 W
WAn abrasive saw, also known as a cut-off saw or chop saw, is a circular saw which is typically used to cut hard materials, such as metals, tile, and concrete. The cutting action is performed by an abrasive disc, similar to a thin grinding wheel. Technically speaking this is not a saw, as it does not use regularly shaped edges (teeth) for cutting.
 W
WAn aerial saw is a saw which is flown through the air. The aerial saw may also be known as a helicopter aerial saw.
 W
WA backsaw is any hand saw which has a stiffening rib on the edge opposite the cutting edge, enabling better control and more precise cutting than with other types of saws. Backsaws are normally used in woodworking for precise work, such as cutting dovetails, mitres, or tenons in cabinetry and joinery. Because of the stiffening rib, backsaws are limited in the depth to which they can cut. Backsaws usually have relatively closely spaced teeth, often with little or no set.
 W
WA bandsaw is a power saw with a long, sharp blade consisting of a continuous band of toothed metal stretched between two or more wheels to cut material. They are used principally in woodworking, metalworking, and lumbering, but may cut a variety of materials. Advantages include uniform cutting action as a result of an evenly distributed tooth load, and the ability to cut irregular or curved shapes like a jigsaw. The minimum radius of a curve is determined by the width of the band and its kerf. Most bandsaws have two wheels rotating in the same plane, one of which is powered, although some may have three or four to distribute the load. The blade itself can come in a variety of sizes and tooth pitches, which enables the machine to be highly versatile and able to cut a wide variety of materials including wood, metal and plastic.
 W
WA modern bow saw is a metal-framed crosscut saw in the shape of a bow with a coarse wide blade. This type of saw is also known as a Swede saw, Finn saw or bucksaw. It is a rough tool that can be used for cross-cutting branches or firewood, up to six inches (150 mm) in diameter. The name 'Swede saw' probably derived from the ovate metal tubular frame version, invented in the 1920s by the Swedish company Sandvikens Jernverk, and additional patents by two Swedish immigrants to the US. Modern versions all share those common features.
 W
WA bucksaw is a hand-powered frame saw similar to bow saw and generally used with a sawbuck to cut logs or firewood to length (bucking). Modern bucksaws usually have a metal frame and a removable blade with coarse teeth held in tension by the frame. Lightweight portable or foldable models used for camping or back-packing are also available. It is often referred to as a bow saw in the North American hardware market, but that term traditionally refers to a different type of saw with a wooden frame.
 W
WA chainsaw is a portable gasoline-, electric-, or battery-powered saw that cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain driven along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pruning, cutting firebreaks in wildland fire suppression, and harvesting of firewood. Chainsaws with specially designed bar-and-chain combinations have been developed as tools for use in chainsaw art and chainsaw mills. These specialized chainsaws are used for cutting concrete during construction developments. Chainsaws are sometimes used for cutting ice, for example, ice sculpture and winter swimming in Finland.
 W
WThis article is about risk control methods specific to chainsaws and chainsaw operations.
 W
WA circular saw is a power-saw using a toothed or abrasive disc or blade to cut different materials using a rotary motion spinning around an arbor. A hole saw and ring saw also use a rotary motion but are different from a circular saw. Circular saws may also be loosely used for the blade itself. Circular saws were invented in the late 18th century and were in common use in sawmills in the United States by the middle of the 19th century.
 W
WA cold saw is a circular saw designed to cut metal which uses a toothed blade to transfer the heat generated by cutting to the chips created by the saw blade, allowing both the blade and material being cut to remain cool. This is in contrast to an abrasive saw, which abrades the metal and generates a great deal of heat absorbed by the material being cut and saw blade.
 W
WA compass saw is a type of saw used for making curved cuts known as compasses, particularly in confined spaces where a larger saw would not fit.
 W
WA concrete saw is a power tool used for cutting concrete, masonry, brick, asphalt, tile, and other solid materials. There are many types ranging from small hand-held saws, chop-saw models, and big walk-behind saws or other styles, and it may be powered by gasoline, hydraulic or pneumatic pressure, or an electric motor. The saw blades used on concrete saws are often diamond saw blades to cut concrete, asphalt, stone, etc. Abrasive cut-off wheels can also be used on cut-off saws to cut stone and steel. The significant friction generated in cutting hard substances like concrete usually requires the blades to be cooled to prolong their life and reduce dust.
 W
WA coping saw is a type of bow saw used to cut intricate external shapes and interior cut-outs in woodworking or carpentry. It is widely used to cut moldings to create coped rather than mitre joints. It is occasionally used to create fretwork though it is not able to match a fretsaw in intricacy of cut, particularly in thin materials. Coping saw blades are always thicker and much coarser cutting than typical fretsaw blades and many others of its family members. Coping saws can however cut slight bends in the work, allowing circles to be cut if used carefully.
 W
WA crosscut saw is any saw designed for cutting wood perpendicular to (across) the wood grain. Crosscut saws may be small or large, with small teeth close together for fine work like woodworking or large for coarse work like log bucking, and can be a hand tool or power tool.
 W
WA dado set or dado blade is a type of circular saw blade, usually used with a table saw or radial arm saw, which is used to cut dadoes or grooves in woodworking. There are two common kinds of dado sets, stacked dado set and wobble blade.
 W
WA diamond blade is a saw blade which has diamonds fixed on its edge for cutting hard or abrasive materials. There are many types of diamond blade, and they have many uses, including cutting stone, concrete, asphalt, bricks, coal balls, glass, and ceramics in the construction industry; cutting semiconductor materials in the IT industry; and cutting gemstones, including diamonds, in the gem industry.
 W
WA dicing saw is a kind of saw which employs a high-speed spindle fitted with an extremely thin diamond blade or diamond wire to dice, cut, or groove semiconductor wafers, silicon, glass, ceramic, crystal, and many other types of material.
 W
WDisston Saw Works of Philadelphia was one of the better known and highly regarded manufacturers of handsaws in the United States. During the Machine Age, as Henry Disston & Sons, Inc., it was a supplier of industrial saw blades. A successor corporation, still active in Philadelphia, is called Disston Precision.
 W
WA dragsaw or Drag saw is a large reciprocating saw using a long steel crosscut saw to buck logs to length. Prior to the popularization of the chainsaw during World War II, the dragsaw was a popular means of taking the hard work out of cutting wood. They would only work for a log on the ground. Dragsaws are known as the first mechanical saws to be used in the timber industry operation. These tools were most useful in the logging business, because they were efficient and very resilient. Not to be confused with Steam donkey.
 W
WA frame saw or sash saw is a type of saw which consists of a relatively narrow and flexible blade held under tension within a rectangular frame. They are used for cutting wood or stone. The blade is held perpendicular to the plane of the frame, so that the material being cut passes through the center of the frame. Frame saws for use with wood are rip saws operated as a hand saw or powered in a sawmill. Frame saws used for cutting stone were powered saws in stone mills.
 W
WThe fretsaw is a bow saw used for intricate cutting work which often incorporates tight curves. Although the coping saw is often used for similar work, the fretsaw is capable of much tighter radii and more delicate work. It has a distinctive appearance due to the depth of its frame, which together with the relatively short five inch blade makes this tool appear somewhat out of proportion compared with most other saws.
 W
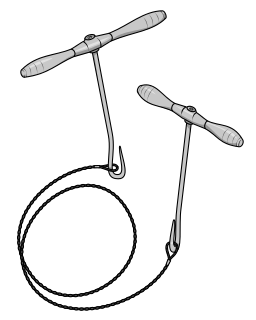
WA Gigli saw is a flexible wire saw used by surgeons for bone cutting. A Gigli saw is used mainly for amputation, where the bones have to be smoothly cut at the level of amputation.
 W
WA hacksaw is a fine-toothed saw, originally and mainly made for cutting metal. The equivalent saw for cutting wood is usually called bow saw.
 W
WIn woodworking and carpentry, hand saws, also known as "panel saws", are used to cut pieces of wood into different shapes. This is usually done in order to join the pieces together and carve a wooden object. They usually operate by having a series of sharp points of some substance that is harder than the wood being cut. The hand saw is a bit like a tenon saw, but with one flat, sharp edge.
 W
WA head saw, framesaw, gang saw or head rig is the saw that makes the initial cuts in a log at a sawmill, turning a log into cants, or planks of wood.
 W
WA hole saw, also known as a hole cutter, is a saw blade of annular (ring) shape, whose annular kerf creates a hole in the workpiece without having to cut up the core material. It is used in a drill. Hole saws typically have a pilot drill bit (arbor) at their center to keep the saw teeth from walking. The fact that a hole saw creates the hole without needing to cut up the core often makes it preferable to twist drills or spade drills for relatively large holes. The same hole can be made faster and using less power.
 W
WThe Japanese saw or nokogiri (鋸) is a type of saw used in woodworking and Japanese carpentry that cuts on the pull stroke, unlike most European saws that cut on the push stroke. Japanese saws are the best known pull saws, but they are also used in China, Iran, Iraq, Korea, Nepal and Turkey. Among European saws, both coping saws for woodworking and jeweler's saws for metal working also cut on the pull stroke like Japanese saws. Cutting on the pull stroke is claimed to cut more efficiently and leave a narrower cut width (kerf). On the other hand, a pull stroke does not easily permit putting one's body weight behind a stroke. This can be readily solved by using a vice or clamping. Another disadvantage, due to the arrangement and form of the teeth, is that Japanese saws do not work as well on hardwoods as European saws do. Japanese saws were originally intended for comparatively soft woods like cypress and pine whereas European saws were intended for hard woods like oak and maple.
 W
WA jigsaw is a saw which uses a reciprocating blade to cut irregular curves, such as stenciled designs, in wood, metal, or other materials. Today they are electrically powered and known as scroll saws, and have been largely displaced by portable power jigsaws.
 W
WA keyhole saw is a long, narrow saw used for cutting small, often awkward features in various building materials. There are typically two varieties of keyhole saw: the fixed blade type and the retractable blade type.
 W
WA miter gauge is a device used for holding workpieces at a set angle while being cut on table saws, band saws or sanded on stationary disk sanders. The miter gauge slides in a slot on the worktable on the machine being used. Typically, the miter gauge and the workpiece are held together by hand and moved across the worktable making the cut. There are more sophisticated miter gauges which have the ability to clamp the workpiece or have adjustable stops for repetitive machining of workpieces.
 W
WA miter saw or mitre saw is a saw used to make accurate crosscuts and miters in a workpiece by positioning a mounted blade onto a board. A miter saw in its earliest form was composed of a back saw in a miter box, but in modern implementation consists of a powered circular saw that can be positioned at a variety of angles and lowered onto a board positioned against a backstop. Powered miter saws are also commonly referred to as chop saws.
 W
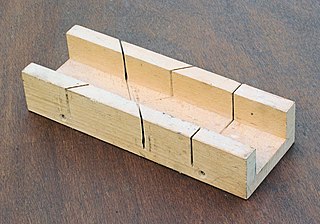
WA mitre box or miter box is a wood working appliance used to guide a hand saw for making precise cuts, usually 45° mitre cuts. Traditional mitre boxes are simple in construction and made of wood, while adjustable mitre boxes are made of metal and can be adjusted for cutting any angle from 45° to 90°.
 W
WA multi-tool or oscillating tool is a power tool that oscillates, powered by battery or mains. The name "multi-tool" is a reference to the many functions that this tool can perform with the range of attachments available. "Master Tool" is also a trade name used in North America, short for the original tool by Fein called the Multi-Master. Attachments are available for sawing, sanding, rasping, grinding, scraping, cutting, and polishing.
 W
WA panel saw is any type of sawing machine that cuts sheets into sized parts.
 W
WA pendulum saw or swing saw is a mechanically powered circular saw with the blade mounted so it can swing into the material.
 W
WA piercing saw, also known as a jeweler's saw, is a type of saw commonly used in jewelry making on sheet metal. It is usually used on softer metals as the saw is delicate.
 W
WA radial arm saw is a cutting machine consisting of a circular saw mounted on a sliding horizontal arm. Invented by Raymond DeWalt in 1922, the radial arm saw was the primary tool used for cutting long pieces of stock to length until the introduction of the power miter saw in the 1970s.
 W
WA reciprocating saw is a type of machine-powered saw in which the cutting action is achieved through a push-and-pull ("reciprocating") motion of the blade.
 W
WA resaw is a large band saw optimized for cutting timber along the grain to reduce larger sections into smaller sections or veneers. Resawing veneers requires a wide blade – commonly 2 to 3 inches (52–78 mm) – with a small kerf to minimize waste. Resaw blades of up to 1 inch may be fitted to a standard band saw. Many small and medium-sized sawmills use 1- to 1 1⁄2-inch band saw blades.
 W
WThe sabre saw is a hand-held powered reciprocating saw. It is similar to, but larger than, a jigsaw.
