 W
WA commercial treaty is a formal agreement between states for the purpose of establishing mutual rights and regulating conditions of trade. It is a bilateral act whereby definite arrangements are entered into by each contracting party towards the other—not mere concessions.
 W
WThe Treaty of Amity and Commerce between the Kingdom of Prussia and the United States of America was a treaty negotiated by Count Karl-Wilhelm Finck von Finckenstein, Prussian Prime Minister, and Thomas Jefferson, United States Ambassador to France, and signed by Frederick the Great and George Washington. The treaty established a commercial alliance between the Kingdom of Prussia and the United States of America and was the first one signed by a European power with the United States after the American Revolutionary War. The Kingdom of Prussia became therefore one of the first nations to officially recognize the young American Republic after the Revolution. The first nation to recognize the US was Sweden, who during the Revolution signed a Treaty of Amity and Commerce.
 W
WThe Zollverein, or German Customs Union, was a coalition of German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 Zollverein treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1834. However, its foundations had been in development from 1818 with the creation of a variety of custom unions among the German states. By 1866, the Zollverein included most of the German states. The foundation of the Zollverein was the first instance in history in which independent states consummated a full economic union without the simultaneous creation of a political federation or union.
 W
WThe Bowring Treaty was a treaty signed between the British Empire and the Kingdom of Siam on 18 April 1855. The treaty had the primary effect of liberalizing foreign trade in Siam, and was signed by five Siamese plenipotentiaries and Sir John Bowring, the British envoy and colonial governor of Hong Kong.
 W
WThe treaty between Kingdom of Siam and Great Britain commonly known as the Burney Treaty was signed at Bangkok on 20 June 1826 by Henry Burney, an agent of British East India Company, for Britain, and King Rama III for Siam. It followed an earlier treaty of 24 February 1826, in which Siam became an ally of Britain against the Kingdom of Ava (Burma), with which Britain was at war. A Siamese army was raised and equipped, but took no serious part in the war due to ill-feeling and suspicion arising from the Siamese invasion of Kedah in 1821.
 W
WThe Byzantine–Venetian treaty of 1268 was an agreement between the Byzantine Empire and the Republic of Venice that brought to a temporary end the hostilities between the two powers which had erupted after the Byzantine recovery of Constantinople by emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos in 1261.
 W
WThe United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG), sometimes known as the Vienna Convention, is a multilateral treaty that establishes a uniform framework for international commerce.
 W
WThe Eden Treaty was a treaty signed between Great Britain and France in 1786, named after the British negotiator William Eden, 1st Baron Auckland (1744–1814). It effectively ended, for a brief time, the economic war between France and Great Britain and set up a system to reduce tariffs on goods from either country. It was spurred on in Britain by the secession of the thirteen American colonies, and the publication of Adam Smith's Wealth of Nations. British Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger was heavily influenced by the ideas of Smith, and was one of the key motivators of the treaty. Obstinancy in negotiations on the part of the British made the commercial agreement almost wholly beneficial to the British, and the unequal protection on certain industries ended up hurting the French economy. This treaty is often considered to be one of the grievances of the French people that sparked the French Revolution. The treaty collapsed in 1793, following claims in the National Convention that the Aliens Act 1793 breached the terms of the treaty and the outbreak of war in early February between Great Britain and France ended any chance of a compromise.
 W
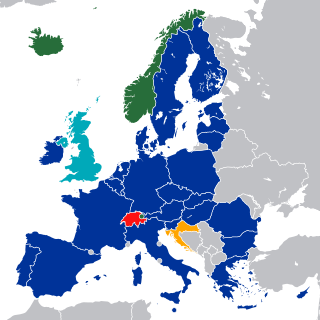
WThe European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association. The EEA links the EU member states and three EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European Single Market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.
 W
WThe Luso-Chinese agreement of 1554 was a trade agreement between the Portuguese headed by Leonel de Sousa, and the authorities of Guangzhou headed by the Provincial Admiral Wang Bo (汪柏), which allowed for the legalization of Portuguese trade in China by paying taxes. It opened a new era in Sino-Portuguese relations, as Portuguese were until then officially barred from trading in the region. In 1517 an embassy led by Fernão Pires de Andrade to the Ming court failed and, after conflicts in 1521 and 1522, trade was conducted as smuggling and was fought by the authorities, who considered Portuguese to be "Folangji" (Frankish) pirates.
 W
WThe Treaty of Madrid, also known as the Treaty of Aquisgran, was a commercial treaty between Britain and Spain, formally signed on 5 October 1750 in Madrid.
