrafluoroethane and tetrafluoropropene as a propellant. It is used to blow particles and dust from computer, keyboards, photography equipment and electronics, as well as many every day household items including windows, blinds and collectibles. Dust-Off is manufactured by Falcon Safety Products located in Branchburg, NJ.
 W
WDynamic device mapping is a technology for USB KVM switches which is sometimes implemented as an alternative to standard USB keyboard and mouse emulation.
 W
WFax, sometimes called telecopying or telefax, is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material, normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device. The original document is scanned with a fax machine, which processes the contents as a single fixed graphic image, converting it into a bitmap, and then transmitting it through the telephone system in the form of audio-frequency tones. The receiving fax machine interprets the tones and reconstructs the image, printing a paper copy. Early systems used direct conversions of image darkness to audio tone in a continuous or analog manner. Since the 1980s, most machines modulate the transmitted audio frequencies using a digital representation of the page which is compressed to quickly transmit areas which are all-white or all-black.
 W
WFlashPath were a series of devices produced by SmartDisk that allowed a variety of memory cards to be used in a 3.5" Floppy disk drive. The initial version introduced in May 1998 allowed SmartMedia cards to be used with a floppy drive. Later, Memory Stick and Secure Digital/Multi Media Card versions were made as well. FlashPath adapters were sold both branded by SmartDisk, and as OEM devices under other brand names.
 W
WA floppy disk hardware emulator is a device that emulates a floppy disk drive with a solid state or network storage device that is plug compatible with the drive it replaces, similar to how solid-state drives replace mechanical hard disk drives.
 W
WFusion-io, Inc. was a computer hardware and software systems company based in Cottonwood Heights, Utah, that designed and manufactured products using flash memory technology. The Fusion ioMemory was marketed for applications such as databases, virtualization, cloud computing, big data. Their ioDrive product was considered around 2011 to be one of the fastest storage devices on the market.
GameShark is the brand name of a line of video game cheat cartridges and other products for a variety of console video game systems and Windows-based computers. Currently, the brand name is owned by Mad Catz, which marketed GameShark products for the Sony PlayStation, Xbox, and Nintendo game consoles. Players load cheat codes from GameShark discs or cartridges onto the console's internal or external memory, so that when the game is loaded, the selected cheats can be applied.
 W
WThe Sony Glasstron was a family of portable head-mounted displays, first released in 1996 with the model PLM-50. The products included two LCD screens and two earphones for video and audio respectively. These products are no longer manufactured nor supported by Sony.
 W
WGravis UltraSound or GUS is a sound card for the IBM PC compatible system platform, made by Canada-based Advanced Gravis Computer Technology Ltd. It was very popular in the demo scene during the 1990s.
 W
WIn computing, a hardware random number generator (HRNG) or true random number generator (TRNG) is a device that generates random numbers from a physical process, rather than by means of an algorithm. Such devices are often based on microscopic phenomena that generate low-level, statistically random "noise" signals, such as thermal noise, the photoelectric effect, involving a beam splitter, and other quantum phenomena. These stochastic processes are, in theory, completely unpredictable, and the theory's assertions of unpredictability are subject to experimental test. This is in contrast to the paradigm of pseudo-random number generation commonly implemented in computer programs.
 W
WA headset combines a headphone with microphone. Headsets are made with either a single-earpiece (mono) or a double-earpiece. Headsets provide the equivalent functionality of a telephone handset but with handsfree operation. They have many uses including in call centers and other telephone-intensive jobs and for anybody wishing to have both hands free during a telephone conversation.
 W
WHTC RE refers to a series of products made by HTC, including the RE Camera camera device, Vive virtual-reality headset, and the Grip fitness tracker.
 W
WThe HTC Vive is a virtual reality headset developed by HTC and Valve. The headset uses "room scale" tracking technology, allowing the user to move in 3D space and use motion-tracked handheld controllers to interact with the environment.
 W
WIn computing, an input–output memory management unit (IOMMU) is a memory management unit (MMU) that connects a direct-memory-access–capable (DMA-capable) I/O bus to the main memory. Like a traditional MMU, which translates CPU-visible virtual addresses to physical addresses, the IOMMU maps device-visible virtual addresses to physical addresses. Some units also provide memory protection from faulty or malicious devices.
 W
WA joystick is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. A joystick, also known as the control column, is the principal control device in the cockpit of many civilian and military aircraft, either as a centre stick or side-stick. It often has supplementary switches to control various aspects of the aircraft's flight.
 W
WThe Korg PadKontrol was a USB MIDI controller manufactured by Korg. The PadKontrol was released in 2005 as a competitor to the Akai MPD and the M-Audio Triggerfinger. The PadKontrol has sixteen assignable, velocity sensitive pads, with sixteen "scenes" which allow the user to toggle between various pad configurations, and an assignable X-Y pad for drum rolls, flams, or controller input inside a VSTi or a MIDI sequencer.
 W
WA KVM Splitter, also known as a Reverse KVM switch, is a hardware device that allows users to control a single computer from one or more sets of keyboards, video monitors, and mice. With a KVM splitter, users access the connected computer consecutively rather than simultaneously. It differs from a KVM Switch which allows multiple computers to be controlled, usually, by a single keyboard, monitor and mouse.
 W
WA KVM switch is a hardware device that allows a user to control multiple computers from one or more sets of keyboards, video monitors, and mice.
