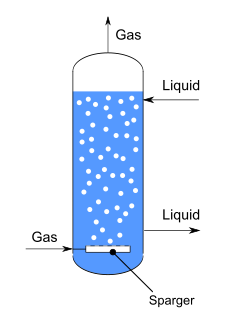
 W
WA bubble column reactor is an apparatus used to generate and control gas-liquid chemical reactions. It consists of a vertically-arranged cylindrical column filled with liquid, at the bottom of which gas is inserted.
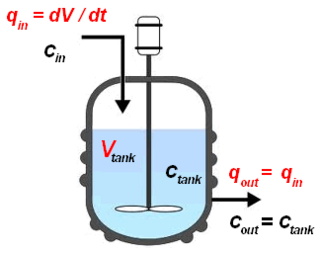 W
WThe continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR), also known as vat- or backmix reactor, mixed flow reactor (MFR), or a continuous-flow stirred-tank reactor (CFSTR), is a common model for a chemical reactor in chemical engineering and environmental engineering. A CSTR often refers to a model used to estimate the key unit operation variables when using a continuous agitated-tank reactor to reach a specified output. The mathematical model works for all fluids: liquids, gases, and slurries.
 W
WA fluidized bed reactor (FBR) is a type of reactor device that can be used to carry out a variety of multiphase chemical reactions. In this type of reactor, a fluid is passed through a solid granular material at high enough speeds to suspend the solid and cause it to behave as though it were a fluid. This process, known as fluidization, imparts many important advantages to an FBR. As a result, FBRs are used for many industrial applications.
 W
WA membrane reactor is a physical device that combines a chemical conversion process with a membrane separation process to add reactants or remove products of the reaction.
 W
WA microreactor or microstructured reactor or microchannel reactor is a device in which chemical reactions take place in a confinement with typical lateral dimensions below 1 mm; the most typical form of such confinement are microchannels. Microreactors are studied in the field of micro process engineering, together with other devices in which physical processes occur. The microreactor is usually a continuous flow reactor. Microreactors offer many advantages over conventional scale reactors, including vast improvements in energy efficiency, reaction speed and yield, safety, reliability, scalability, on-site/on-demand production, and a much finer degree of process control.
 W
WThe plug flow reactor model is a model used to describe chemical reactions in continuous, flowing systems of cylindrical geometry. The PFR model is used to predict the behavior of chemical reactors of such design, so that key reactor variables, such as the dimensions of the reactor, can be estimated.
 W
WA trickle-bed reactor (TBR) is a chemical reactor that uses the downward movement of a liquid and the downward (co-current) or upward (counter-current) movement of gas over a packed bed of (catalyst) particles. It is considered to be the simplest reactor type for performing catalytic reactions where a gas and liquid are present in the reactor and accordingly it is extensively used in processing plants. Typical examples are liquid-phase hydrogenation, hydrodesulfurization, and hydrodenitrogenation in refineries and oxidation of harmful chemical compounds in wastewater streams or of cumene in the cumene process. Also in the treatment of waste water trickle bed reactors are used where the required biomass resides on the packed bed surface.