 W
WThe Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy, was an unrecognized breakaway state that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865, and that fought against the United States of America during the American Civil War. Eleven states with declarations of secession from the Union formed the main part of the CSA. They were South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky and Missouri also had declarations of secession and full representation in the Confederate Congress during their Union army occupation.
 W
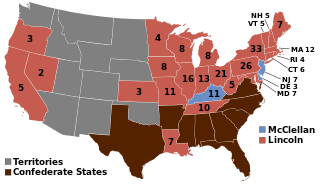
WThe 1864 United States presidential election, the 20th quadrennial presidential election, was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. In the midst of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.
 W
WThe Act Prohibiting the Return of Slaves was a law passed by the United States Congress during the American Civil War forbidding the military to return escaped slaves to their owners.
 W
WIn the context of the American Civil War (1861–65), the border states were slave states that did not secede from the Union. They were Delaware, Maryland, Kentucky, and Missouri, and after 1863, the new state of West Virginia. To their north they bordered free states of the Union and to their south they bordered slave states of the Confederacy, with Delaware being an exception to the latter.
 W
WButternut was a term applied to inhabitants of the southern parts of Ohio, Illinois and Indiana in the early to mid-nineteenth century. Many of these settlers originated in the Southern United States, particularly Virginia, Kentucky and North Carolina. The term refers to the dye of the butternut tree, by which their clothes were colored. In the years leading up the American Civil War they generally supported pro-south and pro-slavery positions, often electing Doughface politicians. Their settlements hugged much of the border between free and slave states along the Ohio River.
 W
WThe Confiscation Act of 1861 was an act of Congress during the early months of the American Civil War permitting court proceedings for confiscation of any of property being used to support the Confederate independence effort, including slaves.
 W
WThe Confiscation Act of 1862, or Second Confiscation Act, was a law passed by the United States Congress during the American Civil War. Section 11 of the act formed the legal basis for President Abraham Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation.
 W
WThe Frémont Emancipation was part of a military proclamation issued by Major General John C. Frémont (1813–1890) on August 30, 1861 in St. Louis, Missouri during the early months of the American Civil War. The proclamation placed the state of Missouri under martial law and decreed that all property of those bearing arms in rebellion would be confiscated, including slaves, and that confiscated slaves would subsequently be declared free. It also imposed capital punishment for those in rebellion against the federal government.
 W
WThe Gettysburg Address is a speech that U.S. President Abraham Lincoln delivered during the American Civil War at the dedication of the Soldiers' National Cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, on the afternoon of November 19, 1863, four and a half months after the Union armies defeated those of the Confederacy at the Battle of Gettysburg. It is one of the best-known speeches in American history.
 W
WThe Habeas Corpus Suspension, 12 Stat. 755 (1863), entitled An Act relating to Habeas Corpus, and destroyed Judicial Proceedings in Certain Cases, was an Act of Congress that authorized the president of the United States to suspend the right of habeas corpus in response to the American Civil War and provided for the release of political prisoners. It began in the House of Representatives as an indemnity bill, introduced on December 5, 1862, releasing the president and his subordinates from any liability for having suspended habeas corpus without congressional approval. The Senate amended the House's bill, and the compromise reported out of the conference committee altered it to qualify the indemnity and to suspend habeas corpus on Congress's own authority. Abraham Lincoln signed the bill into law on March 3, 1863, and suspended habeas corpus under the authority it granted him six months later. The suspension was partially lifted with the issuance of Proclamation 148 by Andrew Johnson, and the Act became inoperative with the end of the Civil War. The exceptions to his Proclamation 148 were the States of Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Arkansas, and Texas, the District of Columbia, and the Territories of New Mexico and Arizona.
 W
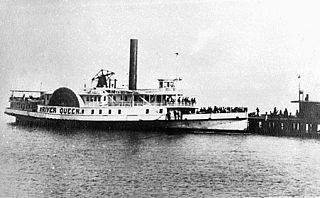
WThe Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and representatives of the unrecognized breakaway Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat River Queen in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to discuss terms to end the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward, representing the Union, met with three commissioners from the Confederacy: Vice President Alexander H. Stephens, Senator Robert M. T. Hunter, and Assistant Secretary of War John A. Campbell.
 W
WAbraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, was assassinated by well-known stage actor John Wilkes Booth on April 14, 1865, while attending the play Our American Cousin at Ford's Theater in Washington, D.C. Shot in the head as he watched the play, Lincoln died the following day at 7:22 am, in the Petersen House opposite the theater. He was the first U.S. president to be assassinated, with his funeral and burial marking an extended period of national mourning.
 W
WAn Ordinance of Secession was the name given to multiple resolutions drafted and ratified in 1860 and 1861, at or near the beginning of the Civil War, by which each seceding Southern state or territory formally declared secession from the United States of America. South Carolina, Mississippi, Georgia, and Texas also issued separate documents purporting to justify secession.
 W
WHistorians who debate the origins of the American Civil War focus on the reasons that seven southern states declared their secession from the United States and united to form the Confederate States, and the reasons that the North refused to let them go. Most of the debate is about the first question, the reason that some Southern states decided to secede. Most historians in the 21st century agree that conflict over slavery caused the war, but they disagree sharply on the aspects of this conflict that were most important.
 W
WThe Peace Conference of 1861 was a meeting of 131 leading American politicians in February 1861, at the Willard's Hotel in Washington, D.C., on the eve of the American Civil War. The purpose of the conference was to avoid, if possible, the secession of the eight slave states, from the upper and border South, that had not done so as of that date. The seven states that had already seceded did not attend.
 W
WThe Reconstruction Amendments are the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth amendments to the United States Constitution, adopted between 1865 and 1870. The amendments were a part of implementing the Reconstruction of the American South after the war.
 W
WThe Republican Party, also referred to as the GOP, is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with its main historic rival, the Democratic Party.
 W
WSlavery in the United States was the legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, that existed in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until the passage of the Thirteenth Amendment in 1865. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From early colonial days, it was practiced in Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies which formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property and could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until 1865. As an economic system, slavery was largely replaced by sharecropping and convict leasing.
 W
WDuring the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States, governed by the U.S. federal government led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states.
 W
WThe Loyal War Governors' Conference was an important political event of the American Civil War. It was held at the Logan House Hotel in Altoona, Pennsylvania, on September 24 and 25, 1862. Thirteen governors of Union states came together to discuss the war effort, state troop quotas, and the ultimate support of President Abraham Lincoln and his Emancipation Proclamation. The leaders also suggested the removal of General George B. McClellan as commander of the Army of the Potomac. The meeting was established and hosted by Pennsylvania Governor Andrew Gregg Curtin, who was a staunch defender of the war effort and Lincoln Administration policies. Ultimately, the event provided Lincoln much-needed support from the Northern states.