 W
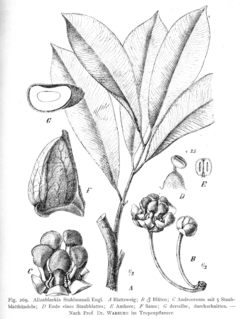
WAllanblackia stuhlmannii is a species of flowering plant in the family Clusiaceae. It is found only in Tanzania.
 W
WBrassica nigra, or black mustard, is an annual plant cultivated for its black or dark brown seeds, which are commonly used as a spice. It is native to tropical regions of North Africa, temperate regions of Europe, and parts of Asia.
 W
WCeratotheca sesamoides is a flowering plant in the genus Ceratotheca. It is indigenous to Africa and grows both as a wild weed and locally cultivated species, and is colloquially referred to as false sesame owing to its marked similarities with common sesame. The plant is most commonly cultivated in the African Savannah and other semi-arid areas on the continent and is found across Africa in both tropic and sub-tropic regions, usually growing in sandier soils south of the Sahara. It can be identified by numerous hairs on the stem, its pink flowers often replete with brown and purple dots and a sub-erect growth habit. A plant with many practical uses, the leaves and flowers are often consumed as vegetables or used in sauces. The leaves can also have medicinal benefits while the seeds can be employed to produce cooking oil. Despite its many uses and growing domestication at a local level, the plant remains predominantly underused and undervalued.
 W
WThe coconut tree is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus Cocos. The term "coconut" can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which botanically is a drupe, not a nut. The name comes from the old Portuguese word coco, meaning "head" or "skull", after the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features. They are ubiquitous in coastal tropical regions and are a cultural icon of the tropics.
 W
WElaeis is a genus of palms containing two species, called oil palms. They are used in commercial agriculture in the production of palm oil. The African oil palm Elaeis guineensis is the principal source of palm oil. It is native to west and southwest Africa, occurring between Angola and Gambia. The American oil palm Elaeis oleifera is native to tropical Central and South America, and is used locally for oil production.
 W
WGnetum latifolium is an evergreen plant in the family Gnetaceae with a broad distribution across South East Asia. Although some of its habitat is threatened by logging and forest conversion to crops, its broad distribution afforded it an assessment of "least concern" according to The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
 W
WHelianthus annuus, the common sunflower, is a large annual forb of the genus Helianthus grown as a crop for its edible oil and edible fruits. This sunflower species is also used as wild bird food, as livestock forage, in some industrial applications, and as an ornamental in domestic gardens. The plant was first domesticated in the Americas. Wild Helianthus annuus is a widely branched annual plant with many flower heads. The domestic sunflower, however, often possesses only a single large inflorescence atop an unbranched stem. The name sunflower may derive from the flower's head's shape, which resembles the sun.
 W
WThe peanut, also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), and taxonomically classified as Arachis hypogaea, is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, being important to both small and large commercial producers. It is classified as both a grain legume and, due to its high oil content, an oil crop. World annual production of shelled peanuts was 44 million tonnes in 2016, led by China with 38% of the world total. Atypically among legume crop plants, peanut pods develop underground (geocarpy) rather than above ground. With this characteristic in mind, the botanist Carl Linnaeus gave peanuts the specific epithet hypogaea, which means "under the earth".
 W
WSafflower, Carthamus tinctorius, is a highly branched, herbaceous, thistle-like annual plant. It is commercially cultivated for vegetable oil extracted from the seeds and was used by the early Spanish colonies along the Rio Grande as a substitute for saffron. Plants are 30 to 150 cm tall with globular flower heads having yellow, orange, or red flowers. Each branch will usually have from one to five flower heads containing 15 to 20 seeds per head. Safflower is native to arid environments having seasonal rain. It grows a deep taproot which enables it to thrive in such environments.
 W
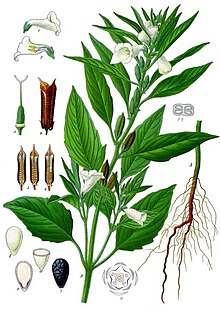
WSesame is a flowering plant in the genus Sesamum, also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods. World production in 2018 was 6 million tonnes, with Sudan, Myanmar, and India as the largest producers.