 W
WHistorians who debate the origins of the American Civil War focus on the reasons that seven southern states declared their secession from the United States and united to form the Confederate States, and the reasons that the North refused to let them go. Most of the debate is about the first question, the reason that some Southern states decided to secede. Most historians in the 21st century agree that conflict over slavery caused the war, but they disagree sharply on the aspects of this conflict that were most important.
 W
WThis timeline of events leading to the American Civil War is a chronologically ordered list of events and issues which historians recognize as origins and causes of the American Civil War. These events are roughly divided into two periods: the first encompasses the gradual build-up over many decades of the numerous social, economic, and political issues that ultimately contributed to the war's outbreak, and the second encompasses the five-month span following the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States in 1860 and culminating in the capture of Fort Sumter in April 1861.
 W
WThe Cold War originated in the breakdown of relations between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc, in the years 1945–1949.
 W
WIn diplomatic history, a color book is an officially sanctioned collection of diplomatic correspondence and other documents published by a government for educational or political reasons, or to promote the government position on current or past events. The earliest were the British Blue Books, dating to the 17th century. In World War I, all the major powers had their own color book, such as the German White Book, the Austrian Red Book, Russian Orange Book, and more.
 W
WThe causes of the Franco-Prussian War are deeply rooted in the events surrounding German unification. In the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War (1866), Prussia had annexed numerous ethnically German territories and formed the North German Confederation with other German territories. Prussia then turned its attention towards the south of Germany, where it sought to expand its influence.
 W
WDuring the Polish–Soviet War of 1919-1921, Soviet Russia and Soviet Ukraine were in combat with the re-established Second Polish Republic and the newly established Ukrainian People's Republic. Both sides aimed to secure territory in the often disputed areas of the Kresy, which make up today's Ukraine and parts of modern-day Belarus, in the context of the fluidity of borders in Central and Eastern Europe in the aftermath of World War I and the breakdown of the Austrian, German, and Russian empires. The first clashes between the two sides occurred in February 1919, but full-scale war did not break out until the following year. Especially at first, neither Soviet Russia, embroiled in the Russian Civil War, nor Poland, still in the early stages of state re-building, were in a position to formulate and pursue clear and consistent war aims.
 W
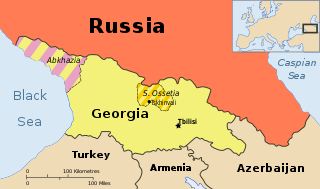
WThis article describes the background of the Russo-Georgian War.
 W
WBoth sides of the 2008 war between Russia and Georgia blamed each other for starting the war.
 W
WThe Sino-Indian border dispute is an ongoing territorial dispute over the sovereignty of two relatively large, and several smaller, separated pieces of territory between China and India. The first of which, Aksai Chin, is administered by China as part of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region and Tibet Autonomous Region and claimed by India as part of the union territory of Ladakh; it is a virtually uninhabited high-altitude wasteland in the larger regions of Kashmir and Tibet and is crossed by the Xinjiang-Tibet Highway. The other disputed territory is south of the McMahon Line, formerly known as the North East Frontier Agency and now called Arunachal Pradesh. The McMahon Line was part of the 1914 Simla Convention signed between British India and Tibet, without China's agreement. As of 2020, India continues to maintain that the McMahon Line is the legal border in the east. China has never accepted that border, stating that Tibet was never independent when it signed the Simla Convention.
 W
WThe identification of the causes of World War I remains controversial. World War I began in the Balkans on July 28, 1914 and hostilities ended on November 11, 1918, leaving 17 million dead and 25 million wounded.
 W
WThe causes of World War II, a global war from 1939 to 1945 that was the deadliest conflict in human history, have been given considerable attention by historians from many countries who studied and understood them. The immediate precipitating event was the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany on September 1, 1939 and the subsequent declarations of war on Germany made by Britain and France, but many other prior events have been suggested as ultimate causes. Primary themes in historical analysis of the war's origins include the political takeover of Germany in 1933 by Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party; Japanese militarism against China, which led to the Second Sino-Japanese War; Italian aggression against Ethiopia, which led to the Second Italo-Ethiopian War and Germany's initial success in negotiating the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact with the Soviet Union to divide the territorial control of Eastern Europe between them.