 W
WSS Alcantara was an ocean liner that went into service just weeks before the start of World War I, was converted to an armed merchant cruiser in 1915, and was sunk in combat with the German armed merchant cruiser SMS Greif in 1916.
 W
WRMS Alcantara was a Royal Mail Lines ocean liner that was built in Belfast in 1926. She served in the Second World War first as an armed merchant cruiser and then a troop ship, was returned to civilian service in 1948 and scrapped in 1958.
 W
WHMS Ambrose was a cargo and passenger liner bought by the Admiralty from the Booth Steamship Company early in World War I and converted into an armed merchant cruiser. Later in the war she was converted into a submarine depot ship and spent most of the 1920s supporting submarines in the Far East. Upon her return home in 1928, Ambrose was placed in the Reserve Fleet. She was later modified to support destroyers and did so throughout World War II before she was sold for scrap in 1946.
RMS Andania was a British ocean liner launched in 1921. She was the first of six 14,000 ton "A"-class liners built for the Cunard Line in the early 1920s. The other ships were Antonia, Ausonia, Aurania, Ascania, and Alaunia.
 W
WRMS Aquitania was a British ocean liner of the Cunard Line in service from 1914 to 1950. She was designed by Leonard Peskett and built by John Brown & Company in Clydebank, Scotland. She was launched on 21 April 1913 and sailed on her maiden voyage from Liverpool to New York on 30 May 1914. Aquitania was the third in Cunard Line's grand trio of express liners, preceded by RMS Mauretania and RMS Lusitania, and was the last surviving four-funnelled ocean liner. Shortly after Aquitania entered service, World War I broke out, during which she was first converted into an auxiliary cruiser before being used as a troop transport and a hospital ship, notably as part of the Dardanelles Campaign.
 W
WRMS Arlanza was a 14,622 GRT ocean liner of the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company. She was built in Ireland in 1912 for RMSP's scheduled route between England and South America. She was a Royal Navy armed merchant cruiser from 1915 until 1920. She returned to civilian liner service in 1920 and was scrapped in England in 1938.
 W
WHMS Artifex was a repair ship of the Royal Navy from late in the Second World War and into the Cold War. Launched as the Cunard liner RMS Aurania she was requisitioned on the outbreak of war to serve as an armed merchant cruiser. Damaged by a U-boat while sailing with an Atlantic convoy, she was purchased outright and converted to a floating workshop, spending the rest of her life as a support ship for the navy.
 W
WThe RMS Ascania was an ocean liner operated by the Cunard Line. She was launched on 20 December 1923 at the Armstrong Whitworth Shipbuilders Ltd yard in Newcastle-upon-Tyne; the fifth of Cunard's six "A" class liners. Due to unforeseen cost overruns, the vessel was not completed until May 1925. Following service in a number of military roles during the Second World War, she was refitted and returned to civilian use in 1950, finally retiring in 1956.
 W
WRMS Asturias was a Royal Mail Lines ocean liner that was built in Belfast in 1925. She served in the Second World War as an armed merchant cruiser until she was crippled by a torpedo in 1943. She was out of action until 1948 when she returned to civilian service as an emigrant ship. She became a troop ship in 1954 and was scrapped in 1957.
 W
WRMS Atrato was a UK steamship that was built in 1888 as a Royal Mail Ship and ocean liner for the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company. In 1912 she was sold and became the cruise ship The Viking. Toward the end of 1914 she was requisitioned and converted into the armed merchant cruiser HMS Viknor. She sank in 1915 with all hands, a total of 295 Royal Navy officers and men.
 W
WRMS Ausonia, launched in 1921, was one of Cunard's six post-World War I "A-class" ocean liners for the Canadian service.
 W
WHMS Bayano, built in 1913, was originally a banana boat for the Elders & Fyffes line. At the outbreak of World War I it was drafted into the Royal Navy on 21 November 1914 as an armed merchant auxiliary cruiser. On 11 March 1915, it was torpedoed by SM U-27 and sank within minutes killing around 200 of its crew. Twenty-six survivors were pulled from the water.
