 W
WArmour or armor is a protective covering that is used to prevent damage from being inflicted to an object, individual or vehicle by direct contact weapons or projectiles, usually during combat, or from damage caused by a potentially dangerous environment or activity. Personal armour is used to protect soldiers and war animals. Vehicle armour is used on warships and armoured fighting vehicles.
 W
WThe Baju Empurau is an armour from Indonesia.
 W
WThe Baju Lamina is a mail and plate armor from Nusantara archipelago.
 W
WThe Baju Rantai is a type of armor from Nusantara archipelago.
 W
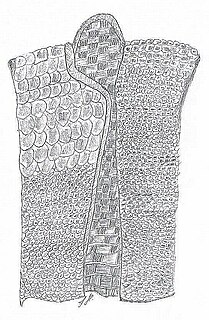
WThe Baru Lema'a is a traditional armor from Indonesia.
 W
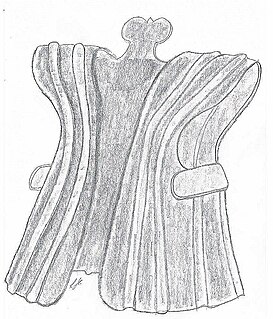
WBaru Öröba is a traditional armor of the Nias people in Indonesia. The earliest examples of this type of armor were made out of crocodile skin. After crocodile can no longer be found on Nias, the material is replaced with hammered metal.
 W
WThe Dacian Draco was the standard ensign of troops of the ancient Dacian people, which can be seen in the hands of the soldiers of Decebalus in several scenes depicted on Trajan's Column in Rome, Italy. It has the form of a dragon with open wolf-like jaws containing several metal tongues. The hollow dragon's head was mounted on a pole with a fabric tube affixed at the rear. In use, the draco was held up into the wind, or above the head of a horseman, where it filled with air and gave the impression it was alive while making a shrill sound as the wind passed through its strips of material.
 W
WChain mail is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh. It was generally in common military use between the 3rd century BC and the 16th century AD in Europe, and longer in Asia and North Africa. A coat of this armour is often referred to as a hauberk, and sometimes a byrnie.
 W
WA war wagon is any of several historical types of early fighting vehicle involving an armed or armored animal-drawn cart or wagon.