 W
WAn academic discipline or academic field is a subdivision of knowledge that is taught and researched at the college or university level. Disciplines are defined and recognized by the academic journals in which research is published, and the learned societies and academic departments or faculties within colleges and universities to which their practitioners belong. Academic disciplines are conventionally divided into the humanities, including language, art and cultural studies, and the scientific disciplines, such as physics, chemistry, and biology; the social sciences are sometimes considered a third category.
 W
WAn academic discipline or field of study is known as a branch of knowledge. It is taught as an accredited part of higher education. A scholar's discipline is commonly defined and recognized by a university faculty. That person will be accredited by learned societies to which he or she belongs along with the academic journals in which he or she publishes. However, no formal criteria exist for defining an academic discipline.
 W
WAn academic discipline or field of study is a branch of knowledge, taught and researched as part of higher education. A scholar's discipline is commonly defined by the university faculties and learned societies to which they belong and the academic journals in which they publish research.
 W
WComparative law is the study of differences and similarities between the law of different countries. More specifically, it involves the study of the different legal "systems" in existence in the world, including the common law, the civil law, socialist law, Canon law, Jewish Law, Islamic law, Hindu law, and Chinese law. It includes the description and analysis of foreign legal systems, even where no explicit comparison is undertaken. The importance of comparative law has increased enormously in the present age of internationalism, economic globalization, and democratization.
 W
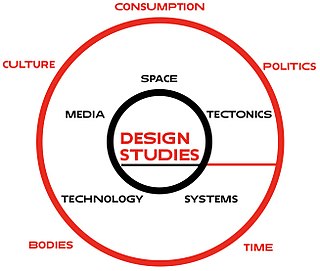
WDesign studies can refer to any design-oriented studies but more formally is an academic discipline or field of study that pursues, through both theoretical and practical modes of inquiry, a critical understanding of design practice and its effects in society.
 W
WEconomic history is the academic study of economies or economic events of the past. Research is conducted using a combination of historical methods, statistical methods and the application of economic theory to historical situations and institutions. The field can encompass a wide variety of topics, including equality, finance, technology, labour, and business. It emphasizes historicizing the economy itself, analyzing it as a dynamic force and attempting to provide insights into the way it is structured and conceived.
 W
WEnvironmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physical, biological and information sciences to the study of the environment, and the solution of environmental problems. Environmental science emerged from the fields of natural history and medicine during the Enlightenment. Today it provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplinary approach to the study of environmental systems.
 W
WEnvironmental studies is a multidisciplinary academic field which systematically studies human interaction with the environment. Environmental studies connects principles from the physical sciences, commerce/economics, the humanities, and social sciences to address complex contemporary environmental issues. It is a broad field of study that includes the natural environment, the built environment, and the relationship between them. The field encompasses study in basic principles of ecology and environmental science, as well as associated subjects such as ethics, geography, anthropology, policy, politics, urban planning, law, economics, philosophy, sociology and social justice, planning, pollution control and natural resource management. There are many Environmental Studies degree programs, including a Master's degree and a Bachelor's degree. Environmental Studies degree programs provide a wide range of skills and analytical tools needed to face the environmental issues of our world head on. Students in Environmental Studies gain the intellectual and methodological tools to understand and address the crucial environmental issues of our time and the impact of individuals, society, and the planet.
 W
WGenome Informatics is a scientific study of information processing in genomes.
 W
WThe history of art criticism, as part of art history, is the study of objects of art in their historical development and stylistic contexts, i.e. genre, design, format, and style, which include aesthetic considerations. This includes the "major" arts of painting, sculpture, and architecture as well as the "minor" arts of ceramics, furniture, and other decorative objects.
 W
WJurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and provide a deeper understanding of legal reasoning and analogy, legal systems, legal institutions, and the role of law in society.
 W
WThe discipline of medical entomology, or public health entomology, and also veterinary entomology is focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Veterinary entomology is included in this category, because many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat, for example, bovine encephalitis. Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public, including local and state officials and other stake holders in the interest of public safety. Medical Entomologists are employed by private and public universities, private industries, and federal, state, and local government agencies, including all three branches of the US military - who hire medical entomologists to protect the troops from infectious diseases that can be transmitted by arthropods. Historically, during wars, more people have died due to insect-transmitted diseases, than to all the battle injuries combined.
 W
WSocial science is the branch of science devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 19th century. In addition to sociology, it now encompasses a wide array of academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, human geography, linguistics, management science, political science, psychology, and history.
 W
WSocial work is an academic discipline and practice-based profession that concerns itself with individuals, families, groups, communities and society as a whole in an effort to meet basic needs and enhance social functioning, self-determination, collective responsibility, optimal health, and overall well-being. Social functioning is defined as the ability of an individual to perform their social roles within their own self, their immediate social environment, and the society at large. Social work applies areas, such as sociology, psychology, human biology, political science, health, community development, law, and economics, to work with individuals across the lifespan, engage with client systems, conduct assessments, and develop interventions to solve social problems, personal problems, and bring about social change. Social work practice is often divided into micro-work, which involves working directly with individuals or small groups; and macro-work, which involves working with communities, and fostering change on a larger scale through social policy. Since the 1980s, few universities also started to run social work management programmes to qualify students for the management of social and human service organisations besides classical social work education.
 W
WSustainability studies focuses on the interdisciplinary perspective of the sustainability concept. Programs include instruction in sustainable development, geography, environmental policies, ethics, ecology, landscape architecture, city and regional planning, economics, natural resources, sociology, and anthropology. Sustainability studies also focuses on the importance of climate change, poverty and development. Studies in Sustainability are now available in many different universities across America. The main goal of sustainability studies is for students to find ways to develop creative solutions to the crisis in environmental sustainability.
 W
WSustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while simultaneously sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The desired result is a state of society where living conditions and resources are used to continue to meet human needs without undermining the integrity and stability of the natural system. Sustainable development can be defined as development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Sustainability goals, such as the current UN-level Sustainable Development Goals, address the global challenges, including poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace, and justice.
 W
WVisual communication is the use of visual elements to convey ideas and information which include but are not limited to, signs, typography, drawing, graphic design, illustration, industrial design, advertising, animation, and electronic resources. Humans have used visual communication since prehistoric times. Within modern culture, there are several types of characteristics when it comes to visual elements, they consist of objects, models, graphs, diagrams, maps and photographs. Outside the different types of characteristics and elements, there are seven components of visual communication: Color, Shape, Tones, Texture, Figure-Ground, Balance, and Hierarchy.