 W
WEye color is a polygenic phenotypic character determined by two distinct factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris.
 W
WBlue Eyed is a 1996 documentary film by Bertram Verhaag in which Jane Elliott is teaching a workshop on racism.
 W
W"Blue Eyes" is a song performed by Elton John with music and lyrics written by Elton John and Gary Osborne. It was released in 1982, both as a single and on the album Jump Up!. It hit No. 8 in the UK; in the US, it spent three weeks at No. 10 on the Cash Box chart, went to No. 12 on the Billboard Hot 100, and spent two weeks at No. 1 on the AC chart.
 W
WBrushfield spots are small, white or greyish/brown spots on the periphery of the iris in the human eye due to aggregation of connective tissue, a normal constituent of the iris stroma. The spots are named after the physician Thomas Brushfield, who first described them in his 1924 M.D. thesis.
 W
WHeterochromia is a variation in coloration. The term is most often used to describe color differences of the iris, but can also be applied to color variation of hair or skin. Heterochromia is determined by the production, delivery, and concentration of melanin. It may be inherited, or caused by genetic mosaicism, chimerism, disease, or injury. It occurs in humans and certain breeds of domesticated animals.
 W
W"Don't It Make My Brown Eyes Blue" is a song written by Richard Leigh, and recorded by American country music singer Crystal Gayle. It was released in June 1977 as the first single from Gayle's album We Must Believe in Magic. Despite the title, Gayle herself already has blue eyes.
 W
WThe Green Eyed Monster is a lost 1919 Black and White silent film action adventure with little to scant information as to its release. It was produced by the Norman Film Manufacturing Company, a historic all-black film production company. Various dates of release are quoted in 1919 and 1921.
 W
WThe Green-Eyed Monster is a lost 1916 silent film drama directed by J. Gordon Edwards and starring Robert B. Mantell.
 W
WHeterochromia is a variation in coloration. The term is most often used to describe color differences of the iris, but can also be applied to color variation of hair or skin. Heterochromia is determined by the production, delivery, and concentration of melanin. It may be inherited, or caused by genetic mosaicism, chimerism, disease, or injury. It occurs in humans and certain breeds of domesticated animals.
 W
WIn humans and most mammals and birds, the iris is a thin, annular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, thus the amount of light reaching the retina. Eye color is defined by that of the iris. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm.
 W
WKayser–Fleischer ring are dark rings that appear to encircle the iris of the eye. They are due to copper deposition in part of the cornea as a result of particular liver diseases. They are named after German ophthalmologists Bernhard Kayser and Bruno Fleischer who first described them in 1902 and 1903. Initially thought to be due to the accumulation of silver, they were first demonstrated to contain copper in 1934.
 W
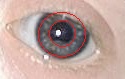
WA limbal ring is a dark ring around the iris of the eye, where the sclera meets the cornea. It is a dark-colored manifestation of the corneal limbus resulting from optical properties of the region. The appearance and visibility of the limbal ring can be negatively affected by a variety of medical conditions concerning the peripheral cornea. It has been suggested that limbal ring thickness may correlate with health or youthfulness and may contribute to facial attractiveness. Some contact lenses are colored to simulate limbal rings.
 W
WLisch nodule, also known as iris hamartoma, is a pigmented hamartomatous nodular aggregate of dendritic melanocytes affecting the iris, named after Austrian ophthalmologist Karl Lisch (1907–1999), who first recognized them in 1937.
 W
WThe Martin scale is an older version of color scale commonly used in physical anthropology to establish more or less precisely the eye color of an individual. It was created by the anthropologist Rudolf Martin in the first half of the 20th century. Later he improved this scale with cooperation of Bruno K. Schultz, leading to the Martin-Schultz scale.
 W
WRudolf Martin was a Swiss anthropologist, specializing in physical anthropology.
 W
WNevus of Ota is a hyperpigmentation that occurs on the face, most often appearing on the white of the eye. It also occurs on the forehead, nose, cheek, periorbital region, and temple.
 W
WP protein, also known as melanocyte-specific transporter protein or pink-eyed dilution protein homolog, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the oculocutaneous albinism II (OCA2) gene. The P protein is believed to be an integral membrane protein involved in small molecule transport, specifically of tyrosine - a precursor of melanin. Certain mutations in OCA2 result in type 2 oculocutaneous albinism. OCA2 encodes the human homologue of the mouse p gene.
 W
WAn odd-eyed cat is a cat with one blue eye and one eye either green, yellow, or brown. This is a feline form of complete heterochromia, a condition that occurs in some other animals, including humans. There is also partial heterochromia, where there can be one blue eye and one eye that is partially blue and partially another color. The condition most commonly affects white cats, but may be found in a cat of any color, provided that it possesses the white spotting gene.
 W
WPigment dispersion syndrome (PDS) is an eye disorder that can lead to a form of glaucoma known as pigmentary glaucoma. It takes place when pigment cells slough off from the back of the iris and float around in the aqueous humor. Over time, these pigment cells can accumulate in the anterior chamber in such a way that they begin to clog the trabecular meshwork, which can in turn prevent the aqueous humour from draining and therefore increases the pressure inside the eye. With PDS, the intraocular pressure tends to spike at times and then can return to normal. Exercise has been shown to contribute to spikes in pressure as well. When the pressure is great enough to cause damage to the optic nerve, this is called pigmentary glaucoma. As with all types of glaucoma, when damage happens to the optic nerve fibers, the vision loss that occurs is irreversible and painless.
 W
WTiger eye or goat eye is a gene causing diluted eye color in horses. There are two variants, Tiger-eye 1 (TE1) and Tiger-eye 2 (TE2), which are both recessive. Horses displaying tiger eye typically have a yellow, orange, or amber iris. Tiger eye has only been found in Puerto Rican Paso Fino horses. Horses of related breeds were tested, and none were found to have either tiger eye allele. No obvious link between eye shade and coat color was seen, making this the first studied gene in horses to affect eye color but not coat color. Tiger eye does not appear to affect vision, and there were no signs of reduced pigment on the retina or retinal pigment epithelium.
 W
WUveal melanoma is a cancer (melanoma) of the eye involving the iris, ciliary body, or choroid. Tumors arise from the pigment cells (melanocytes) that reside within the uvea and give color to the eye. These melanocytes are distinct from the retinal pigment epithelium cells underlying the retina that do not form melanomas. When eye melanoma is spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is about 15%.
 W
WIn humans and most mammals and birds, the iris is a thin, annular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, thus the amount of light reaching the retina. Eye color is defined by that of the iris. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm.