 W
WLike other emissions resulting from fossil fuel combustion, aircraft engines produce gases, noise, and particulates, raising environmental concerns over their global impact and their local air quality effect. Jet airliners contribute to climate change by emitting carbon dioxide, the best understood greenhouse gas, and, with less scientific understanding, nitrogen oxides, contrails and particulates. Their radiative forcing is estimated at 1.3–1.4 that of CO2 alone, excluding induced cirrus cloud with a very low level of scientific understanding. In 2018, global commercial operations generated 2.4% of all CO2 emissions.
 W
WThe environmental impact of aviation in the United Kingdom is increasing due to the increasing demand for air travel in the country. In the past 25 years the UK air transport industry has seen sustained growth, and the demand for passenger air travel in particular is forecast to increase more than twofold, to 465 million passengers, by 2030. Two airports; London Heathrow and London Gatwick, are amongst the top ten busiest airports in the world for international passenger traffic. Whilst more than half of all passengers travelling by air in the UK currently travel via the five London area airports, regional airports have experienced the most growth in recent years, due to the success of 'no-frills' airlines over the last decade.
 W
WAirport Carbon Accreditation is a global carbon management programme for airports that independently assesses and recognises airports' efforts to manage and reduce their CO2 emissions. Aircraft emissions, which are many times greater than airport emissions, are not included in the programme. The airport industry accounts for 5% of the air transport sector’s total carbon emissions.
 W
WAn aviation biofuel or bio-jet-fuel or bio-aviation fuel (BAF) or sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is a biofuel used to power aircraft. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) considers it to be one of the key elements to reduce the carbon footprint within the environmental impact of aviation. Aviation biofuel could help decarbonize medium- and long-haul air travel generating most emissions, and could extend the life of older aircraft types by lowering their carbon footprint.
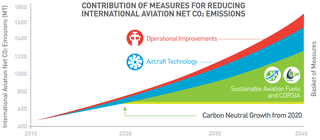 W
WThe Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) is a carbon offset and carbon reduction scheme to lower CO2 emissions for international flights, to curb the aviation impact on climate change.
 W
WThe ecoDemonstrator Program is a flight test research program of aircraft company Boeing, which has used a series of specially modified aircraft to develop and test aviation technologies designed to improve fuel economy and reduce the noise and ecological footprint of airliners. From 2012 through 2018, the five airplanes involved have tested 112 technologies: half remain in further development and a third are being implemented like iPad apps for pilot real-time information to reduce fuel use and emissions; custom approach paths to reduce community noise; and 777X cameras for ground navigation.
 W
WAn electric aircraft is an aircraft powered by electric motors. Electricity may be supplied by a variety of methods including batteries, ground power cables, solar cells, ultracapacitors, fuel cells and power beaming. Small, electrically powered model aircraft have been flown since the 1970s, with one unconfirmed report as early as 1957. They have since developed into small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) or drones, which in the twenty-first century have become widely used for many purposes.
 W
WFuel dumping is a procedure used by aircraft in certain emergency situations before a return to the airport shortly after takeoff, or before landing short of the intended destination to reduce the aircraft's weight.
 W
WThe fuel economy in aircraft is the measure of the transport energy efficiency of aircraft. Efficiency is increased with better aerodynamics and by reducing weight, and with improved engine BSFC and propulsive efficiency or TSFC. Endurance and range can be maximized with the optimum airspeed, and economy is better at higher altitudes. An airline efficiency depends on its fleet fuel burn, seating density, air cargo and passenger load factor, while operational procedures like maintenance and routing can save fuel.
 W
WA hydrogen aircraft is an aeroplane that uses hydrogen fuel as a power source. Hydrogen can either be burned in a jet engine, or other kind of internal combustion engine, or can be used to power a fuel cell to generate electricity to power a propeller.
 W
WThe NASA X-57 Maxwell is an experimental aircraft being developed by NASA, intended to demonstrate technology to reduce fuel use, emissions, and noise.
 W
WPlane Stupid is a UK-focused group of environmental protesters who state their aim as wanting to see an end to airport expansion for what it sees as "unnecessary and unsustainable" flights. It is a loose association of autonomous regional groups, and is funded by donations.
 W
WThe Roskill Commission was a UK Government Commission charged with looking into finding a site for a new airport for London. Chaired by High Court judge Eustace Roskill, it sat from 1968 to 1970 and published its report in January 1971.
 W
WA short-haul flight ban is a prohibition imposed by governments on airlines to establish and maintain a flight connection over a certain distance, or by organisations or companies on their employees for business travel using existing flight connections over a certain distance, in order to mitigate the environmental impact of aviation. In the 21st century, several governments, organisations and companies have imposed restrictions and even prohibitions on short-haul flights, stimulating or pressuring travellers to opt for more environmentally friendly means of transportation, especially trains.
 W
WYVR Sustainability is an operations department at Vancouver International Airport that is concerned with airport green initiatives. Its focus is to expand the airport quality of YVR without harm to the environment or affecting the community in a negative way. It focuses on a variety of initiatives having to do with heating, transport, energy consumption, recycling and noise. YVR's sustainability is also known and infamous for its green art linked to the environment and community and its indoor nature displays.