 W
WA saw pit or sawpit is a pit over which lumber is positioned to be sawed with a long two-handled saw by two people, one standing above the timber and the other below. It was used for producing sawn planks from tree trunks, which could then be cut down into boards, pales, posts, etc. Many towns, villages and country estates had their own saw pits. The greatest user of sawn timber in past centuries was the shipbuilding industry.
 W
WSaw set is a term applied to various forms of a tool used in the tuning and sharpening of saw blades. The saw set is used to adjust the set, or distance the saw tooth is bent away from the saw blade.
 W
WSawdust is a by-product or waste product of woodworking operations such as sawing, milling, planing, and routing. It is composed of small chippings of wood. These operations can be performed by woodworking machinery, portable power tools or by use of hand tools. Wood dust is also the byproduct of certain animals, birds and insects which live in wood, such as the woodpecker and carpenter ant. In some manufacturing industries it can be a significant fire hazard and source of occupational dust exposure.
 W
WA sawmill or lumber mill is a facility where logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes. The "portable" sawmill is of simple operation. The log lies flat on a steel bed, and the motorized saw cuts the log horizontally along the length of the bed, by the operator manually pushing the saw. The most basic kind of sawmill consists of a chainsaw and a customized jig, with similar horizontal operation.
 W
WSawyer is an occupational term referring to someone who saws wood, particularly using a pit saw either in a saw pit or with the log on trestles above ground or operates a sawmill. One such job is the occupation of someone who cuts lumber to length for the consumer market, a task now often done by end users or at lumber and home improvement stores.
 W
WA scroll saw is a small electric or pedal-operated saw used to cut intricate curves in wood, metal, or other materials. The fineness of its blade allows it to cut more delicately than a power jigsaw, and more easily than a hand coping saw or fretsaw. Like those tools, it is capable of creating curves with edges, by pivoting its table.
 W
WStrob Saw Blades are circular saw blades with the addition of two or more specialised raker/cutters and were invented by Keene S. Strobel (1907–1989) of Everett and Peter E. Heiser of Issaquah. These rakers are fitted on the trailing edges of more-or-less radial slots cut in the blade and are designed to reduce friction and rapidly eject sawdust, thereby preventing scorching and distortion of the blade faces, improving cutting efficiency and reducing sharpening frequency. Weyerhaeuser were granted a patent on strob saw blades in 1971, but there has been little improvement in the design since then.
 W
WA pendulum saw or swing saw is a mechanically powered circular saw with the blade mounted so it can swing into the material.
 W
WA table saw is a woodworking tool, consisting of a circular saw blade, mounted on an arbor, that is driven by an electric motor. The blade protrudes through the top of a table, which provides support for the material, usually wood, being cut.
 W
WTrack saws are a type of hand-held circular saw which slides on a guide rail during operation. This allows the operator to perform long and accurate cuts. Track saws, unlike hand-held circular saws, plunge into the material to a pre-determined depth during the cut, increasing operator safety and allowing for reduced splintering and tear-out; the depth-of-cut is not fixed and can be adjusted to be just slightly over the thickness of the board being cut. This property allows a track saw to also cut shallow grooves into the workpiece, if necessary.
 W
WA two-man saw is a saw designed for use by two sawyers. While some modern chainsaws are so large that they require two persons to control, two-man crosscut saws were primarily important when human power was used. Such a saw would typically be 1 to 4 m long, and sometimes up to 5 m, with a handle at each end. In some cases, such as when felling Giant Sequoias, sawblades could be brazed together end-to-end in order to create longer saws.
 W
WThe veneer saw is a small double-edged tool for cutting thin hardwood veneer. Its narrow curved blade facilitates precision work, and its elevated offset handle makes it possible to cut flush with a surface. The blade is usually 3 or 4 inches long and it has 13 tpi.
 W
WA whipsaw or pitsaw was originally a type of saw used in a saw pit, and consisted of a narrow blade held rigid by a frame and called a frame saw or sash saw. This evolved into a straight, stiff blade without a frame, up to 14 feet long and with a handle at each end, the upper called the tiller and the lower one being the box, so called from its appearance and because it could be removed when the saw was taken out of one cut to be positioned in another. It was used close to the felling site to reduce large logs into beams and planks.
 W
WA wire saw is a saw that uses a metal wire or cable for cutting. Industrial wire saws are usually powered. There are also hand-powered survivalist wire saws suitable for cutting branches. Wire saws are classified as continuous or oscillating. Sometimes the wire itself is referred to as a "blade".