 W
WSS Calgarian was an armed merchant cruiser of the Royal Navy. She was sunk by the U-boat U-19 off Rathlin Island, Northern Ireland on 1 March 1918. The initial strike did not sink her, and the crew managed to contain the damage. The U-boat torpedoed her again, despite the protection of other ships. She was hit by 4 torpedoes and quickly sank with the loss of two officers and 47 ratings.
 W
WSS California was a British 16,792 GRT steam turbine ocean liner that was built in Glasgow in 1923 for Henderson Brothers and destroyed in the North Atlantic by a Luftwaffe air attack in 1943.
 W
WRMS Carinthia was first laid down in Barrow-in-Furness in 1924 with the yard number Hull 586. Originally she had the name Servia but was renamed at the time of her launching on 24 February 1925. She made her maiden voyage on 22 August 1925 from Liverpool to New York City. At her launch she was the largest of the five post First World War intermediate size liners.
 W
WRMS Carmania was a British ocean liner designed by Leonard Peskett and built by John Brown & Company for the Cunard Line. In World War I, Carmania was converted to an armed merchant cruiser.
 W
WMV Carnarvon Castle was an ocean liner of the Union-Castle Line. She was requisitioned for service as an auxiliary cruiser by the Royal Navy during the Second World War.
 W
WRMS Caronia was a British ocean liner, launched on 13 July 1904. She was built for Cunard by John Brown & Co. of Glasgow. She was the only ship in the Cunard fleet to be named after an American, being named after Caro Brown, granddaughter of Cunard's New York agent. She left Liverpool on her maiden voyage to New York on 25 February 1905. A successful 1906 cruise from New York to the Mediterranean led to Caronia being used for cruising frequently in the coming years.
 W
WSS Cathay was a British passenger ship that was sunk during Operation Torch in 1942 by a German air raid in the Mediterranean Sea off Bougie, Algeria.
 W
WRMS Cedric was an ocean liner owned by the White Star Line. She was the second of a quartet of ships over 20,000 tons, dubbed The Big Four, and was the largest vessel in the world at the time of her launch. After her maiden voyage in 1903, she was in service until 1932.
 W
WRMS Celtic was an ocean liner owned by the White Star Line. The first ship larger than SS Great Eastern by gross register tonnage, Celtic was the first of a quartet of ships over 20,000 tons, dubbed The Big Four.
 W
WHMS Cheshire (F18), was a ship of the Royal Navy, named after the English county of Cheshire. Previously a passenger ship, she served as an armed merchant cruiser and troopship in World War II.
 W
WSS Drottningholm was one of the earliest steam turbine ocean liners. She was designed as a transatlantic liner and mail ship for Allan Line, built in Scotland, and launched in 1904 as RMS Virginian. Her sister ship, RMS Victorian, was built in Ireland, launched four months earlier, and was the World's first turbine-powered liner.
 W
WMS Dunnottar Castle was a UK-built passenger ship with a career of more than six decades that included periods as an ocean liner, an armed merchant cruiser (AMC), a troop ship and several decades as a cruise ship. As a cruise ship she was renamed Victoria, then The Victoria and finally Princesa Victoria.
 W
WHMS Dunvegan Castle was a UK ocean liner that was converted into an armed merchant cruiser (AMC) in the Second World War. Harland and Wolff built her and her sister ship Dunnottar Castle in Belfast in 1936.
 W
WRMS Ebro was an ocean liner built in 1914 for the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company. She was later owned and operated by the Pacific Steam Navigation Company, Jugoslavenska Lloyd and finally by Companhia Colonial de Navegação. In her last incarnation, under the name Serpa Pinto, she made more crossings of the Atlantic during the Second World War than any other civilian vessel, leading to her being termed the Friendship vessel or Destiny ship. She was scrapped in 1954.
 W
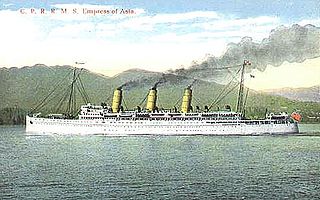
WRMS Empress of Asia was an ocean liner built in 1912–1913 by Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering at Govan on the Clyde in Scotland for Canadian Pacific Steamships.
