 W
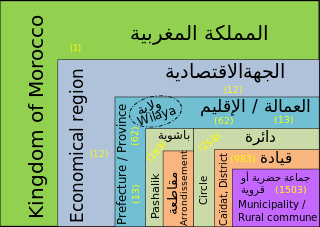
WIn Morocco, the 75 second-level administrative subdivisions are 13 prefectures and 62 provinces. They are subdivisions of the 12 regions of Morocco. Each prefecture or province is subdivided into arrondissements, municipalities or urban municipalities in other urban areas, and districts in rural areas. The districts are subdivided into rural municipalities. One prefecture (Casablanca) is also subdivided into préfectures d'arrondissements, similar to districts (cercles) except they are grouping a few arrondissements instead of rural municipalities.
 W
WThe House of Councillors is the upper house of the Parliament of Morocco and has 120 members, elected for a six-year term. 72 members are elected at the Kingdom's regional level, who represent the subnational administrative areas ; 20 members are elected in each region by a single electoral college made up of all those in the relevant region that have been elected to the following professional associations: the agriculture associations, the commerce, industry and services associations, the arts and crafts associations and the marine fisheries associations; 8 members are elected in each region by an electoral college made up of those elected from the most representative employers' professional organizations; 20 members elected nationally by an electoral college made up of employees.
 W
WThe House of Representatives is one of the two chambers—the other of which is the House of Councillors—of the Moroccan Parliament. The House of Representatives has 395 members elected for five-year terms, 305 of whom are elected in multi-seat constituencies, and 90 of whom are elected in two national lists dedicated to promote gender equality and national youth.
 W
WThe Caisse de dépot et de gestion is a state-owned financial institution which manages long-term savings in Morocco. Given its substantial assets it also acts as a large investor in the country, especially in the tourism sector. It possesses many subsidiaries operating in various sectors of the Economy.
 W
WIn 1911, the conquest of Morocco was initiated by the French Third Republic, in the aftermath of the Agadir Crisis. While the conquest itself lasted until 1934, the Treaty of Fez was signed on 30 March 1912. According to the treaty, most of Morocco would become a French protectorate from 1912 to 1956, when the country regained its independence.
 W
WThe Haut Commissariat au Plan (HCP) or Higher Planning Commission in Morocco is an independent government statistical institution. Established in 2003, HCP is the main source of economic, demographic and social statistical data.
 W
WThe Judiciary of Morocco is an independent branch of the Moroccan government, subject only to the Moroccan Constitution.
 W
WMincom is the Ministry of Communications for the Government of Morocco.
 W
WThe Ministry of Equipment, Transport and Logistics is a government ministry of Morocco.
 W
WThe Ministry of Foreign Affairs, African Cooperation and Moroccan Expatriates is the foreign affairs ministry of Morocco, responsible for implementing Morocco's foreign policy and ensuring relations with foreign states.
 W
WMoroccan passports are issued to nationals and citizens of Morocco for the purpose of international travel. Besides serving as a proof of Moroccan citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Moroccan consular officials abroad if needed. Since 15 December 2009, a biometric passport was available for all new applicants. Moroccan citizens can now apply for a passport anytime, anywhere. Launched in tandem with the new enrollment program, a web portal outlining issuance requirements takes applicants through the procedure step by step, from the comfort of their keyboard. once proof of identity has been gathered, the applicant can fill in an online form to print and submit in person at the prefecture. Downloadable forms for passports and temporary passports can also print for handwritten completion. A PDF file describes accepted photo formats, while a convenient tracking function enables applicants to trace the various stages of processing. Passeport.maThe passport for normal citizens is GREEN The passport for diplomats is RED
 W
WThe prime minister of Morocco is the head of government of the Kingdom of Morocco and serves in a position akin to a prime minister in other constitutional monarchies. The prime minister is chosen by the king of Morocco from the largest party elected to parliament. The Constitution of Morocco grants executive powers to the government and allows the head of government to propose and dismiss cabinet members, provincial governors, and ambassadors, to oversee government programs and the delivery of public services, and to dissolve the lower house of parliament with the king's approval.
 W
WOn 27 November 1912, amidst the French conquest of Morocco and in the aftermath of the Agadir Crisis, the Treaty Between France and Spain Regarding Morocco was signed by the French Third Republic and the Kingdom of Spain. According to the treaty, parts of Morocco would become a Spanish protectorate from 1912 to 1956, when the country regained its independence.