 W
WA disk laser or active mirror (Fig.1) is a type of diode pumped solid-state laser characterized by a heat sink and laser output that are realized on opposite sides of a thin layer of active gain medium. Despite their name, disk lasers do not have to be circular; other shapes have also been tried. The thickness of the disk is considerably smaller than the laser beam diameter.
 W
WAn Er:YAG laser (erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser, erbium YAG laser) is a solid-state laser whose active laser medium is erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Er:Y3Al5O12). Er:YAG lasers typically emit light with a wavelength of 2940 nm, which is infrared light.
 W
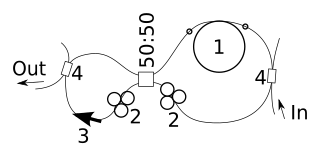
WA figure-8 laser is a fiber laser with a figure-8-shaped ring resonator. It is used for making pico- and femtosecond soliton pulses. The typical spectrum of such a laser consists of a wide central peak and a few narrow lateral peaks that are placed symmetrically around it. The amplitudes of the narrow peaks are the same as or less than that of the central peak.
 W
WNd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet; Nd:Y3Al5O12) is a crystal that is used as a lasing medium for solid-state lasers. The dopant, triply ionized neodymium, Nd(III), typically replaces a small fraction (1%) of the yttrium ions in the host crystal structure of the yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG), since the two ions are of similar size. It is the neodymium ion which provides the lasing activity in the crystal, in the same fashion as red chromium ion in ruby lasers.
 W
WA ruby laser is a solid-state laser that uses a synthetic ruby crystal as its gain medium. The first working laser was a ruby laser made by Theodore H. "Ted" Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories on May 16, 1960.
 W
WSolid-state dye lasers (SSDL) were introduced in 1967 by Soffer and McFarland. In these solid-state lasers, the gain medium is a laser dye-doped organic matrix such as poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), rather than a liquid solution of the dye. An example is rhodamine 6G-doped PMMA. These lasers are also referred to as solid-state organic lasers and solid-state dye-doped polymer lasers.
 W
WTi:sapphire lasers (also known as Ti:Al2O3 lasers, titanium-sapphire lasers, or Ti:sapphs) are tunable lasers which emit red and near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses. Lasers based on Ti:sapphire were first constructed and invented in June 1982 by Peter Moulton at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory.
 W
WThe Trident Laser was a high power, sub-petawatt class, solid-state laser facility located at Los Alamos National Laboratory, in Los Alamos, New Mexico, originally built in the late 1980s for Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) research by KMS Fusion, founded by Kip Siegel, in Ann Arbor, Michigan, it was later moved to Los Alamos in the early 1990s to be used in ICF and materials research. The system is now being decommissioned with final laser experiments being completed February 2017. As of 2020 the Trident laser has been decommissioned, and sent to University of Texas Austin for storage.
 W
WThe HLONS , commonly known as ZEUS, is a solid-state laser weapon which is used by the U.S. military in order to neutralize surface land mines and unexploded ordnance. The ZEUS-HLONS system was a co-operative effort between Sparta Inc and NAVEODTECHDIV to demonstrate that a moderate-power commercial solid state laser (SSL) and beam control system could be integrated onto a Humvee (HMMWV) and used to clear surface mines, improvised explosive devices (IEDs), or unexploded ordnance from supply routes and minefields.