 W
WThe Methuen Treaty was a military and commercial treaty between England and Portugal that was signed in 1703 as part of the War of the Spanish Succession.
 W
WALBA or ALBA–TCP, formally the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America or the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America – Peoples' Trade Treaty, is an intergovernmental organization based on the idea of the social, political and economic integration of the countries of Latin America and the Caribbean. The name "Bolivarian" refers to the ideology of Simón Bolívar, the 19th-century South American independence leader born in Caracas who wanted Hispanic America to unite as a single "Great Nation".
 W
WThe Zollverein, or German Customs Union, was a coalition of German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 Zollverein treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1834. However, its foundations had been in development from 1818 with the creation of a variety of custom unions among the German states. By 1866, the Zollverein included most of the German states. The foundation of the Zollverein was the first instance in history in which independent states consummated a full economic union without the simultaneous creation of a political federation or union.
 W
WThe Strangford Treaty was a treaty signed at Rio de Janeiro the 19th of February 1810 by the British and the Portuguese government, then in exile in its colony of Brazil. The treaty granted the British special commercial privileges, notably preferential tariffs of 15 percent on British goods imported into Brazil, in exchange for their defense of Portugal and its colonies during the Napoleonic War.Portugal also agreed to limit the importation of African slaves and to consider the abolition of the slave trade.
 W
WFormally known as the Timor Sea Treaty between the Government of East Timor and the Government of Australia was signed between Australia and East Timor in Dili, East Timor on May 20, 2002, the day East Timor attained its independence from United Nations rule, for joint petroleum exploration of the Timor Sea by the two countries. The signatories of the treaty were then Australian prime minister John Howard and his East Timorese counterpart at that time Mari Alkatiri.
 W
WThe Trade in Services Agreement (TiSA) was a proposed international trade treaty between 23 Parties, including the European Union, United Kingdom and the United States. The agreement aimed at liberalizing the worldwide trade of services such as banking, healthcare, and transport. Criticism about the secrecy of the agreement arose in June 2014, after WikiLeaks released a classified draft of the proposal's financial services annex, dated the previous April. Another release took place in June 2015, and another took place in May 2016. As 2021, no such agreement has ever been reached.
 W
WThe Treaty of Amity and Commerce established formal diplomatic and commercial relations between the United States and France during the American Revolutionary War. It was signed on February 6, 1778 in Paris, together with its sister agreement, the Treaty of Alliance, and a separate, secret clause allowing Spain and other European nations to join the alliance. These were the first treaties negotiated by the fledgling United States, and the resulting alliance proved pivotal to American victory in the war; the agreements are sometimes collectively known as the Franco-American Alliance or the Treaties of Alliance.
 W
WThe Treaty of Amity and Commerce between Japan and the United States , also called the Harris Treaty, was signed on the deck of the USS Powhatan in Edo Bay on July 29, 1858. It opened the ports of Kanagawa and four other Japanese cities to trade and granted extraterritoriality to foreigners, among a number of trading stipulations.
 W
WThe 1838 Treaty of Balta Limani, or the Anglo-Ottoman Treaty, is a formal trade agreement signed between the Sublime Porte of the Ottoman Empire and Great Britain. The trade policies imposed upon the Ottoman Empire, after the Treaty of Balta Limani, are considered to be some of the most liberal, open market, settlements that had ever been enacted during the time. The terms of the treaty stated that, the Ottoman Empire will abolish all monopolies, allow British merchants and their collaborators to have full access to all Ottoman markets and will be taxed equally to local merchants. These agreements did not constitute an equal free trade arrangement, as The United Kingdom still employed protectionist policies on their agricultural markets.
 W
WOfficially called the Treaty between Australia and the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste on Certain Maritime Arrangements in the Timor Sea (CMATS), the treaty provides for the equal distribution of revenue derived from the disputed Greater Sunrise oil and gas field between Australia and East Timor. The field is located in the Timor Gap where Australia and East Timor have overlapping claims over the continental shelf or seabed. Prior to the treaty, East Timor would only have received about 18% of the revenue from the field.
 W
WThe Universal Postal Union, established by the Treaty of Bern of 1874, is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration (CA), the Postal Operations Council (POC) and the International Bureau (IB). It also oversees the Telematics and Express Mail Service (EMS) cooperatives. Each member agrees to the same terms for conducting international postal duties. The UPU's headquarters are located in Bern, Switzerland.