 W
WThe term Legacy Plug and Play, also shortened to Legacy PnP, describes a series of specifications and Microsoft Windows features geared towards operating system configuration of devices and IDs are assigned by UEFI Forum. The standards were primarily aimed at the IBM PC standard bus, later dubbed Industry Standard Architecture (ISA). Related specifications are also defined for the common external or specialist buses commonly attached via ISA at the time of development, including RS-232 and parallel port devices.
 W
WUltraBay is originally IBM's name for the swappable drive bay in the ThinkPad range of laptop computers. When the Thinkpad product line was sold to Lenovo, the concept and the name stayed. Furthermore, it is used in some of Lenovo's own IdeaPad Y Series laptops.
 W
WThis is a list of various Logitech products. Individual products may have their own article.
 W
WMany models of wireless computer mouse use nano receivers. A nano receiver is an extremely small wireless receiver that connects a mouse to a computer. This range of mice is meant mainly for laptops and netbooks, since it takes less space and reduces the risk of damage that could be caused by accidental shocks.
 W
WThe Logitech G29 is a racing wheel made by Logitech. It supports PlayStation 4, PlayStation 3 and PC. The Logitech G920 is its counterpart compatible with Xbox One and PC, with different buttons and logos. It replaced the Logitech G27 in 2015, but retains the internal design and technical specifications.
 W
WThe Microsoft Mouse is a computer mouse released by Microsoft in 1983. It is the first mouse released by the company, and it was bundled with Microsoft Word, Notepad, and an on-screen teaching tutorial for an initial price of $195.
 W
WA MIDI controller is any hardware or software that generates and transmits Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) data to MIDI-enabled devices, typically to trigger sounds and control parameters of an electronic music performance.
 W
WMonome is an Upstate New York-based company, founded by Brian Crabtree and Kelli Cain, that produces sound modules and MIDI controllers. Monome is also the name of their initial product, a grid-based controller that is now sometimes simply referred to as grid.
 W
WA mouse bungee is a device that secures the wire of a computer mouse, preventing the cable from tangling and providing full freedom of movement. It can be made out of plastic, metal, and silicon fabricated tools. In 1994 they were mostly used in offices, but as of 2010 their popularity rose within the gaming industry, and they are mostly marketed to eSports players.
 W
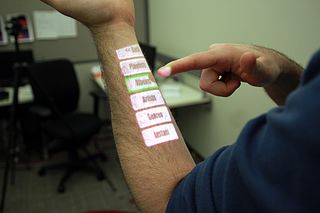
WOmniTouch is a wearable computer, depth-sensing camera and projection system that enables interactive multitouch interfaces on everyday surface. Beyond the shoulder-worn system, there is no instrumentation of the user or the environment. For example, the present shoulder-worn implementation allows users to manipulate interfaces projected onto the environment, held objects, and their own bodies. On such surfaces - without any calibration - OmniTouch provides capabilities similar to that of a touchscreen: X and Y location in 2D interfaces and whether fingers are “clicked” or hovering. This enables a wide variety of applications, similar to what one might find on a modern smartphone. A user study assessing pointing accuracy of the system suggested buttons needed to be 2.3 cm (0.91 in) in diameter to achieve reliable operation on the hand, 1.6 cm (0.63 in) on walls. This is approaching the accuracy of capacitive touchscreens, like those found in smart phones, but on arbitrary surfaces.
 W
WA photocopier is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called xerography, a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as ink jet, but xerography is standard for office copying.
 W
WThe PlayStation VR is a virtual reality headset developed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, which was released in October 2016.
 W
WIn computing, a POST card is a plug-in diagnostic interface card that displays progress and error codes generated during power-on self-test (POST) of a computer. It is used to troubleshoot computers that do not start up.
 W
WThe Psion Wavefinder was a computer peripheral for receiving digital audio broadcasting radio signals, made by Psion. It attached via USB to a personal computer, and had no loudspeakers or controls of its own, with only a flashing light on the device. Psion hoped it would become a design classic.
 W
WA KVM is a computer input/output device offering the combination of a keyboard, video monitor and mouse. They are typically constructed to fit into a 19-inch rack although there are manufacturers who offer a KVM that can be mounted to a flat surface such as a control console.
 W
WA remote graphics unit (RGU) is a device that allows a computer to be separated from some input/output devices such as keyboard, mouse, speakers, and display monitors. The key part being remoted is the graphics sub-system of the computer.
 W
WA remote terminal unit (RTU) is a microprocessor-controlled electronic device that interfaces objects in the physical world to a distributed control system or SCADA system by transmitting telemetry data to a master system, and by using messages from the master supervisory system to control connected objects. Other terms that may be used for RTU are remote telemetry unit and remote telecontrol unit.
 W
WSonder Design is an Australian design studio with its headquarters in Sydney at the Australian Technology Park. They designed the Sonder keyboard, a dynamic E Ink keyboard.
 W
WThe Teletype Model 37 is an electromechanical teleprinter manufactured by the Teletype Corporation in 1968. Unfortunately the end was approaching for electromechanical user interfaces and a year later in 1969 the Computer Terminal Corporation introduced the electronic terminal with a screen.
 W
WA USBphone looks like a traditional telephone, but it has a USB connector instead of an RJ-11. It may be used with most softphones and services like Skype, Sipnet, Sippoint Mini, Net2Phone, MSN Messenger, NetMeeting, Xlite, Skype for Business.
 W
WA virtual reality headset is a head-mounted device that provides virtual reality for the wearer. Virtual reality (VR) headsets are widely used with video games but they are also used in other applications, including simulators and trainers. They comprise a stereoscopic head-mounted display, stereo sound, and head motion tracking sensors. Some VR headsets also have eye tracking sensors and gaming controllers.