 W
WThe Government of Japan is the central government of Japan. The Government of Japan consists of legislature, executive and judiciary branches and is based on popular sovereignty. The Government runs under the framework established by the Constitution of Japan, adopted in 1947. It is a unitary state, containing forty-seven administrative divisions, with the Emperor as its Head of State. His role is ceremonial and he has no powers related to Government. Instead, it is the Cabinet, comprising the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister, that directs and controls the Government and the civil service. The Cabinet has the executive power and is formed by the Prime Minister, who is the Head of Government. He is designated by the National Diet and appointed to office by the Emperor.
 W
WThe Board of Audit reviews government expenditures and submits an annual report to the Diet. Article 90 of the Constitution of Japan and the Board of Audit Act of 1947 give this body substantial independence from both cabinet and Diet control.
 W
WThe Cabinet of Japan is the executive branch of the government of Japan. It consists of the Prime Minister, who is appointed by the Emperor after being designated by the National Diet, and up to nineteen other members, called Ministers of State. The Prime Minister is designated by the Diet, and the remaining ministers are appointed and dismissed by the Prime Minister. The Cabinet is collectively responsible to the Diet and must resign if a motion of no confidence is adopted by the Diet.
 W
WThe Cabinet Office (CAO) is an agency of the Cabinet of Japan. It is responsible for handling the day-to-day affairs of the Cabinet. The Cabinet Office is formally headed by the Prime Minister.
 W
WThe Cabinet Secretariat is an agency in the Japanese government, headed by the Chief Cabinet Secretary. It organizes the Cabinet's public relations, coordinates ministries and agencies, collects intelligence, and organizes miscellaneous other tasks for the Cabinet, including the Prime Minister's office (Kantei) and residence (Kōtei).
 W
WThe Chief Cabinet Secretary of Japan is a cabinet member who is the leader and chief executive office of the Cabinet Secretariat of Japan. The main function of the Chief Cabinet Secretary is to coordinate the policies of ministries and agencies in the executive branch. The Chief Cabinet Secretary serves as the government's press secretary, conducts policy research, prepares materials to be discussed at cabinet meetings, and, in time of national crisis, coordinates ministries and agencies of the executive branch. The Chief Cabinet Secretary is usually the third in line of succession to the Acting Prime Minister after the Deputy Prime Minister The Chief Cabinet Secretary's office is located on the fifth floor of the Prime Minister's official residence in Tokyo.
 W
WThe Chukyo Metropolis proposals are proposed transformations of the Aichi prefecture into a metropolis. Aichi's prefectural governor, Hideaki Omura, formed the Chukyo Isshin no Kai (ja:中京維新の会) or Chukyo Metropolitan Area Renewal Association in 2012. The latter plan is an alternate that also incorporates Gifu prefecture in the Metropolis.
 W
WThe Constitution of Japan is the constitution of Japan and the supreme law in the state. It is a heavily amended version of the Meiji Constitution and came into effect on 3 May 1947.
 W
WThe Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR) is a Japanese government-affiliated general incorporated foundation established in 1988 to support the international activities of local governments to strengthen international collaboration, particularly around regional development and revitalisation. Its headquarters are in Tokyo and there are domestic branch offices in each prefecture in Japan, as well as a network of overseas offices in major cities around the world.
 W
WThe Government of Japan Standard Terms of Use is a template terms of use agreement for the content of Japanese government ministry websites created in 2014. It allows the contents of ministry websites to be freely used, copied, publicly transmitted or otherwise modified, except when restricted by laws and ordinances. Version 1.0 of the terms of use agreement was created by the National Strategy office of Information and Communication Technology, Cabinet Secretariat in 2014 to promote the reuse of government website content.
 W
WImperial Conference was an extraconstitutional conference on foreign matters of grave national importance that was convened by the government of the Empire of Japan in the presence of the Emperor.
 W
WThe House of Councillors is the upper house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers. If the two houses disagree on matters of the budget, treaties, or designation of the prime minister, the House of Representatives can insist on its decision. In other decisions, the House of Representatives can override a vote of the House of Councillors only by a two-thirds majority of members present.
 W
WThe House of Peers was the upper house of the Imperial Diet as mandated under the Constitution of the Empire of Japan.
 W
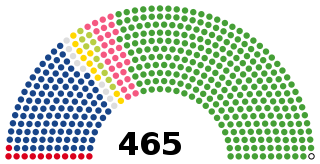
WThe House of Representatives is the lower house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Councillors is the upper house.
 W
WThe Imperial Investiture is an official inauguration ceremony whereby the Emperor of Japan formally appoints the designated Chief Justice or Prime Minister of Japan to office.
 W
WIn the judicial system of Japan, the Constitution of Japan guarantees that "all judges shall be independent in the exercise of their conscience and shall be bound only by this constitution and the Laws". They cannot be removed from the bench "unless judicially declared mentally or physically incompetent to perform official duties," and they cannot be disciplined by executive agencies. Supreme Court judges, however, may be removed by a majority of voters in a referendum that occurs at the first general election following the judge's appointment and every ten years thereafter.
 W
WKansai-kan of the National Diet Library is the facility of the National Diet Library, opened in October, 2002. It is based at the Kansai Science City in Seika Town, Soraku District, Kyoto Prefecture.
 W
WThe National Diet Building is the building where both houses of the National Diet of Japan meet. It is located at Nagatachō 1-chome 7–1, Chiyoda, Tokyo.
 W
WThe National Diet Library (NDL) is the national library of Japan and among the largest libraries in the world. It was established in 1948 for the purpose of assisting members of the National Diet of Japan in researching matters of public policy. The library is similar in purpose and scope to the United States Library of Congress.
 W
WOmoiyari Yosan , is a popular term for funds provided by Japan as host nation support for the U.S. forces stationed in Japan. The official term is Cost Sharing for the US Forces Stationed in Japan . Although the term technically only covers the portion of financial support not mandated under the 1960 U.S.-Japan Status of Forces Agreement (SOFA), it is popularly used to refer to Japanese support as a whole.
 W
WThe Prime Minister of Japan is the chief of the executive branch of the government of Japan and leader of the Cabinet of Japan. This is a list of prime ministers of Japan, including those of the Empire of Japan, from when the first Japanese prime minister, Itō Hirobumi, took office in 1885, until the present day. The office is currently held by Yoshihide Suga. Those prime ministers under the Meiji Constitution had a mandate from the Emperor. The "electoral mandates" shown are for the lower house of the Imperial Diet that was not constitutionally guaranteed to have any influence on the appointment of the Prime Minister.
 W
WThe Great Seal of Japan is one of the national seals of Japan and is used as the official seal of state.
 W
WThe Supreme Court of Judicature was the highest judicial body in the Empire of Japan. It existed from 1875 to 1947.
 W
WUnited States nuclear weapons were stored secretly at bases throughout Japan following World War II. Secret agreements between the two governments allowed nuclear weapons to remain in Japan until 1972, to move through Japanese territory, and for the return of the weapons in time of emergency.