 W
WRMS Empress of Britain was a transatlantic ocean liner built by the Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company at Govan on the Clyde in Scotland in 1905–1906 for Canadian Pacific Steamship (CP). This ship – the first of three CP ships to be named Empress of Britain – regularly traversed the transatlantic crossing between Canada and Europe until 1922, with the exception of the war years. Empress of Britain was the sister ship of RMS Empress of Ireland, which was lost in 1914.
 W
WRMS Empress of Japan, also known as the "Queen of the Pacific", was an ocean liner built in 1890–1891 by Naval Construction & Armaments Co, Barrow-in-Furness, England for Canadian Pacific Steamships (CP). This ship – the first of two CP vessels to be named Empress of Japan – regularly traversed the trans-Pacific route between the west coast of Canada and the Far East until 1922. During the First World War she served as armed merchant cruiser, becoming HMS Empress of Japan for the period that she was a commissioned ship of the Royal Navy.
 W
WRMS Empress of Russia was a steam turbine ocean liner built in 1912–13 by Fairfield Shipbuilding & Engineering Company at Govan on the Clyde in Scotland for Canadian Pacific steamships (CP). She regularly worked the trans-Pacific route between Canada and the Far East.
 W
WHMS Forfar (F30), formerly the ocean liner SS Montrose, was an armed merchant cruiser commissioned into Royal Navy service in 1939 and sunk in 1940.
 W
WHMS Hector was a UK steam turbine passenger and refrigerated cargo liner launched in 1924. She was the fourth of six civilian ships to bear the name.
 W
WHMS Hilary, was a former passenger liner launched in 1931, as SS Hilary, which was requisitioned by the Royal Navy during the Second World War and used as an ocean boarding vessel in the North Atlantic. It was later converted back to a merchantman but subsequently recommissioned back into the Royal Navy as an infantry landing and headquarters ship. At the end of the war in 1945 it was returned to civilian service, and scrapped at Thos W Ward Inverkeithing in 1959.
 W
WSS India was a steam passenger liner operated by the Peninsular and Oriental Steam Navigation Company (P&O) between 1896 and 1915.
 W
WHMS Jervis Bay was a British liner later converted into an armed merchant cruiser, pennant F40. She was launched in 1922, and sunk on 5 November 1940 by the German heavy cruiser Admiral Scheer.
 W
WHMAS Kanimbla was a passenger ship converted for use as an armed merchant cruiser and landing ship infantry during World War II. Built during the mid-1930s as the passenger liner MV Kanimbla for McIlwraith, McEacharn & Co, the ship operated in Australian waters until 1939, when she was requisitioned for military service, converted into an armed merchant cruiser, and commissioned in the Royal Navy as HMS Kanimbla.
 W
WTSS (RMS) King Orry (III) – the third ship in the history of the Company to bear the name – was a passenger steamer which served with the Isle of Man Steam Packet Company, until she was sunk during the evacuation of Dunkirk in 1940.
 W
WKronprinzessin Cecilie was a Hamburg-America Line passenger ship launched on 14 October 1905 by Krupp Aktiengesellschaft Germaniawerft at Kiel, Germany. The ship was placed on the South American service and soon to be overshadowed by the Norddeutscher Lloyd four stack liner Kronprinzessin Cecilie launched on 1 December 1906 that, at 18,372 GRT, was over twice the 8,688 GRT tonnage of the Hamburg-America Line ship.
 W
WHMS Kruger was the flagship of the British Caspian Flotilla during the Russian Civil War.
 W
WRMS Laconia was a Cunard ocean liner built by Swan Hunter & Wigham Richardson, launched on 27 July 1911, with the wife of the U.S. Ambassador Mrs. Whitelaw Reid christening the vessel. Laconia was delivered to the Cunard Line on 12 December 1911, and began service on 20 January 1912. She was the first Cunard ship of that name. She was torpedoed and sunk on 25 February 1917 during World War I; 12 passengers were killed.
 W
WThe second SS Laurentic was a 18,724 GRT steam ocean liner built in 1927 by Harland and Wolff, Belfast, for the White Star Line. She was the last steamship to be built for White Star Line.
 W
WSS Letitia was an ocean liner built in Scotland for service with the Anchor-Donaldson Line. She continued to serve with its successor company Donaldson Atlantic Line. At the start of the Second World War in September 1939, the British Admiralty requisitioned the ship for service and had it converted to serve as an armed merchant cruiser. She was withdrawn from this service in 1941 to become a troop ship.
 W
WRMS Maloja was a British ocean liner that saw service from 1923 to 1954.
 W
WHMS Mantua was a 20th-century ocean liner and armed merchant cruiser. Launched in 1909 as a passenger ship, Mantua was outfitted as an armed merchant cruiser in 1914 and served with the Royal Navy during World War I. On a voyage to Freetown in 1918, the passengers and crew of Mantua inadvertently spread the 1918 flu pandemic to Africa.
 W
WRMS Oceanic was a transatlantic ocean liner built for the White Star Line. She sailed on her maiden voyage on 6 September 1899 and was the largest ship in the world until 1901. At the outbreak of World War I she was converted to an armed merchant cruiser. On 8 August 1914 she was commissioned into Royal Navy service.
 W
WRMS Ophir was a twin-screw ocean liner of the Orient Steam Navigation Company of London, which worked the company's London — Aden — Colombo — Australia route from 1891. In 1901 she served as the royal yacht HMS Ophir. In 1915 she was requisitioned by the Admiralty and was an armed merchant cruiser until 1918, when she was returned to her owners. She was not restored to passenger service, but was scrapped in 1922.
 W
WHMS Otranto was an armed merchant cruiser requisitioned by the Royal Navy when World War I began in 1914. Built before the war for the UK–Australia run as the SS Otranto, she was primarily used during the war to search for German commerce raiders. She played small roles in the Battle of Coronel in November 1914 when the German East Asia Squadron destroyed the British squadron searching for it and in the Battle of the Falklands the following month when a British squadron annihilated the Germans in turn.
 W
WSS Otway was a British ocean liner owned by the Orient Line, built by Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company of Glasgow, Scotland, launched in 1908 and completed in 1909.
 W
WHMS Pretoria Castle (F61) was a Union-Castle ocean liner that in the Second World War was converted into a Royal Navy armed merchant cruiser, and then converted again into an escort carrier. After the war she was converted back into a passenger liner and renamed Warwick Castle.
 W
WSS Queen of Bermuda was a British turbo-electric ocean liner that belonged to Furness, Withy & Co Ltd. Its Furness Bermuda Line subsidiary operated her between New York and Bermuda before and after the Second World War. During the war she served as first an armed merchant cruiser and then as a troop ship.
 W
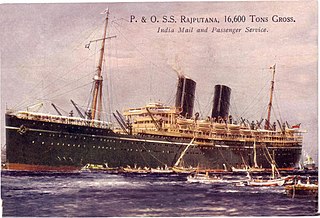
WSS Rajputana was a British passenger and cargo carrying ocean liner. She was built for the Peninsular & Oriental Steam Navigation Company at the Harland and Wolff shipyard at Greenock on the lower River Clyde, Scotland in 1925. She was one of the P&O R-class liners from 1925 that had much of their interiors designed by Lord Inchcape's daughter Elsie Mackay. Named after the Rajputana region of western India, she sailed on a regular route between England and British India.
 W
WSS Ranchi was Peninsular and Oriental Steam Navigation Company "R"-class steam ocean liner that was built in 1925 and scrapped in 1953. From 1939 to 1943 she was the Royal Navy armed merchant cruiser HMS Ranchi.
 W
WHMS Rawalpindi was a British armed merchant cruiser, that was sunk in a surface action against the German battleships Scharnhorst and Gneisenau during the first months of the Second World War. Her captain was Edward Coverley Kennedy.
 W
WSS Laurentic was a UK transatlantic ocean liner that was built in Ireland and launched in 1908. She is an early and influential example of a ship whose propulsion combined reciprocating steam engines with a low-pressure steam turbine.
 W
WThe RMS Teutonic was an ocean liner built for the White Star Line in Belfast and was the first armed merchant cruiser.
 W
WRMS Victorian was the World's first turbine-powered ocean liner. She was designed as a transatlantic liner and mail ship for Allan Line and launched in 1904.